Supplementary Materials
|
|
|
- Emma Alyson Foster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Materials Using Multi objective Optimization to Identify Dynamical Network Biomarkers as Early warning Signals of Complex Diseases Fatemeh Vafaee 1, 2 1 Charles Perkins Centre, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia 2 School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia fatemeh.vafaee@sydney.edu.au Table of Contents Supplementary Texts... 2 Permutation test to assess the significance of a DNB s signal intensity... 2 Supplementary Figures... 3 Figure S Figure S Supplementary Tables... 5 Table S Table S Table S Table S4... 8
2 Supplementary Texts Permutation test to assess the significance of a DNB s signal intensity In order to assess the significance of the elevation of a DNB composite index at the pre disease time, a permutation test has been conducted for each of the compared methods. The test statistic is, where is the pre disease time. For a DNB of size predicted by a compared algorithm, the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypnosis is obtained by randomly generating a group of genes from the gene pool (i.e., the set of all differentially expressed genes), and repeating this for 1000 times. The test statistic is then computed for each of the random DNBs using the predisease time as predicted by the compared algorithm. The p value is estimated as the fraction of random DNBs whose test statistic is equal or higher than the of the DNB of the compared algorithm.
3 Supplementary Figures Figure S h 1h 4h 8h 12h 24h 48h 72h 0 0.5h 1h 4h 8h 12h 24h 48h 72h Method1 Method h 1h 4h 8h 12h 24h 48h 72h h 1h 4h 8h 12h 24h 48h 72h Method3 Method4 Figure S1: Temporal behaviors of DNBs predicted by different methods in terms of the change of the corresponding composite indices over time; Method 1: [Chen et al, 2012], Method 2: [Yu et al, 2013], Method 3: [Zeng et al, 2014], Method 4: [Li et al, 2015]. Information for Method 1 and Method 4 were extracted from the original papers. Method 3 has provided the java source code of the proposed algorithm. The code was run on acute lung injury (ALI) data, and the identified modules were extracted for consequent analysis. Method 2 was reproduced for ALI database.
4 Figure S2 Figure S2: Distribution of genes deregulated at different time points. Each bar of the histogram shows the number of genes whose deregulation commenced at the corresponding time. The significance is assessed according to the FDR q value and the threshold is set to 0.05 in pale orange histogram and to 0.01 in dark orange histogram.
5 Supplementary Tables Table S1 Table S1: List of 89 genes included in the extended DNB (EDNB). Genes in Extended DNB ALDH3A1 ECT2 LGALS1 SHISA2 ANLN EGR1 LGALS3 SLC4A1 APLNR ERCC6L LTF SNCA ASF1B FCER1G MAD2L1 SOCS3 AURKA FKBP5 MCM5 SPAG5 BID FOS MELK SPC25 BIRC5 GADD45G MKI67 STEAP3 CCNB1 HELLS MYC STIL CCNB2 HMGB2 NCAPG2 TACC3 CCNF HSP90AA1 NUF2 TGFBI CDC20 HSPA1B PBK TK1 CDCA5 HSPA8 PLK1 TK1 CDK1 HSPA9 PMAIP1 TNXB CDKN2C HSPB1 PRC1 TOP2A CENPA HSPD1 RACGAP1 TOP2A CEP55 HSPH1 RAD51 TPX2 CHST15 JUN RRM2 TRIP13 CKS1B KIF20A RTP3 TTN CKS2 KIF23 S100A4 TUBA4A CLEC2D KRT18 S100A8 UBE2C COL6A3 KRT8 S100A9 UHRF1 CTSK LCN2 SHCBP1 XDH, and ZBTB16
