Supplemental Data. Di Giorgio et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc
|
|
|
- Christopher McKenzie
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Figure 1. Synteny analysis of NIP4;1 and NIP4;2. Examination of the NIP4;1-NIP4;2 region in rabidopsis thaliana and equivalent evolutionary regions in other dicot genomes are shown on the left panel. Phylogenetic relationships among plants and. thaliana NIP4;1-NIP4;2 deduced from syntenic analysis are indicated in the right panel. Genomes (putative QP loci): rabidopsis thaliana (T5G37810, T5G37820), rabidopsis lyrata (Loc330314, Loc891407), apsella rubella (arubv m, arubv m), rassica rapa (rapara025437, rapara025436, rapara02543), Thellungiella halophila (Thhalv m, Thhalv m, Thhalv m), arica papaya (evm.model.supercontig_65.137), Theobroma cacao (Thecc1EG019213t1), Vitis vinifera (GSVIVT ) and Solanum tuberosum (PGS0003DMP ). PF00230: QP protein, PF00010: helix-loop-helix DN-binding domain containing protein, PF00069: protein kinase family protein, PF00036: Osam2 - almodulin, PF08543: kinase, pfk family, PF00403: heavy-metal-associated domain-containing protein, PF06886: Targeting protein for Xklp2, PF00035: Double-stranded RN binding motif, F00226: dnaj domain containing protein, PF oxoprolinase. 1
2 T4G19030 (NIP1;1) T4G18910 (NIP1;2) T2G34390 (NIP2;1) T1G31885 (NIP3;1) T5G37810, T5G37820 (NIP4;1, NIP4;2) T4G10380 (NIP5;1) T1G80760 (NIP6;1) T3G06100 (NIP7;1) T3G61430 (PIP1;1) T2G45960 (PIP1;2) T1G01620 (PIP1;3) T4G00430 (PIP1;4) T4G23400 (PIP1;5) T3G53420 (PIP2;1) T2G37170, T2G37180 (PIP2;2, PIP2;3) T5G60660 (PIP2;4) T3G54820 (PIP2;5) T2G39010 (PIP2;6) T4G35100, T2G16850 (PIP2;7, PIP2;8) T3G04090 (SIP1;1) T5G18290 (SIP1;2) T3G56950 (SIP2;1) T2G36830 (TIP1;1) T3G26520 (TIP1;2) T4G01470 (TIP1;3) T3G16240 (TIP2;1) T4G17340 (TIP2;2) T5G47450 (TIP2;3) T1G73190 (TIP3;1) T1G17810 (TIP3;2) T2G25810 (TIP4;1) T3G47440 (TIP5;1) # of samples Supplemental Figure 2. Expression patterns of rabidopsis thaliana aquaporin genes. Heat map of normalized absolute expression values of 35 rabidopsis thaliana QP genes obtained using GENEVESTIGTOR ( Pollen-specific QPs are in red and QPs expressed in pollen and also in sporophytic tissues are in blue (107 microarrays consulted). 2
3 D x NIP4;1 pro :GUS NIP4;1 pro :GUS x x NIP4;2 pro :GUS NIP4;2 pro :GUS x E F G H I NIP4;1 pro :GUS J K L M N NIP4;2 pro :GUS O P Q R S 5 days 10 days Supplemental Figure 3. GUS staining of pistils and seedlings. GUS staining of pistils crossed with transgenic NIP4;1 pro :GUS () and NIP4;2 pro :GUS () pollen, and reciprocal crosses (,D). Transgenic NIP4;1 pro :GUS (E-I) and NIP4;2 pro :GUS (J-N) seedlings grown for 5 and 10 days in 0.8% agar supplemented with asta 12.5 mg/l. plants were used as control (O-S). 3
4 D E F Supplemental Figure 4. Pollen bombardment assays. onstructs EGFP-NIP4;1 (,), EGFP-NIP4;2 (,D) and LT52 pro :RFP-LT52 pro :ami356 (E,F) were validated by tobacco pollen bombardment and epifluorescence microscopy. White arrows indicate positive pollen tubes (,D) and a pollen grain (F). ar = 200 µm. 4
5 F 60min 60min 1min G 10min D 60 min H 20min E 60min 60min I J K Supplemental Figure 5. Disruption of EGFP-NIP4;1 cycling. (-H) rabidopsis pollen tubes were germinated for 30 min in PGM and then treated with 3 µg/ml F before imaging using a confocal microscope for up to 60 min. Representative fluorescence confocal images (left panels) and differential interference contrast (DI) optics (right panels). ar = 10 µm. () Effect of F treatment for 60 min in a pollen tube, showing the formation of a bubble tip as control of growth arrest. (-E) Effect of F treatment on EGFP- NIP4;1 pollen tubes (line /NIP4;1-20) after 1 (), 10 (), 20 (D) and 60 min (E). (F) Effect of F treatment for 60 min in a grain used as control. (G) Effect of F treatment for 60 min on EGFP-NIP4;1 mature pollen. (H) Effect of F treatment for 60 min on EGFP-NIP4;2 mature pollen, used as negative control. (I-K) rabidopsis pollen tubes were germinated for 30 min in PGM and then treated with 1 µm FM4-64 and either with 6 µg/ml F or 100 µm 23. Fluorescence confocal images of GFP and FM4-64 signals and DI are shown. ar = 10 µm. (I) GFP and FM4-64 signal in a LT52 pro :EGFP-NIP4;1 pollen tube as control. (J) Effect of F treatment on a EGFP-NIP4;1 pollen tube after 25 min. (K) Effect of 23 treatment on a EGFP-NIP4;1 pollen tube after 10 min. total of 13 independent germinations analyzing at least 20 grains and pollen tubes for each genotype and condition were performed. 5
6 La1 La1 1 3 RP038 RP007 LP038 LP007 LP013 2 RP013 La1 tnip4;1 L1 RP835 2 LP835 LP142 1 RP142 La1 tnip4;2 DN ladder (kb) nip4;1-1 nip4;1-2 nip4;1-3 nip4;2-1 nip4; Supplemental Figure 6. Single T-DN nip4;1 and nip4;2 mutant lines. Schematic diagram of NIP4;1 () and NIP4;2 () genes. lack boxes represent exons, and predicted promoter and 5 and 3 UTRs are shown as grey boxes. T-DN insertions are indicated with different colored triangles. Right (RP) and Left (LP) primers used for genotyping are indicated with arrows using the same colors as the triangles. Left border primer (L) is also shown. () Genotyping PRs were performed from genomic DN (gdn) from homozygous mutant plants nip4;1-1, nip4;1-2, and nip4;1-3 and nip4;2-1 and nip4;2-2, using line-specific sets of RP, LP and L primers. gdn was used as control in each PR. 6
7 cdn E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 ami260 ami356 Target genes NIP4;1 & NIP4;2 5 3 / : amirn 260: Target genes NIP4;1 & NIP4;2 5 3 / : amirn 356: TGGTTGTTTTTTG GTTGGTGT **** ************** GGTTTGTTTGGTG TGGTTTTT ******************* L Pf amirn ami- KanR T35S RFP LT52pro LT52pro S T35S ami-s Pr 260/356 II R Pf amirn-pr 260 II gdn cdn water Pf amirn-pr 356 II gdn cdn water 313 bp Supplemental Figure 7. Double knockdown amirn lines. () Schematic description of the hypothesized duplexes formed by interactions between NIP4,1 and NIP4;2 genes and the two amirns (ami260 and ami356). Paired bases are indicated by asterisks. () Schematic diagram of binary plasmid pk7wg2d expressing amirn sense (ami-s) and antisense (ami-) sequences. The LT52 pro :RFP reporter gene was included in the construct to identify pollen carrying the amirns. Forward (Pf amirn) and reverse (Pr 260 II and 356 II) primers used for genotyping PR and RT-PR assays are indicated with arrows. () Genotyping PRs with genomic DN (gdn) and RT-PR assays (cdn) from double knockdown ami260-4 and ami356-1 plants, using line-specific primers. gdn and cdn were used as control. 7
8 D E F G H I J Supplemental Figure 8. Double knockdown amirn lines expressing the RFP reporter gene. (, D, G, H) right-field images. (, E, I, J) Epifluorescence images showing nuclei stained with Hoechst (blue filter), and insets in E and J showing the three nuclei in detail. (, F) Epifluorescence images showing RFP expression (red filter). (-) Mature pollen grain of the ami260-4 line. ar = 20 µm. (D-F) Pollen tube of the ami356-1 line germinated in vitro for 4h. ar = 50 µm. pollen grain (G, I) and tube (H, J) were included as controls. ar = 20 µm (G,I) and 50 µm (H-J). 8
9 D E F Supplemental Figure 9. SEM images of pollinated pistils and developing seeds. (-D) Pollinated pistils from () and double knockdown qrt (), ami356-1 () and ami260-4 (D) opened flowers (stages late 13 and 14). Yellow arrows indicate pollen grains with defects in pollen rehydration showing a collapsed shape. (E-F) Developing seeds in manually opened siliques of (E) and ami356-1 (F) plants. Yellow arrow indicates an unfertilized ovule. 9
10 ami260-4 nip4;1-2 D nip4;2-2 Supplemental Figure 10. Pollen microgametogenesis. Development of (), double knockdown ami260-4 (), single mutant nip4;1-2 () and nip4;2-2 (D) pollen grains. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst Insets show a representative pollen grain in detail. White arrows indicate bicellular pollen grains. ar = 200 µm. 10
11 D E F Supplemental Figure 11. Viability of mature pollen grains. Mature pollen was stained with FD for 10 min. Epifluorescence images of viable (green) and non-viable (blue) pollen grains of (), double knockdown ami260-4 () and ami356-1 () and single T-DN mutants nip4;1-3 (D), nip4;1-1 (E) and nip4;2-1 (F). White arrows show non-viable, collapsed pollen grains. ar = 50 μm. 11
12 ami260-4 ami356-1 nip4;1-3 nip4;2-1 Supplemental Figure 12. Pollen tube growth in self-crossed pistils. Decolorized aniline blue staining images of self-crossed pistils of (n=10), double knockdown (ami260-4, n=14 and ami356-1, n=17) and single mutant (nip4;1-3, n=8 and nip4;2-1, n=9) flowers at stage 15 post-fertilization. Only pistils with completely pollinated stigmas were analyzed. White asterisks indicate non-fertilized ovules. ar = 200 μm. 12
13 Pollen tube length (µm) ** * ns ns ns ns ami260-4 ami X 5X 10X Kl Pollen tube length (µm) ** * ns ns ami260-4 ami Temperature Pollen tube length (µm) ** * * ns ami260-4 ami M 0.08 M Glycerol Supplemental Figure 13. Effect of temperature, salt, and osmotic stress on pollen tube growth. (-) In vitro pollen germination of wild type () and amirn (ami260-4 and ami356-1) plants on standard or modified solid PGM. Mean tube length ± SEM of ami260-4/ and ami356-1/ pollen germinated in solid PGM with () standard (1X = 5 mm Kl) or increasing salt concentrations (5X and 10X), at () standard (22 ) or higher (28 ) temperature, and () without (0 M) or with 0.08 M glycerol. ssays were performed in duplicate and repeated twice; 100 pollen tubes were measured for each replicate. Data was analyzed by one-way NOV and Tukey s test, (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ns: not significant). 13
14 D Supplemental Figure 14. Subcellular localization of EGFP-NIP4;1 and EGFP-NIP4;2 in Xenopus oocytes. Radial (x z) confocal images of Xenopus laevis oocytes expressing EGFP-NIP4;1 () EGFP-NIP4;2 (), EGFP- NIP4;1-S267 () and EGFP-NIP4;2-S267 (D) (green), previously injected with TMR-Dextran (red). ar = 10 µm. These are representative images of a total of three independent assays analyzing at least 20 eggs. 14