6 Table S2 Table S2: List of 293 target genes (TGs) of the extended DNB significantly deregulated after time 4h. TGs de regulated in t>4h (FDR p value <0.05) ABCA1 CHRNB1 FUT1 LZTR1 NID1 PSMD3 SRF ABCB10 CLN3 FXR1 MAFF NME1 PSMD5 SRI ABCB6 CLU GADD45A MAGOH NPM1 PTGER2 SRM ACE CNPY2 GALC MAN2A1 NQO1 PTGES3 SRPR ACTR3 CNTN1 GAPDH MAPRE2 NR1D1 PTGS2 STOM ACYP2 COL1A1 GCLC MBD1 NR3C1 PTOV1 SYN2 ADCY9 COL5A1 GCLM MCCC2 NRF1 PTP4A1 TBXA2R ADRB1 COPS2 GDF15 MCL1 NTHL1 PTPN6 TFF1 ALDH9A1 COPS3 GJA1 MCM3 ODC1 PTPRF TGFB1 ALDOA COX7A2L GSS MDM2 PA2G4 RARA TGFB2 AMD1 CR2 GSTO1 ME1 PCF11 RARB TGFB3 AMPD3 CRADD HBEGF MEIS1 PCMT1 RBM3 TGM1 APP CSTB HERPUD1 MEN1 PCNA RBM8A THBS1 AREG CXCR4 HEY1 MFNG PDE6D RFC2 TIMP1 ARF4 CYR61 HIF1A MGEA5 PDGFA RFX5 TIMP2 ASCL2 DBI HMOX1 MGST1 PDGFB RGS2 TNC ATF3 DBP HNRNPA1 MKNK1 PDGFRB RNF4 TOMM20 ATF4 DDIT3 HNRPDL MMP14 PDK2 RPL10 TOP1 ATP1A2 DDX1 HOXA5 MMP15 PECAM1 RPL15 TPR ATP2A2 DGCR6 HOXB2 MMP19 PKM2 RPS6KA2 TRIM25 BAZ1B DLEU2 HSD11B2 MMP2 PLA2G4A SARS TSC2 BCL2 DPYSL3 HSPA1A MMP3 PLAT SARS2 TSHB BCL3 E2F1 HSPA8 MMP8 PLAUR SCNN1B TYK2 BID EAPP HSPD1 MSN PLCB3 SEC23B U2AF1 BMP4 EDN1 HSPE1 MSR1 PMAIP1 SERPINE1 UBA52 BRD7 EGR1 IER2 MTCH1 PMVK SERPINE2 UBE2D3 CAPZA1 EIF2S1 IFNAR1 MUC1 POLA2 SFTPA1 UBE2G2 CBS EIF4A1 IFRD2 MUC5B POLE3 SFTPD UCHL1 CBX5 EIF4E ING1 MYB PON1 SIRT1 USO1 CCL2 ESD ISG20 MYC POR SLC20A1 USP11 CCRL2 ETF1 ITGA2 MYCL1 PPARG SLC31A1 VAPA CCT5 ETS1 ITGA5 MYCT1 PPP2CA SLC39A8 VASP CCT7 ETS2 JUN NAB2 PRDX3 SLC3A2 VCAM1 CCT8 F3 JUNB NAP1L1 PRDX6 SLC9A3R2 VCP CD14 FABP4 KLK1B4 NCBP2 PREP SMAD4 VEGFA CD82 FANCA LAIR1 NCL PRKCSH SNRPB VHL CD9 FASN LAMA4 NDRG1 PRKDC SOD2 VIM CDKN1A FGFR4 LAMP1 NDUFB5 PSAP SPAST WDR36 CDKN2B FLT1 LAMP2 NFAT5 PSMA1 SPIB XDH CEBPB FOS LDLR NFE2L1 PSMA5 SPINT1 ZFP36 CEBPD FOSL1 LHB NFIL3 PSMB5 SPP1 ZFP36L2 CEBPZ FUS LMNA NFKBIL1 PSMD14 SQSTM1
7 Table S3 Table S3: List of 61 genes in DisGeNet related to acute lung injury. Those genes which are among the deregulated TGs of the extended DNB are colored in red. Genes related to acute lung injury in DisGeNet ACVR1 GSTM1 NOS2 ADRA2A GSTP1 P2RY12 AGER GSTT1 PECAM1 ALB ICAM1 PLA2G2A APOA1 IFNG PLAU ASCL1 IL10 PPARG CAT IL13 PTGS2 CCL2 IL18 SCGB1A1 CCL4L1 IL1B SERPINE1 CXCL3 IL1RL1 SOD3 CXCL6 IL1RN TFF1 CYP1A1 IL2 TFF2 EDN1 IL6 TGFB1 EPHX2 ITGB2 TIRAP F2 KDR TLR4 FAS MMP7 TNF FASLG MST1R TXN FCGR1A MTHFR VEGFA FCGR2B MYLK VIP GJA1 NFE2L2 GSR NOD2
8 Table S4 Table S4: GO terms (corrected p-value < 0.01) enriched by the extended DNB using BiNGO tool. corrected GO-ID Description Genes in test set p-value E-29 cell division E-28 cell cycle E-28 M phase E-26 cell cycle phase E-26 cellular E-25 organelle organization E-25 cell cycle E-25 cellular component organization E-24 nuclear division E-24 mitosis E-24 M phase of mitotic cell cycle E-24 organelle fission E-22 mitotic cell cycle E-10 positive regulation of cellular E-10 developmental E-10 positive regulation of biological E-10 biological regulation E-09 Table continues to the next page. multicellular organismal development CKS1B, PRC1, AURKA, ANLN, CEP55, ZBTB16, SPC25, NCAPG2, TOP2A, CDCA5, HELLS, ERCC6L, CDK1, CCNF, TPX2, NUF2, BIRC5, CDC20, UBE2C, RACGAP1, MCM5, CCNB1, CCNB2, MAD2L1, PLK1, SPAG5 STEAP3, CKS1B, PRC1, AURKA, ANLN, CEP55, SPC25, CDKN2C, NCAPG2, CDCA5, HELLS, ERCC6L, TRIP13, CDK1, MKI67, CCNF, TPX2, NUF2, CDC20, BIRC5, RACGAP1, UBE2C, TACC3, RAD51, CCNB1, UHRF1, CCNB2, MAD2L1, PLK1, SPAG5, CKS2 CDK1, MKI67, CCNF, NUF2, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, AURKA, ANLN, CEP55, TACC3, UBE2C, RAD51, CCNB1, SPC25, CCNB2, MAD2L1, PLK1, NCAPG2, SPAG5, CKS2, CDCA5, HELLS, TRIP13, ERCC6L CDK1, MKI67, CCNF, NUF2, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, AURKA, ANLN, CEP55, TACC3, UBE2C, RAD51, CCNB1, SPC25, CCNB2, MAD2L1, PLK1, NCAPG2, SPAG5, CKS2, CDCA5, HELLS, TRIP13, ERCC6L