15 i) ii) Supplemental Figure 15. Functional assays of NIP4;1 and mutant NIP4;1-S267 in yeast () Water transport assays were done in yeast spheroplasts transformed with NIP4;1, NIP4;1-S267 or human QP8 as a positive control, prepared and mixed in a stopped flow apparatus with hyposmotic solution to induce cell swelling. Spheroplasts from yeast cells (Y4741) transformed with the pyedp60u empty vector or containing the indicated QP homologs, were suspended in 0.5 M sorbitol plus 0.4 M potassium sulfate at an OD 600 of 2.0 and mixed in a fast kinetics instrument with an equal volume of hypotonic buffer 0.5 M sorbitol at 10 (300 mosmol difference). Each line represents the average of measurements. Data points were collected each 500 µs for 3 s. Measurements from the first 2 s are displayed. Representative result of two independent experiments. () Yeast growth and survival on synthetic medium with different concentrations of H 2 O 2. Yeast strains YNVW1 ( dur3) (i) and mep1-3 (ii) transformed with the empty vector pyedp60u or pyedp60u containing the indicated QP homologs, were spotted at an OD 600 of 0.02 and 2 on medium containing various concentrations (0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.2, 1.8, 2.4 mm) of H 2 O 2. Growth was recorded after 8 days at 28. ll data were duplicated in three independent experiments. () Yeast growth and survival on synthetic medium with different concentrations of urea. YNVW1 ( dur3) yeast mutants transformed with the pyedp60u empty vector or containing the indicated QP homologs, were spotted at an OD 600 of 2, 0.02 or on medium containing various concentrations of urea or arginine as sole nitrogen source and growth was recorded after 9 days at 28. ll data were duplicated in three independent experiments. 15
16 SUPPLEMENTL TLES Supplemental Table 1. Microgametogenesis of single mutant nip4;1 and nip4;2 and double knockdown pollen. Microgametogenesis TP P+UP Mean SEM Mean SEM a a 0.18 ami b b 0.98 ami b b 0.79 nip4; b b 0.63 nip4; ab ab 0.30 Mean percentages of tricellular (TP), and bicellular and unicellular (P+UP) ± SEM pollen grains of, double knockdowns ami356-1 and ami260-4 and single mutants nip4;1-2 and nip4;2-2. ssays were performed in 4 replicates (i.e., plants) for each genotype. For each replicate, 10 flowers and >100 pollen grains were analyzed. olumns with different letters indicate significant difference (p<0.05, one-way NOV, Tukey s test). ollapsed-shape grains were excluded from this analysis. 16
17 Supplemental Table 2. Viability and hydration capacity of mature pollen. FD Relative % lethality SEM staining volume SEM 2.32 a a 0.02 ami b b 0.04 ami b b 0.03 nip4; b b 0.01 nip4; b b 0.02 nip4; ab a 0.03 nip4; ab a 0.02 Mean lethality percentage and relative volume ± SEM of, double knockdowns ami356-1 and ami260-4, and single mutants nip4;1-1 and nip4;1-3 and nip4;2-1 and nip4;2-1. ssays were performed in 6 replicates (i.e. plants) per genotype. For each replicate 5-8 flowers incubated for 10 min with FD and 100 and 30 pollen grains were analyzed for viability and volume assays, respectively. Different letters indicate significant difference (p<0.05, one-way NOV, Tukey s test). 17
Supplemental Information. Figures. Figure S1
 Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Open Flower. Juvenile leaf Flowerbud. Carpel 35 NA NA NA NA 61 NA 95 NA NA 15 NA 41 3 NA
 PaxDB Root Juvenile leaf Flowerbud Open Flower Carpel Mature Pollen Silique Seed Sec3a Sec3b Sec5a Sec5b Sec6 Sec8 Sec10a/b Sec15a Sec15b Exo84a Exo84b Exo84c Exo70A1 Exo70A2 Exo70A3 49 47 8 75 104 79
PaxDB Root Juvenile leaf Flowerbud Open Flower Carpel Mature Pollen Silique Seed Sec3a Sec3b Sec5a Sec5b Sec6 Sec8 Sec10a/b Sec15a Sec15b Exo84a Exo84b Exo84c Exo70A1 Exo70A2 Exo70A3 49 47 8 75 104 79
Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. FIM5 is preferentially expressed in stamen and mature pollen. The expression data of FIM5 was extracted from Arabidopsis efp browser (http://www.bar.utoronto.ca/efp/development/),
Supplemental Figure 1. FIM5 is preferentially expressed in stamen and mature pollen. The expression data of FIM5 was extracted from Arabidopsis efp browser (http://www.bar.utoronto.ca/efp/development/),
Supplemental Data. Beck et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
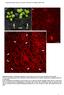 Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypic comparison of the rosette leaves of four-week-old mpk4 and Col-0 plants. A mpk4 vs Col-0 plants grown in soil. Note the extreme dwarfism of the mpk4 plants (white arrows)
Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypic comparison of the rosette leaves of four-week-old mpk4 and Col-0 plants. A mpk4 vs Col-0 plants grown in soil. Note the extreme dwarfism of the mpk4 plants (white arrows)
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
The Rab GTPase RabA4d Regulates Pollen Tube Tip Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 21: 526 544, February 2009, www.plantcell.org ã 2009 American Society of Plant Biologists The Rab GTPase RabA4d Regulates Pollen Tube Tip Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana W Amy L. Szumlanski
The Plant Cell, Vol. 21: 526 544, February 2009, www.plantcell.org ã 2009 American Society of Plant Biologists The Rab GTPase RabA4d Regulates Pollen Tube Tip Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana W Amy L. Szumlanski
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) .
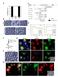 Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Hybridization between Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. and Lycopersicon pennellii Cor.: Pollen Fertility and Viability in F 1.
 767 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), 767-774 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences Hybridization between Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. and Lycopersicon pennellii Cor.: Pollen Fertility
767 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), 767-774 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences Hybridization between Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. and Lycopersicon pennellii Cor.: Pollen Fertility
ddm1a (PFG_3A-51065) ATG ddm1b (PFG_2B-60109) ATG osdrm2 (PFG_3A-04110) osdrm2 osdrm2 osdrm2
 Relative expression.6.5.4.3.2.1 OsDDM1a OsDDM1b OsDRM2 TG TG TG ddm1a (PFG_3-5165) P1 P3 ddm1b (PFG_2-619) P2 531bp 5233bp P1 P4 P3 P2 F1 R1 F1 TG TG TG F1 R1 C ddm1a -/- -/- ddm1b -/- +/- +/- -/- D (PFG_3-411)
Relative expression.6.5.4.3.2.1 OsDDM1a OsDDM1b OsDRM2 TG TG TG ddm1a (PFG_3-5165) P1 P3 ddm1b (PFG_2-619) P2 531bp 5233bp P1 P4 P3 P2 F1 R1 F1 TG TG TG F1 R1 C ddm1a -/- -/- ddm1b -/- +/- +/- -/- D (PFG_3-411)
Light triggers PILS-dependent reduction in nuclear auxin signalling for growth transition
 In the format provided y the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 217.15 Light triggers PILS-dependent reduction in nuclear auxin signalling for growth transition Chloé
In the format provided y the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 217.15 Light triggers PILS-dependent reduction in nuclear auxin signalling for growth transition Chloé
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Lee et al. 10.1073/pnas.0910950106 Fig. S1. Fe (A), Zn (B), Cu (C), and Mn (D) concentrations in flag leaves from WT, osnas3-1, and OsNAS3-antisense (AN-2) plants. Each measurement
Supporting Information Lee et al. 10.1073/pnas.0910950106 Fig. S1. Fe (A), Zn (B), Cu (C), and Mn (D) concentrations in flag leaves from WT, osnas3-1, and OsNAS3-antisense (AN-2) plants. Each measurement
Reproduction 19/02/2016. Asexual Reproduction. Budding: Types of asexual reproduction: SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL
 Asexual Reproduction Reproduction SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL One parent cell divides by mitosis to produce 2 daughter cells which are clones of the parent Types of asexual reproduction: Budding: 1. Budding 2.
Asexual Reproduction Reproduction SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL One parent cell divides by mitosis to produce 2 daughter cells which are clones of the parent Types of asexual reproduction: Budding: 1. Budding 2.
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Flowering plants can be pollinated by wind or animals.
 Wed 4/5 Activities Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Describe the reproductive organs and fertilization of flowering plants.
Wed 4/5 Activities Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Describe the reproductive organs and fertilization of flowering plants.