STEAP3, PRC1, SNCA, S100A9, AURKA, PMAIP1, TTN, HSPH1, FOS, CDKN2C, TGFBI, LTF, SLC4A1, TOP2A, MYC, CDCA5, EGR1, CDK1, HSP90AA1, SOCS3, CCNF, TPX2, PBK, TACC3, UBE2C, ECT2, MCM5, RAD51, UHRF1, KRT18, MAD2L1, SPAG5, JUN, RRM2, GADD45G, TUBA4A, MELK, BID, XDH, CKS1B, HMGB2, FKBP5, ANLN, HSPA1B, CEP55, ZBTB16, ALDH3A1, TK1, SPC25, CENPA, NCAPG2, KRT8, FCER1G, ASF1B, HELLS, HSPA8, TRIP13, ERCC6L, HSPA9, TNXB, MKI67, LGALS3, LGALS1, NUF2, CDC20, BIRC5, RACGAP1, CCNB1, LCN2, CCNB2, PLK1, CKS2, HSPD1, KIF20A BID, HMGB2, S100A9, SNCA, AURKA, ANLN, PMAIP1, HSPA1B, CEP55, TTN, SPC25, NCAPG2, CENPA, KRT8, ASF1B, TOP2A, MYC, CDCA5, HELLS, ERCC6L, CDK1, CCNF, NUF2, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, TACC3, UBE2C, CCNB1, CCNB2, MAD2L1, PLK1, SPAG5, JUN CDK1, MKI67, CCNF, NUF2, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, AURKA, ANLN, CEP55, TACC3, UBE2C, RAD51, CCNB1, SPC25, CCNB2, MAD2L1, PLK1, NCAPG2, SPAG5, CKS2, CDCA5, HELLS, TRIP13, ERCC6L BID, HMGB2, S100A9, SNCA, AURKA, ANLN, CEP55, PMAIP1, HSPA1B, TTN, SPC25, CENPA, NCAPG2, KRT8, TGFBI, FCER1G, ASF1B, TOP2A, MYC, CDCA5, HELLS, ERCC6L, CDK1, TNXB, LGALS3, CCNF, NUF2, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, TACC3, UBE2C, ECT2, CCNB1, LCN2, CCNB2, MAD2L1, PLK1, SPAG5, JUN, RRM2, TUBA4A CDK1, CCNF, NUF2, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, AURKA, ANLN, CEP55, UBE2C, CCNB1, SPC25, CCNB2, MAD2L1, PLK1, SPAG5, NCAPG2, CDCA5, HELLS, ERCC6L CDK1, CCNF, NUF2, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, AURKA, ANLN, CEP55, UBE2C, CCNB1, SPC25, CCNB2, MAD2L1, PLK1, SPAG5, NCAPG2, CDCA5, HELLS, ERCC6L CDK1, CCNF, NUF2, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, AURKA, ANLN, CEP55, UBE2C, CCNB1, SPC25, CCNB2, MAD2L1, PLK1, SPAG5, NCAPG2, CDCA5, HELLS, ERCC6L CDK1, CCNF, NUF2, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, AURKA, ANLN, CEP55, UBE2C, CCNB1, SPC25, CCNB2, MAD2L1, PLK1, SPAG5, NCAPG2, CDCA5, HELLS, ERCC6L CDK1, CCNF, NUF2, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, AURKA, ANLN, CEP55, UBE2C, CCNB1, SPC25, CCNB2, MAD2L1, PLK1, SPAG5, NCAPG2, CDCA5, HELLS, ERCC6L BID, STEAP3, EGR1, CDK1, HMGB2, HSP90AA1, SOCS3, LGALS1, SNCA, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, ZBTB16, PMAIP1, ALDH3A1, RAD51, CCNB1, LCN2, FOS, RRM2, JUN, FCER1G, HSPD1, MYC, TOP2A XDH, STIL, HMGB2, ZBTB16, TTN, FOS, SHISA2, NCAPG2, KRT8, TOP2A, MYC, HELLS, TRIP13, EGR1, CDK1, HSP90AA1, LGALS3, SOCS3, LGALS1, CCNF, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, RACGAP1, TACC3, ECT2, RAD51, CCNB1, UHRF1, CCNB2, JUN, GADD45G STEAP3, BID, HMGB2, SNCA, PMAIP1, HSPA1B, ZBTB16, ALDH3A1, FOS, FCER1G, TOP2A, MYC, EGR1, CDK1, HSP90AA1, SOCS3, LGALS1, TPX2, BIRC5, CDC20, RAD51, CCNB1, LCN2, JUN, RRM2, HSPD1 STEAP3, STIL, SNCA, S100A9, PMAIP1, FOS, CDKN2C, LTF, MYC, TOP2A, EGR1, CDK1, HSP90AA1, SOCS3, TPX2, UBE2C, TACC3, ECT2, MCM5, RAD51, CTSK, UHRF1, MAD2L1, KRT18, JUN, RRM2, GADD45G, BID, XDH, HMGB2, HSPA1B, ZBTB16, ALDH3A1, APLNR, KRT8, CLEC2D, FCER1G, ASF1B, HSPA8, HELLS, TNXB, LGALS1, NUF2, BIRC5, CDC20, RACGAP1, LCN2, CCNB1, CCNB2, HSPD1 XDH, STIL, HMGB2, ZBTB16, TTN, FOS, SHISA2, NCAPG2, KRT8, TOP2A, MYC, HELLS, EGR1, CDK1, HSP90AA1, LGALS3, SOCS3, LGALS1, CCNF, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, RACGAP1, TACC3, RAD51, CCNB1, UHRF1, CCNB2, JUN, GADD45G