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.112.108993 Supplemental Figure 1. 3-MA Treatment Reduces the Growth of Seedlings. Two-week-old Nicotiana benthamiana seedlings germinated on
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.112.108993 Supplemental Figure 1. 3-MA Treatment Reduces the Growth of Seedlings. Two-week-old Nicotiana benthamiana seedlings germinated on
20. Incompatibility and male sterility and their utilization in crop improvement
 20. Incompatibility and male sterility and their utilization in crop improvement elf-incompatibility elf-incompatibility and sterility are the two mechanis, which encourage crosspollination. More than
20. Incompatibility and male sterility and their utilization in crop improvement elf-incompatibility elf-incompatibility and sterility are the two mechanis, which encourage crosspollination. More than
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction
 Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Genetics & The Work of Mendel. AP Biology
 Genetics & The Work of Mendel Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas u used experimental method u used
Genetics & The Work of Mendel Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas u used experimental method u used
Biology. Chapter 13. Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits. Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr. Cengage Learning 2015
 Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 13 Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits Cengage Learning 2015 Cengage Learning 2015 After completing today s activities, students should
Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 13 Observing Patterns in Inherited Traits Cengage Learning 2015 Cengage Learning 2015 After completing today s activities, students should
Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions
 nature methods Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions Mandy Glaß, Andreas Busche, Karen Wagner, Martin Messerle & Eva Maria Borst Supplementary figures and text:
nature methods Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions Mandy Glaß, Andreas Busche, Karen Wagner, Martin Messerle & Eva Maria Borst Supplementary figures and text:
Plants Provision for Life. Chapter 2 7 th Grade
 Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
A role for LORELEI, a putative glycosylphosphatidylinositolanchored protein, in Arabidopsis thaliana double fertilization and early seed development
 The Plant Journal (2010) 62, 571 588 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04177.x A role for LORELEI, a putative glycosylphosphatidylinositolanchored protein, in Arabidopsis thaliana double fertilization and
The Plant Journal (2010) 62, 571 588 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04177.x A role for LORELEI, a putative glycosylphosphatidylinositolanchored protein, in Arabidopsis thaliana double fertilization and
EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663]
![EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663]](/thumbs/87/96059079.jpg) EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] Student Class Date 1. A particular peach tree produces peaches that are more resistant to disease than other peaches. What method would reproduce these EXACT
EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] Student Class Date 1. A particular peach tree produces peaches that are more resistant to disease than other peaches. What method would reproduce these EXACT
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures
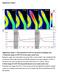 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Characterization of CerTN-L15 expressed in Arabidopsis roots. a. Ratiometric images of CerTN-L15 in roots under osmotic stress Ratiometric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Characterization of CerTN-L15 expressed in Arabidopsis roots. a. Ratiometric images of CerTN-L15 in roots under osmotic stress Ratiometric
Generative and sperm cell isolation in Bauhinia blakeana (Fabaceae)
 Ann. Bot. Fennici 49: 1 6 ISSN 3-3847 (print) ISSN 1797-2442 (online) Helsinki 26 April 212 Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing Board 212 Generative and sperm cell isolation in Bauhinia blakeana
Ann. Bot. Fennici 49: 1 6 ISSN 3-3847 (print) ISSN 1797-2442 (online) Helsinki 26 April 212 Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing Board 212 Generative and sperm cell isolation in Bauhinia blakeana
REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage about reproduction in flowering plants and then complete it by filling the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The male reproductive organs
QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage about reproduction in flowering plants and then complete it by filling the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The male reproductive organs
Plant Life Cycles. Plant life cycles alternate between. producing gametes. Life cycle phases look different among various
 Plant Life Cycles Plant life cycles alternate between two cycles: Producing spores and producing gametes A two phase life cycle is called alternation of generations Diploid phase Haploid phase Alternates
Plant Life Cycles Plant life cycles alternate between two cycles: Producing spores and producing gametes A two phase life cycle is called alternation of generations Diploid phase Haploid phase Alternates
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Whole Mount X-Gal Staining Whole tissues were collected, rinsed with PBS and fixed with 4% PFA. Tissues were then rinsed in rinse buffer (100 mm Sodium Phosphate ph
Supplementary Materials and Methods Whole Mount X-Gal Staining Whole tissues were collected, rinsed with PBS and fixed with 4% PFA. Tissues were then rinsed in rinse buffer (100 mm Sodium Phosphate ph
MII. Supplement Figure 1. CapZ β2. Merge. 250ng. 500ng DIC. Merge. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material. GFP-CapZ β2 DNA
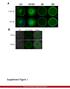 A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
Introduction to Genetics and Heredity
 Introduction to Genetics and Heredity Although these dogs have similar characteristics they are each unique! I. Early Ideas About Heredity A. The Theory of Blending Inheritance Each parent contributes
Introduction to Genetics and Heredity Although these dogs have similar characteristics they are each unique! I. Early Ideas About Heredity A. The Theory of Blending Inheritance Each parent contributes
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from
 Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Mastery. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter Content CHAPTER 3 LESSON 1. Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions.
 Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Supplemental Data. Deinlein et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 µm Zn 2+ 15 µm Zn 2+ Growth (% of control) empty vector NS1 NS2 NS3 NS4 S. pombe zhfδ Supplemental Figure 1. Functional characterization of. halleri NS genes in Zn 2+ hypersensitive S. pombe Δzhf mutant
µm Zn 2+ 15 µm Zn 2+ Growth (% of control) empty vector NS1 NS2 NS3 NS4 S. pombe zhfδ Supplemental Figure 1. Functional characterization of. halleri NS genes in Zn 2+ hypersensitive S. pombe Δzhf mutant
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by
 The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
Plant Reproduction fertilization
 Plant Reproduction In the plant kingdom, both sexual and asexual reproduction occur. Recall from Chapter 3 that plants reproduce sexually by sporic reproduction, which is also called alternation of generations.
Plant Reproduction In the plant kingdom, both sexual and asexual reproduction occur. Recall from Chapter 3 that plants reproduce sexually by sporic reproduction, which is also called alternation of generations.
1.3 - Sexually Reproduction What is Sexual Reproduction?