9 GO-ID corrected p-value Description Genes in test set E-09 anatomical structure development XDH, STIL, HMGB2, ZBTB16, TTN, FOS, NCAPG2, KRT8, MYC, HELLS, TRIP13, EGR1, CDK1, HSP90AA1, LGALS3, SOCS3, LGALS1, CCNF, TPX2, CDC20, RACGAP1, TACC3, ECT2, RAD51, CCNB1, CCNB2, JUN, GADD45G E-09 regulation of cellular XDH, BID, STEAP3, STIL, HMGB2, S100A9, SNCA, ZBTB16, HSPA1B, PMAIP1, ALDH3A1, APLNR, FOS, CDKN2C, KRT8, CLEC2D, FCER1G, ASF1B, TOP2A, MYC, HELLS, HSPA8, EGR1, CDK1, TNXB, HSP90AA1, SOCS3, LGALS1, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, RACGAP1, TACC3, ECT2, MCM5, RAD51, CCNB1, LCN2, UHRF1, KRT18, MAD2L1, JUN, RRM2, GADD45G, HSPD E-08 response to stimulus XDH, HMGB2, S100A8, S100A9, SNCA, PMAIP1, HSPA1B, ALDH3A1, FOS, HSPH1, KRT8, CLEC2D, FCER1G, MYC, HSPA8, TRIP13, HSPA9, EGR1, CDK1, HSP90AA1, TACC3, RAD51, LCN2, UHRF1, JUN, GADD45G, HSPB1, HSPD E-08 regulation of biological XDH, BID, STEAP3, STIL, HMGB2, S100A9, SNCA, ZBTB16, HSPA1B, PMAIP1, ALDH3A1, APLNR, FOS, CDKN2C, KRT8, CLEC2D, FCER1G, ASF1B, TOP2A, MYC, HELLS, HSPA8, EGR1, CDK1, TNXB, HSP90AA1, SOCS3, LGALS1, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, RACGAP1, TACC3, UBE2C, ECT2, MCM5, RAD51, CCNB1, LCN2, UHRF1, KRT18, MAD2L1, JUN, RRM2, GADD45G, HSPD E-08 response to stress CDK1, HSP90AA1, SNCA, PMAIP1, HSPA1B, TACC3, RAD51, ALDH3A1, LCN2, HSPH1, UHRF1, JUN, KRT8, CLEC2D, FCER1G, HSPB1, HSPD1, HSPA8, TRIP13, HSPA E-07 regulation of apoptosis STEAP3, BID, STIL, SNCA, BIRC5, PMAIP1, HSPA1B, ZBTB16, RAD51, JUN, FCER1G, HSPD1, MYC, HELLS E-07 regulation of programmed cell death STEAP3, BID, STIL, SNCA, BIRC5, PMAIP1, HSPA1B, ZBTB16, RAD51, JUN, FCER1G, HSPD1, MYC, HELLS E-07 regulation of cell death STEAP3, BID, STIL, SNCA, BIRC5, PMAIP1, HSPA1B, ZBTB16, RAD51, JUN, FCER1G, HSPD1, MYC, HELLS E-07 cellular component assembly CDK1, TNXB, TPX2, TTN, CCNB1, LCN2, CENPA, RRM2, KRT8, TUBA4A, ASF1B, MYC, HELLS E-07 multicellular organismal XDH, STIL, HMGB2, SNCA, ZBTB16, TTN, FOS, APLNR, SHISA2, NCAPG2, KRT8, TOP2A, MYC, HELLS, TRIP13, EGR1, CDK1, TNXB, HSP90AA1, LGALS3, SOCS3, LGALS1, CCNF, TPX2, CDC20, BIRC5, RACGAP1, TACC3, RAD51, CCNB1, UHRF1, CTSK, CCNB2, JUN, GADD45G E-07 response to chemical stimulus EGR1, XDH, CDK1, HMGB2, HSP90AA1, S100A8, SNCA, S100A9, HSPA1B, ALDH3A1, LCN2, FOS, JUN, KRT8, FCER1G, HSPD1, MYC E-07 cellular response to stimulus EGR1, CDK1, SNCA, S100A9, PMAIP1, HSPA1B, RAD51, LCN2, FOS, UHRF1, JUN, FCER1G, MYC, TRIP E-07 negative regulation of cellular EGR1, STIL, SOCS3, LGALS1, SNCA, BIRC5, PMAIP1, HSPA1B, ZBTB16, RAD51, CCNB1, MAD2L1, CDKN2C, JUN, CLEC2D, FCER1G, HSPD1, MYC, HELLS E-07 system development XDH, EGR1, STIL, CDK1, HMGB2, HSP90AA1, LGALS3, SOCS3, LGALS1, CCNF, CDC20, ZBTB16, RACGAP1, TTN, TACC3, RAD51, FOS, CCNB2, JUN, KRT8, GADD45G, MYC, HELLS E-07 negative regulation of biological EGR1, STIL, SOCS3, LGALS1, SNCA, BIRC5, ZBTB16, PMAIP1, HSPA1B, TACC3, RAD51, CCNB1, MAD2L1, CDKN2C, JUN, CLEC2D, FCER1G, HSPD1, MYC, HELLS E-06 regulation of cell cycle CDK1, MAD2L1, JUN, GADD45G, TPX2, BIRC5, TACC3, MYC, HSPA E-06 cellular component biogenesis CDK1, TNXB, TPX2, TTN, CCNB1, LCN2, CENPA, RRM2, KRT8, TUBA4A, ASF1B, MYC, HELLS E-06 DNA packaging CDK1, CENPA, NCAPG2, ASF1B, TOP2A, HELLS E-06 cellular developmental EGR1, HMGB2, HSP90AA1, LGALS3, SOCS3, LGALS1, TPX2, CDC20, ZBTB16, RACGAP1, TTN, TACC3, ECT2, RAD51, CCNB1, JUN, KRT8, GADD45G, HELLS, TRIP E-06 embryonic development CCNB1, STIL, CCNB2, NCAPG2, SOCS3, KRT8, BIRC5, ZBTB16, RACGAP1, TTN, TOP2A, MYC, RAD E-06 DNA conformation change CDK1, CENPA, NCAPG2, ASF1B, TOP2A, HELLS E-06 DNA metabolic UHRF1, RRM2, HSPA1B, TOP2A, MYC, HELLS, MCM5, TRIP13, TK1, RAD E-06 negative regulation of apoptosis STIL, SNCA, FCER1G, BIRC5, HSPD1, HSPA1B, MYC, HELLS, RAD E-06 release of cytochrome c from mitochondria BID, JUN, PMAIP1, MYC E-06 negative regulation of programmed cell death STIL, SNCA, FCER1G, BIRC5, HSPD1, HSPA1B, MYC, HELLS, RAD51 Table continues to the next page.
10 GO-ID corrected p-value Description Genes in test set E-06 cell differentiation EGR1, HMGB2, HSP90AA1, LGALS3, SOCS3, LGALS1, TPX2, CDC20, ZBTB16, RACGAP1, TTN, TACC3, RAD51, CCNB1, JUN, GADD45G, KRT8, HELLS, TRIP E-06 response to protein stimulus EGR1, FOS, HSP90AA1, HSPD1, HSPA1B, MYC E-06 negative regulation of cell death STIL, SNCA, FCER1G, BIRC5, HSPD1, HSPA1B, MYC, HELLS, RAD E-06 regulation of multicellular organismal EGR1, XDH, CDK1, HSP90AA1, LGALS1, SNCA, CDC20, HSPA1B, RAD51, CCNB1, JUN, CLEC2D, FCER1G, HSPD1, MYC E-05 apoptosis BID, STEAP3, KRT18, JUN, KRT8, GADD45G, TPX2, BIRC5, PMAIP1, MYC E-05 apoptotic mitochondrial changes BID, JUN, PMAIP1, MYC E-05 protein folding HSPH1, HSP90AA1, FKBP5, HSPD1, HSPA8, HSPA E-05 programmed cell death BID, STEAP3, KRT18, JUN, KRT8, GADD45G, TPX2, BIRC5, PMAIP1, MYC E-05 in utero embryonic development CCNB1, STIL, CCNB2, NCAPG2, SOCS3, KRT8, TTN, RAD E-05 macromolecular complex assembly CCNB1, LCN2, CDK1, CENPA, RRM2, TUBA4A, ASF1B, MYC, HELLS E-05 cellular macromolecule metabolic FKBP5, AURKA, HSPA1B, TK1, FOS, HSPH1, ASF1B, TOP2A, MYC, HSPA8, HELLS, TRIP13, HSPA9, EGR1, CDK1, HSP90AA1, PBK, UBE2C, MCM5, RAD51, CCNB1, UHRF1, PLK1, JUN, RRM2, GADD45G, HSPD1, MELK E-05 macromolecule metabolic FKBP5, AURKA, HSPA1B, TK1, FOS, HSPH1, ASF1B, TOP2A, MYC, HSPA8, HELLS, TRIP13, HSPA9, EGR1, CDK1, TNXB, HSP90AA1, PBK, UBE2C, MCM5, RAD51, CCNB1, UHRF1, CTSK, PLK1, JUN, RRM2, GADD45G, HSPD1, MELK E-05 cell death BID, STEAP3, KRT18, JUN, KRT8, GADD45G, TPX2, BIRC5, PMAIP1, MYC E-05 macromolecular complex subunit organization CCNB1, LCN2, CDK1, CENPA, RRM2, TUBA4A, ASF1B, MYC, HELLS E-05 death BID, STEAP3, KRT18, JUN, KRT8, GADD45G, TPX2, BIRC5, PMAIP1, MYC E-05 cellular response to stress LCN2, CDK1, UHRF1, JUN, SNCA, HSPA1B, PMAIP1, TRIP13, RAD E-05 regulation of cellular component organization CCNB1, LCN2, MAD2L1, HSP90AA1, LGALS1, S100A9, TPX2, FCER1G, CDC E-04 chaperone mediated protein folding requiring cofactor HSPH1, HSPD1, HSPA E-04 mitochondrion organization BID, JUN, SNCA, PMAIP1, MYC E-04 chaperone-mediated protein folding HSPH1, HSPD1, HSPA E-04 microtubule-based NUF2, TPX2, TUBA4A, BIRC5, TACC3, KIF20A E-04 chromosome organization CDK1, MAD2L1, CENPA, NCAPG2, HSPA1B, ASF1B, TOP2A, HELLS E-04 meiosis MKI67, PLK1, CKS2, TRIP13, RAD E-04 M phase of meiotic cell cycle MKI67, PLK1, CKS2, TRIP13, RAD E-04 meiotic cell cycle MKI67, PLK1, CKS2, TRIP13, RAD E-04 'de novo' protein folding HSPH1, HSPD1, HSPA E-04 'de novo' posttranslational protein folding HSPH1, HSPD1, HSPA E-04 anti-apoptosis BIRC5, HSPD1, HSPA1B, MYC, HELLS E-04 chromosome segregation MAD2L1, NUF2, BIRC5, TOP2A E-04 germ cell development CCNB1, HMGB2, TPX2, ZBTB16, TRIP13 Table continues to the next page.
11 GO-ID corrected p-value Description Genes in test set E-04 regulation of developmental CCNB1, XDH, CDK1, HSP90AA1, SOCS3, LGALS1, JUN, CLEC2D, CDC20, MYC, RAD E-04 chromosome condensation CDK1, NCAPG2, TOP2A E-04 cellular metabolic XDH, FKBP5, SNCA, AURKA, HSPA1B, ALDH3A1, TK1, FOS, HSPH1, ASF1B, TOP2A, MYC, HELLS, HSPA8, TRIP13, HSPA9, EGR1, CDK1, TNXB, HSP90AA1, PBK, UBE2C, MCM5, RAD51, CCNB1, UHRF1, PLK1, JUN, RRM2, GADD45G, HSPD1, MELK E-04 regulation of neuron apoptosis JUN, SNCA, BIRC5, PMAIP1, RAD E-04 cytokinesis PRC1, PLK1, ANLN E-04 regulation of metabolic EGR1, CDK1, HMGB2, TNXB, HSP90AA1, SOCS3, SNCA, S100A9, TPX2, ZBTB16, UBE2C, MCM5, CCNB1, LCN2, FOS, UHRF1, JUN, GADD45G, ASF1B, MYC, TOP2A, HELLS E-04 regulation of cell proliferation CCNB1, CDK1, CDKN2C, RRM2, JUN, CDC20, ZBTB16, PMAIP1, MYC, ALDH3A E-04 response to organic substance EGR1, CDK1, FOS, HMGB2, HSP90AA1, SNCA, HSPD1, HSPA1B, MYC, ALDH3A E-04 response to drug LCN2, FOS, JUN, SNCA, ALDH3A E-04 cytoskeleton organization KRT8, S100A9, NUF2, TPX2, BIRC5, TACC3, TTN E-04 regulation of macromolecule metabolic EGR1, CDK1, HMGB2, TNXB, SOCS3, SNCA, S100A9, TPX2, ZBTB16, UBE2C, MCM5, CCNB1, LCN2, FOS, UHRF1, JUN, ASF1B, MYC, TOP2A, HELLS E-04 mitochondrial membrane organization BID, SNCA, PMAIP E-04 primary metabolic XDH, FKBP5, SNCA, AURKA, HSPA1B, TK1, FOS, HSPH1, ASF1B, TOP2A, MYC, HELLS, HSPA8, TRIP13, HSPA9, EGR1, CDK1, TNXB, HSP90AA1, PBK, UBE2C, MCM5, RAD51, CCNB1, UHRF1, CTSK, PLK1, JUN, RRM2, GADD45G, HSPD1, MELK E-04 chordate embryonic development CCNB1, STIL, CCNB2, NCAPG2, SOCS3, KRT8, TTN, RAD E-04 metabolic STEAP3, XDH, FKBP5, SNCA, AURKA, HSPA1B, TK1, ALDH3A1, FOS, HSPH1, LTF, ASF1B, TOP2A, MYC, HELLS, HSPA8, TRIP13, HSPA9, EGR1, CDK1, TNXB, HSP90AA1, PBK, UBE2C, MCM5, RAD51, CCNB1, UHRF1, CTSK, PLK1, JUN, RRM2, GADD45G, HSPD1, MELK E-04 embryonic development ending in birth or egg hatching CCNB1, STIL, CCNB2, NCAPG2, SOCS3, KRT8, TTN, RAD E-04 positive regulation of metabolic CCNB1, LCN2, EGR1, CDK1, FOS, HMGB2, HSP90AA1, JUN, TPX2, TOP2A, MYC E-04 leukocyte activation EGR1, GADD45G, SNCA, FCER1G, HSPD1, HELLS E-03 positive regulation of developmental CCNB1, CDK1, HSP90AA1, SOCS3, JUN, MYC, RAD E-03 organ development EGR1, XDH, STIL, CDK1, HMGB2, SOCS3, CCNF, TTN, TACC3, CCNB2, JUN, KRT8, GADD45G, MYC, HELLS E-03 cell proliferation UHRF1, MKI67, NCAPG2, RACGAP1, TACC3, HELLS E-03 regulation of immune system HSP90AA1, JUN, SNCA, CLEC2D, FCER1G, HSPD1, HSPA1B E-03 cellular response to chemical stimulus LCN2, EGR1, S100A9, SNCA, FCER1G, MYC E-03 cell activation EGR1, GADD45G, SNCA, FCER1G, HSPD1, HELLS E-03 microtubule cytoskeleton organization NUF2, TPX2, BIRC5, TACC E-03 positive regulation of multicellular organismal CCNB1, CDK1, SNCA, FCER1G, HSPD1, MYC E-03 positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic CCNB1, LCN2, EGR1, CDK1, FOS, HMGB2, JUN, TPX2, TOP2A, MYC E-03 positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic CCNB1, EGR1, CDK1, FOS, HMGB2, HSP90AA1, JUN, TOP2A, MYC Table continues to the next page.