 1.3 - Sexually Reproduction What is Sexual Reproduction? Sexual Reproduction - Genetic information from two cells is combined to produce a new genetically unique organism. Sexual reproduction occurs when
1.3 - Sexually Reproduction What is Sexual Reproduction? Sexual Reproduction - Genetic information from two cells is combined to produce a new genetically unique organism. Sexual reproduction occurs when
Serafino et al. Thymosin α1 activates complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Genetics PPT Part 1 Biology-Mrs. Flannery
 Genetics PPT Part Biology-Mrs. Flannery In an Abbey Garden Mendel studied garden peas because they were easy to grow, came in many readily distinguishable varieties, had easily visible traits are easily
Genetics PPT Part Biology-Mrs. Flannery In an Abbey Garden Mendel studied garden peas because they were easy to grow, came in many readily distinguishable varieties, had easily visible traits are easily
Penetration of the Stigma and Style Elicits a Novel Transcriptome in Pollen Tubes, Pointing to Genes Critical for Growth in a Pistil
 Penetration of the Stigma and Style Elicits a Novel Transcriptome in Pollen Tubes, Pointing to Genes Critical for Growth in a Pistil Yuan Qin 1, Alexander R. Leydon 2, Ann Manziello 3, Ritu Pandey 3, David
Penetration of the Stigma and Style Elicits a Novel Transcriptome in Pollen Tubes, Pointing to Genes Critical for Growth in a Pistil Yuan Qin 1, Alexander R. Leydon 2, Ann Manziello 3, Ritu Pandey 3, David
STEM WORKSHOP on Pollen Biology
 STEM WORKSHOP on Pollen Biology University of Massachusetts Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Department (April 6, 2013) Presented by: Professor Alice Y. Cheung Professor Hen-Ming Wu Dr. Yan-jiao Zou
STEM WORKSHOP on Pollen Biology University of Massachusetts Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Department (April 6, 2013) Presented by: Professor Alice Y. Cheung Professor Hen-Ming Wu Dr. Yan-jiao Zou
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin
 Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Genetics & The Work of Mendel
 Genetics & The Work of Mendel 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Genetics & The Work of Mendel 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
Unit E: Plant Propagation. Lesson 1: Understanding Sexual Reproduction
 Unit E: Plant Propagation Lesson 1: Understanding Sexual Reproduction 1 Vocabulary Cross-pollination Diploid Endosperm Fertilization Gametes Genes Haploid Hybrids Pollination Seed Self-pollination Sexual
Unit E: Plant Propagation Lesson 1: Understanding Sexual Reproduction 1 Vocabulary Cross-pollination Diploid Endosperm Fertilization Gametes Genes Haploid Hybrids Pollination Seed Self-pollination Sexual
Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Supplemental Data. Müller-Xing et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypes of iclf (clf-28 swn-7 CLF pro :CLF-GR) plants. A, Late rescue of iclf plants by renewed DEX treatment; senescent inflorescence with elongated siliques (arrow; 90 DAG,
Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypes of iclf (clf-28 swn-7 CLF pro :CLF-GR) plants. A, Late rescue of iclf plants by renewed DEX treatment; senescent inflorescence with elongated siliques (arrow; 90 DAG,
Genetics & The Work of Mendel
 Genetics & The Work of Mendel 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Genetics & The Work of Mendel 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Phenomena first observed in petunia
 Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Plant Science 1203L Laboratory 5 - Sexual Reproduction (Pollination and Double Fertilization)
 Plant Science 1203L Laboratory 5 - Sexual Reproduction (Pollination and Double Fertilization) Today s lab is about sexual reproduction in plants. As with stem or root structure there are numerous definitions
Plant Science 1203L Laboratory 5 - Sexual Reproduction (Pollination and Double Fertilization) Today s lab is about sexual reproduction in plants. As with stem or root structure there are numerous definitions
Techniques for Viewing Pollen Tubes in Angiosperm Flowers
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2016 Techniques for Viewing Pollen Tubes in Angiosperm Flowers Cameron
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2016 Techniques for Viewing Pollen Tubes in Angiosperm Flowers Cameron
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land
 Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Be able to describe/illustrate the evolutionary relationships of embryophytes. Be able to map major events in the evolution of plant reproduction
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Be able to describe/illustrate the evolutionary relationships of embryophytes. Be able to map major events in the evolution of plant reproduction
Anther/Pollen culture
 Anther/Pollen culture Method to produce haploid plants Spontaneous occurrence in low frequency Induction by physical and/or chemical treatment Chromosome elimination following interspecific hybridization
Anther/Pollen culture Method to produce haploid plants Spontaneous occurrence in low frequency Induction by physical and/or chemical treatment Chromosome elimination following interspecific hybridization
BIOLOGY 3201 REPRODUCTION
 BIOLOGY 3201 REPRODUCTION Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction MODES OF REPRODUCTION (1) Asexual one parent cell divides into two by mitosis to produce 2 identical cells which are clones of the parent (2) Sexual
BIOLOGY 3201 REPRODUCTION Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction MODES OF REPRODUCTION (1) Asexual one parent cell divides into two by mitosis to produce 2 identical cells which are clones of the parent (2) Sexual
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of the AA5x. a, Camera lucida drawing of embryo at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf, modified from Kimmel et al. Dev Dyn. 1995 203:253-310). b, Confocal microangiogram
Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of the AA5x. a, Camera lucida drawing of embryo at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf, modified from Kimmel et al. Dev Dyn. 1995 203:253-310). b, Confocal microangiogram
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
"Our Flowering World" PRE-TEST. Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below:
 1 PRE-TEST Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below: 1. fertilization 2. embryo 3. pollen 4. anther 5. pistil 6. stamen 7. ovule 8. nectar 9. ovary 10. style Directions: Use the