12 GO-ID corrected p-value Description Genes in test set E-03 regulation of mitotic cell cycle CDK1, MAD2L1, TPX2, MYC E-03 positive regulation of cell proliferation CCNB1, CDK1, RRM2, JUN, CDC20, MYC, ALDH3A E-03 negative regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation CCNB1, JUN, SNCA E-03 response to abiotic stimulus KRT8, HSPB1, HSPA1B, PMAIP1, MYC, RAD E-03 regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation CCNB1, TNXB, SOCS3, JUN, SNCA E-03 positive regulation of cellular metabolic CCNB1, EGR1, CDK1, FOS, HMGB2, HSP90AA1, JUN, TPX2, TOP2A, MYC E-03 positive regulation of apoptosis BID, STEAP3, JUN, ZBTB16, PMAIP1, MYC E-03 regulation of cell differentiation XDH, HSP90AA1, SOCS3, LGALS1, JUN, CLEC2D, CDC20, RAD E-03 positive regulation of programmed cell death BID, STEAP3, JUN, ZBTB16, PMAIP1, MYC E-03 meiosis I CKS2, TRIP13, RAD E-03 immune system EGR1, CCNB2, GADD45G, S100A9, SNCA, FCER1G, HSPD1, TACC3, HELLS E-03 response to DNA damage stimulus CDK1, UHRF1, HSPA1B, PMAIP1, TRIP13, RAD E-03 positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic EGR1, CDK1, FOS, HMGB2, HSP90AA1, JUN, TPX2, TOP2A, MYC E-03 reproductive cellular CCNB1, HMGB2, TPX2, ZBTB16, TRIP E-03 positive regulation of cell death BID, STEAP3, JUN, ZBTB16, PMAIP1, MYC E-03 positive regulation of biosynthetic EGR1, CDK1, FOS, HMGB2, HSP90AA1, JUN, TPX2, TOP2A, MYC E-03 regulation of protein metabolic CCNB1, TNXB, SOCS3, JUN, SNCA, TPX2, UBE2C E-03 regulation of cellular metabolic EGR1, CDK1, HMGB2, TNXB, HSP90AA1, SOCS3, SNCA, TPX2, ZBTB16, MCM5, CCNB1, FOS, UHRF1, JUN, GADD45G, ASF1B, MYC, TOP2A, HELLS E-03 oogenesis CCNB1, TPX2, TRIP E-03 multicellular organism reproduction CCNB1, XDH, HMGB2, TPX2, ZBTB16, RACGAP1, TRIP E-03 reproductive in a multicellular organism CCNB1, XDH, HMGB2, TPX2, ZBTB16, RACGAP1, TRIP E-03 protein complex assembly CCNB1, LCN2, CDK1, RRM2, TUBA4A, MYC E-03 protein complex biogenesis CCNB1, LCN2, CDK1, RRM2, TUBA4A, MYC E-03 positive regulation of DNA metabolic CDK1, HMGB2, JUN E-03 cellular protein metabolic CDK1, HSP90AA1, FKBP5, AURKA, PBK, UBE2C, CCNB1, HSPH1, PLK1, GADD45G, HSPD1, MELK, HSPA8, HSPA E-03 reciprocal meiotic recombination TRIP13, RAD E-03 positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation CCNB1, CDK E-03 protein metabolic CDK1, HSP90AA1, FKBP5, AURKA, PBK, UBE2C, CCNB1, HSPH1, CTSK, PLK1, GADD45G, HSPD1, MYC, MELK, HSPA8, HSPA9 Table continues to the next page.