1 PRE-TEST Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below: 1. fertilization 2. embryo 3. pollen 4. anther 5. pistil 6. stamen 7. ovule 8. nectar 9. ovary 10. style Directions: Use the
Ontwikkeling; bevruchting
 Ontwikkeling; bevruchting http://www.lima.ohiostate.edu/biology/archive/flowers. html Young Lily anther x40. Four pollen sacs and a cross section of the fillament are visible. Diploid (2N chromosomes)
Ontwikkeling; bevruchting http://www.lima.ohiostate.edu/biology/archive/flowers. html Young Lily anther x40. Four pollen sacs and a cross section of the fillament are visible. Diploid (2N chromosomes)
Supplemental Data. Hiruma et al. Plant Cell. (2010) /tpc Col-0. pen2-1
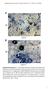 A Ch B Col-0 Cg pen2-1 Supplemental Figure 1. Trypan Blue Staining of Leaves Inoculated with Adapted and Nonadapted Colletotrichum Species.(A) Conidial suspensions of C. higginsianum MAFF305635 (Ch) were
A Ch B Col-0 Cg pen2-1 Supplemental Figure 1. Trypan Blue Staining of Leaves Inoculated with Adapted and Nonadapted Colletotrichum Species.(A) Conidial suspensions of C. higginsianum MAFF305635 (Ch) were
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS
 Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
klp-18 (RNAi) Control. supplementary information. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach
![klp-18 (RNAi) Control. supplementary information. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach klp-18 (RNAi) Control. supplementary information. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach](/thumbs/91/104639484.jpg) DOI: 10.1038/ncb1891 A. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach embryos let hatch overnight transfer to RNAi plates; incubate 5 days at 15 C RNAi food L1 worms adult worms
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1891 A. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach embryos let hatch overnight transfer to RNAi plates; incubate 5 days at 15 C RNAi food L1 worms adult worms
Figure legends of supplementary figures
 Figure legends of supplementary figures Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of rice early flowering1 () plants and enhanced expression of floral identity genes in.. Leaf emergence of,, and plants with complementary
Figure legends of supplementary figures Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of rice early flowering1 () plants and enhanced expression of floral identity genes in.. Leaf emergence of,, and plants with complementary
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction
 Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
Genetics 275 Examination February 10, 2003.
 Genetics 275 Examination February 10, 2003. Do all questions in the spaces provided. The value for this examination is twenty marks (20% of the grade for the course). The value for individual questions
Genetics 275 Examination February 10, 2003. Do all questions in the spaces provided. The value for this examination is twenty marks (20% of the grade for the course). The value for individual questions
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
Supporting Information
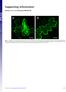 Supporting Information Harries et al. 1.173/pnas.9923916 A Fig. S1. Disruption of microfilaments within epidermal cells after treatment with 5 M Lat. Images of N. benthamiana cells are from plants expressing
Supporting Information Harries et al. 1.173/pnas.9923916 A Fig. S1. Disruption of microfilaments within epidermal cells after treatment with 5 M Lat. Images of N. benthamiana cells are from plants expressing
Supplemental Data. Candat et al. Plant Cell (2014) /tpc Cytosol. Nucleus. Mitochondria. Plastid. Peroxisome. Endomembrane system
 Cytosol Nucleus 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 PSORT MultiLoc YLoc SubLoc BaCelLo WoLF PSORT
Cytosol Nucleus 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 PSORT MultiLoc YLoc SubLoc BaCelLo WoLF PSORT
Cell-FateSwitchofSynergidtoEggCellinArabidopsis eostre Mutant Embryo Sacs Arises from Misexpression of the BEL1-Like Homeodomain Gene BLH1 W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 19: 3578 3592, November 2007, www.plantcell.org ª 2007 American Society of Plant Biologists Cell-FateSwitchofSynergidtoEggCellinArabidopsis eostre Mutant Embryo Sacs Arises from Misexpression
The Plant Cell, Vol. 19: 3578 3592, November 2007, www.plantcell.org ª 2007 American Society of Plant Biologists Cell-FateSwitchofSynergidtoEggCellinArabidopsis eostre Mutant Embryo Sacs Arises from Misexpression
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Edens and Levy, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201406004/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Nuclear shrinking does not depend on the cytoskeleton
Supplemental material Edens and Levy, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201406004/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Nuclear shrinking does not depend on the cytoskeleton
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL
 SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL LIFE SCIENCES DEPARTMENT LIFE SCIENCES CONTROL TEST 2-2017 EXAMINER: T. GABRIELS MODERATOR: Z. SHADE GRADE 11 TIME: 1 HOUR MARKS: 60 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION Read the following
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL LIFE SCIENCES DEPARTMENT LIFE SCIENCES CONTROL TEST 2-2017 EXAMINER: T. GABRIELS MODERATOR: Z. SHADE GRADE 11 TIME: 1 HOUR MARKS: 60 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION Read the following
Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures. for. pirna-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional
 Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures for pirn-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional silencing via specifying the nuclear pirn repertoire Kirsten-ndré
Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures for pirn-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional silencing via specifying the nuclear pirn repertoire Kirsten-ndré
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction
 NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
2.1 Reproduction At the end of this sequence of lessons I can:
 2.1 Reproduction 1. State that reproduction is the method of producing new offspring 2. State that sexual reproduction involves two parents 3. State that sexual reproduction leads to variation in offspring
2.1 Reproduction 1. State that reproduction is the method of producing new offspring 2. State that sexual reproduction involves two parents 3. State that sexual reproduction leads to variation in offspring
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2294 Figure S1 Localization and function of cell wall polysaccharides in root hair cells. (a) Spinning-disk confocal sections of seven day-old A. thaliana seedlings stained with 0.1% S4B
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2294 Figure S1 Localization and function of cell wall polysaccharides in root hair cells. (a) Spinning-disk confocal sections of seven day-old A. thaliana seedlings stained with 0.1% S4B
Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
Pollination biology of Persea americana Fuerte
 South African Avocado Growers Association Yearbook 1987. 10:43-45. Proceedings of the First World Avocado Congress Pollination biology of Persea americana Fuerte LA COETZER and PJ ROBBERTSE Margaretha
South African Avocado Growers Association Yearbook 1987. 10:43-45. Proceedings of the First World Avocado Congress Pollination biology of Persea americana Fuerte LA COETZER and PJ ROBBERTSE Margaretha
Supplemental Data. Jones et al. (2012). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Jones et al. (). Plant Cell.5/tpc..88 Relative ioluminescence C Relative ioluminescence E Relative ioluminescence 8 7 96 8 7 96 STIPL:STIPL-GFP 8 7 96 Relative ioluminescence Relative
Supplemental Data. Jones et al. (). Plant Cell.5/tpc..88 Relative ioluminescence C Relative ioluminescence E Relative ioluminescence 8 7 96 8 7 96 STIPL:STIPL-GFP 8 7 96 Relative ioluminescence Relative
REPRODUCTION: THE CONTINUITY OF LIFE
 Suggested time allotment: 5 to 6 hours MODULE 4 REPRODUCTION: THE CONTINUITY OF LIFE Overview The beginning of a new life is truly a remarkable event. The sight of a chick making its way out of the cracked
Suggested time allotment: 5 to 6 hours MODULE 4 REPRODUCTION: THE CONTINUITY OF LIFE Overview The beginning of a new life is truly a remarkable event. The sight of a chick making its way out of the cracked
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3731
 Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
S C I E N C E POLLINATION AND FERTILIZATION SELF INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS
 Modified In School Off School Approach Modules (MISOSA) Distance Education for Elementary Schools SELF INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS S C I E N C E POLLINATION AND FERTILIZATION 4 Department of Education BUREAU
Modified In School Off School Approach Modules (MISOSA) Distance Education for Elementary Schools SELF INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS S C I E N C E POLLINATION AND FERTILIZATION 4 Department of Education BUREAU
A putative MYB35 ortholog is a candidate for the sex-determining genes in Asparagus
 Supplementary figures for: A putative MYB35 ortholog is a candidate for the sex-determining genes in Asparagus officinalis Daisuke Tsugama, Kohei Matsuyama, Mayui Ide, Masato Hayashi, Kaien Fujino, and
Supplementary figures for: A putative MYB35 ortholog is a candidate for the sex-determining genes in Asparagus officinalis Daisuke Tsugama, Kohei Matsuyama, Mayui Ide, Masato Hayashi, Kaien Fujino, and
For a long time, people have observed that offspring look like their parents.
 Chapter 10 For a long time, people have observed that offspring look like their parents. Even before we knew about genes, people were breeding livestock to get certain traits in the offspring. They knew
Chapter 10 For a long time, people have observed that offspring look like their parents. Even before we knew about genes, people were breeding livestock to get certain traits in the offspring. They knew
Supplemental Information. Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo
 Supplemental Information Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo viability Satoshi Tsukamoto*, Taichi Hara, Atsushi Yamamoto, Seiji Kito, Naojiro Minami, Toshiro Kubota,
Supplemental Information Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo viability Satoshi Tsukamoto*, Taichi Hara, Atsushi Yamamoto, Seiji Kito, Naojiro Minami, Toshiro Kubota,
Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ).
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
16B Flower Dissection
 16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
Supplementary figure legends
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Exposure of CRT occurs independently from the apoptosisassociated loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). (A) HeLa cells treated with MTX
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Exposure of CRT occurs independently from the apoptosisassociated loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). (A) HeLa cells treated with MTX
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Courtheoux et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200902093/dc1 S1 Figure S2. Visualization of multiple merotelic attachments.
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Courtheoux et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200902093/dc1 S1 Figure S2. Visualization of multiple merotelic attachments.
The MADS Domain Protein DIANA Acts Together with AGAMOUS-LIKE80 to Specify the Central Cell in Arabidopsis Ovules W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 20: 2088 2101, August 2008, www.plantcell.org ã 2008 American Society of Plant Biologists The MADS Domain Protein DIANA Acts Together with AGAMOUS-LIKE80 to Specify the Central Cell
The Plant Cell, Vol. 20: 2088 2101, August 2008, www.plantcell.org ã 2008 American Society of Plant Biologists The MADS Domain Protein DIANA Acts Together with AGAMOUS-LIKE80 to Specify the Central Cell
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination
 BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
Studying The Role Of DNA Mismatch Repair In Brain Cancer Malignancy
 Kavya Puchhalapalli CALS Honors Project Report Spring 2017 Studying The Role Of DNA Mismatch Repair In Brain Cancer Malignancy Abstract Malignant brain tumors including medulloblastomas and primitive neuroectodermal
Kavya Puchhalapalli CALS Honors Project Report Spring 2017 Studying The Role Of DNA Mismatch Repair In Brain Cancer Malignancy Abstract Malignant brain tumors including medulloblastomas and primitive neuroectodermal
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Asexual Reproduction
 Asexual Reproduction Only one parent is involved in asexual reproduction. The offspring is genetically identical to the parent. The offspring inherits all of its traits from one parent. Therefore, the
Asexual Reproduction Only one parent is involved in asexual reproduction. The offspring is genetically identical to the parent. The offspring inherits all of its traits from one parent. Therefore, the
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