13 GO-ID corrected p-value Description Genes in test set E-03 response to biotic stimulus LCN2, HSP90AA1, KRT8, FCER1G, HSPD1, HSPA1B E-03 chromatin assembly CENPA, ASF1B, HELLS E-03 regulation of biological quality XDH, BID, EGR1, APLNR, CTSK, CCNB2, JUN, SNCA, NUF2, LTF, HSPA1B, TACC E-03 phosphorylation CCNB1, CDK1, PLK1, GADD45G, SNCA, AURKA, PBK, MELK, TK E-03 regulation of primary metabolic EGR1, CDK1, HMGB2, TNXB, SOCS3, SNCA, TPX2, ZBTB16, UBE2C, MCM5, CCNB1, FOS, UHRF1, JUN, ASF1B, MYC, TOP2A, HELLS E-03 regulation of protein modification CCNB1, TNXB, SOCS3, JUN, SNCA E-03 protein-dna complex assembly CENPA, ASF1B, HELLS E-03 positive regulation of gene expression LCN2, EGR1, CDK1, FOS, HMGB2, JUN, TOP2A, MYC E-03 positive regulation of RNA metabolic CCNB1, EGR1, FOS, HMGB2, JUN, TOP2A, MYC E-03 tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway KRT18, KRT E-03 negative regulation of phosphorylation CCNB1, JUN, SNCA E-03 gamete generation CCNB1, HMGB2, TPX2, ZBTB16, RACGAP1, TRIP E-03 response to external stimulus FOS, S100A8, JUN, S100A9, FCER1G, MYC E-03 negative regulation of protein modification CCNB1, JUN, SNCA E-03 positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic CCNB1, EGR1, CDK1, FOS, HMGB2, JUN, TOP2A, MYC E-03 negative regulation of phosphate metabolic CCNB1, JUN, SNCA E-03 negative regulation of phosphorus metabolic CCNB1, JUN, SNCA E-03 regulation of cellular protein metabolic CCNB1, TNXB, SOCS3, JUN, SNCA, TPX E-03 cell differentiation involved in embryonic placenta development SOCS3, KRT E-03 sarcomere organization KRT8, TTN E-03 negative regulation of neuron apoptosis SNCA, BIRC5, RAD E-03 positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic EGR1, CDK1, FOS, HMGB2, JUN, TPX2, TOP2A, MYC E-03 regulation of phosphorylation CCNB1, TNXB, SOCS3, JUN, GADD45G, SNCA E-03 regulation of cardiac muscle tissue growth CCNB1, CDK E-03 regulation of cardiac muscle tissue development CCNB1, CDK E-03 response to X-ray PMAIP1, RAD E-03 regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation CCNB1, CDK E-03 oocyte maturation CCNB1, TRIP E-03 regulation of biosynthetic E-03 female gamete generation CCNB1, TPX2, TRIP13 Table continues to the next page. EGR1, CDK1, HMGB2, HSP90AA1, SNCA, S100A9, TPX2, ZBTB16, MCM5, FOS, UHRF1, JUN, ASF1B, MYC, TOP2A, HELLS
14 GO-ID corrected p-value Description Genes in test set E-03 female meiosis PLK1, TRIP E-03 regulation of cell projection organization LCN2, HSP90AA1, LGALS1, CDC E-03 regulation of phosphorus metabolic CCNB1, TNXB, SOCS3, JUN, GADD45G, SNCA E-03 regulation of phosphate metabolic CCNB1, TNXB, SOCS3, JUN, GADD45G, SNCA E-03 transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter FOS, JUN, MYC E-03 sexual reproduction CCNB1, HMGB2, TPX2, ZBTB16, RACGAP1, TRIP E-03 regulation of heart growth CCNB1, CDK E-03 bone resorption XDH, CTSK E-03 spermatogenesis HMGB2, TPX2, ZBTB16, RACGAP1, TRIP E-03 male gamete generation HMGB2, TPX2, ZBTB16, RACGAP1, TRIP E-03 cellular macromolecular complex assembly CENPA, TUBA4A, ASF1B, HELLS E-03 chromatin assembly or disassembly CENPA, ASF1B, HELLS E-03 spindle organization TPX2, TACC E-03 regulation of lymphocyte mediated immunity CLEC2D, FCER1G, HSPA1B E-03 regulation of DNA metabolic CDK1, HMGB2, JUN E-03 reproductive developmental CCNB1, HMGB2, TPX2, ZBTB16, TRIP E-03 positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter E-03 mitotic cell cycle checkpoint CDK1, MAD2L1 EGR1, FOS, HMGB2, JUN, TOP2A, MYC E-03 protein localization BID, STEAP3, NUF2, ZBTB16, PMAIP1, TACC3, KIF20A, HSPA9
Supplementary Table 1: List of the 242 hypoxia/reoxygenation marker genes collected from literature and databases
 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1: List of the 242 hypoxia/reoxygenation marker genes collected from literature and databases Supplementary Table 2: Contingency tables used in the fisher exact
Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1: List of the 242 hypoxia/reoxygenation marker genes collected from literature and databases Supplementary Table 2: Contingency tables used in the fisher exact
Is genomic grading killing histological grading?
 Is genomic grading killing histological grading? Christos Sotiriou MD PhD Fonds National de Recherche Scientifique (FNRS) Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB) Institut Jules Bordet Histological Grade and
Is genomic grading killing histological grading? Christos Sotiriou MD PhD Fonds National de Recherche Scientifique (FNRS) Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB) Institut Jules Bordet Histological Grade and
Integrative Radiation Biology
 Dr. Kristian Unger Integrative Biology Group Research Unit of Radiation Cytogenetics Department of Radiation Sciences Helmholtz-Zentrum München 1 Key Questions Molecular mechanisms of radiation-induced
Dr. Kristian Unger Integrative Biology Group Research Unit of Radiation Cytogenetics Department of Radiation Sciences Helmholtz-Zentrum München 1 Key Questions Molecular mechanisms of radiation-induced
HTG EdgeSeq Immuno-Oncology Assay Gene List
 A2M ABCB1 ABCB11 ABCC2 ABCG2 ABL1 ABL2 ACTB ADA ADAM17 ADGRE5 ADORA2A AICDA AKT3 ALCAM ALO5 ANA1 APAF1 APP ATF1 ATF2 ATG12 ATG16L1 ATG5 ATG7 ATM ATP5F1 AL BATF BA BCL10 BCL2 BCL2L1 BCL6 BID BIRC5 BLNK
A2M ABCB1 ABCB11 ABCC2 ABCG2 ABL1 ABL2 ACTB ADA ADAM17 ADGRE5 ADORA2A AICDA AKT3 ALCAM ALO5 ANA1 APAF1 APP ATF1 ATF2 ATG12 ATG16L1 ATG5 ATG7 ATM ATP5F1 AL BATF BA BCL10 BCL2 BCL2L1 BCL6 BID BIRC5 BLNK
Supplementary Material. Table S1. Summary of mapping results
 Supplementary Material Table S1. Summary of mapping results Sample Total reads Mapped (%) HNE0-1 99687516 80786083 (81.0%) HNE0-2 94318720 77047792 (81.7%) HNE0-3 104033900 84348102 (81.1%) HNE15-1 94426598
Supplementary Material Table S1. Summary of mapping results Sample Total reads Mapped (%) HNE0-1 99687516 80786083 (81.0%) HNE0-2 94318720 77047792 (81.7%) HNE0-3 104033900 84348102 (81.1%) HNE15-1 94426598
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA. Table S1. Genes in each pathway selected for analysis.
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1. Genes in each pathway selected for analysis. Gene Chr Start End bp Pathway 1 AKR1C1 10 5000044 5022159 22115 COX 2 AKR1C2 10 5029967 5060207 30240 COX 3 AKR1C3 10 5077549 5149878
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1. Genes in each pathway selected for analysis. Gene Chr Start End bp Pathway 1 AKR1C1 10 5000044 5022159 22115 COX 2 AKR1C2 10 5029967 5060207 30240 COX 3 AKR1C3 10 5077549 5149878
Supplemental Table 1: Enriched GO categories per cluster
 Supplemental Table 1: Enriched GO categories per cluster Cluster Enriched with #genes Raw p-value Corrected p-value Frequency in set (%) Cluster 1 immune response - GO:0006955 32 2.36E-14 0.001 13.5 Cluster
Supplemental Table 1: Enriched GO categories per cluster Cluster Enriched with #genes Raw p-value Corrected p-value Frequency in set (%) Cluster 1 immune response - GO:0006955 32 2.36E-14 0.001 13.5 Cluster
B16F1 B16F10 Supplemental Figure S1
 B16F1 B16F1 Supplemental Figure S1 Representative microangiography images of B16F1 and B16F1 tumors grown in the cranial windows. FITC-dextran (2 million MW) was injected systemically to visualize blood
B16F1 B16F1 Supplemental Figure S1 Representative microangiography images of B16F1 and B16F1 tumors grown in the cranial windows. FITC-dextran (2 million MW) was injected systemically to visualize blood
Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with. unipartite and bipartite structure. Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2
 Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with unipartite and bipartite structure Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2 1 School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beiing 100871, China
Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with unipartite and bipartite structure Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2 1 School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beiing 100871, China
WERNER_FIBRO_DN LEI_MYB_REGULATED_GENES BRCA1_OVEREXP_DN SUBCLASSES_DIFF P21_P53_MIDDLE_DN
 Supplemental Table S1. Full List of Up-Regulated Conserved Biological Modules Between Zebrafish Liver Tumor with Human Liver, Lung, Gastric, and Prostate Tumors LvCMs (ZF liver cancer vs. human liver cancers
Supplemental Table S1. Full List of Up-Regulated Conserved Biological Modules Between Zebrafish Liver Tumor with Human Liver, Lung, Gastric, and Prostate Tumors LvCMs (ZF liver cancer vs. human liver cancers
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array.
 Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
2. PRC1 critical to the formation of the central spindle 4 contributes to the correct formation of the spindle during the metaphase 5
 Supplementary Table 1 The top 70 genes with the highest levels of consistent correlation with tfa in 3 cancer associated data sets were determined as described in the supplementary methods. The genes are
Supplementary Table 1 The top 70 genes with the highest levels of consistent correlation with tfa in 3 cancer associated data sets were determined as described in the supplementary methods. The genes are
Cell cycle and apoptosis
 Cell cycle and apoptosis Cell cycle Definition Stages and steps Cell cycle Interphase (G1/G0, S, and G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, karyokinesis, cytokinesis) Control checkpoints
Cell cycle and apoptosis Cell cycle Definition Stages and steps Cell cycle Interphase (G1/G0, S, and G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, karyokinesis, cytokinesis) Control checkpoints
Moyamoya disease susceptibility gene RNF213 links inflammatory and angiogenic
 Supplementary Information for Moyamoya disease susceptibility gene RNF213 links inflammatory and angiogenic signals in endothelial cells Kazuhiro Ohkubo 1,, Yasunari Sakai 1,*,, Hirosuke Inoue 1, Satoshi
Supplementary Information for Moyamoya disease susceptibility gene RNF213 links inflammatory and angiogenic signals in endothelial cells Kazuhiro Ohkubo 1,, Yasunari Sakai 1,*,, Hirosuke Inoue 1, Satoshi
Transcriptome Profiling of the Theca Interna from Bovine Ovarian Follicles during Atresia
 Transcriptome Profiling of the Theca Interna from Bovine Ovarian Follicles during Atresia Nicholas Hatzirodos, Helen F. Irving-Rodgers, Katja Hummitzsch, Raymond J. Rodgers* Research Centre for Reproductive
Transcriptome Profiling of the Theca Interna from Bovine Ovarian Follicles during Atresia Nicholas Hatzirodos, Helen F. Irving-Rodgers, Katja Hummitzsch, Raymond J. Rodgers* Research Centre for Reproductive
U118MG. Supplementary Figure 1 U373MG U118MG 3.5 A CCF-SSTG
 A172 CCF-SSTG1 15 - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10101112131617192022-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22 T98G U373MG - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7
A172 CCF-SSTG1 15 - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10101112131617192022-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22 T98G U373MG - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature14122 Supplementary Table 1: EZH2 Co-Expression Gene Signature Top 116 genes co-expressed with EZH2 across 9 Oncomine studies Gene Description Symbol ALS2CR4
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature14122 Supplementary Table 1: EZH2 Co-Expression Gene Signature Top 116 genes co-expressed with EZH2 across 9 Oncomine studies Gene Description Symbol ALS2CR4
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature15260 Supplementary Data 1: Gene expression in individual basal/stem, luminal, and luminal progenitor cells. Box plots show expression levels for each gene from the 49-gene differentiation
doi:10.1038/nature15260 Supplementary Data 1: Gene expression in individual basal/stem, luminal, and luminal progenitor cells. Box plots show expression levels for each gene from the 49-gene differentiation
Case Study - Informatics
 bd@jubilantbiosys.com Case Study - Informatics www.jubilantbiosys.com Validating as a Prognostic marker and Therapeutic Target for Multiple Cancers Introduction Human genome projects and high throughput
bd@jubilantbiosys.com Case Study - Informatics www.jubilantbiosys.com Validating as a Prognostic marker and Therapeutic Target for Multiple Cancers Introduction Human genome projects and high throughput
Molecular BioSystems
 The gene expression profiling for hepatocellular carcinoma by network analysis approach shows a dominance of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDPs) between HUB nodes Journal: Manuscript ID: MB-ART-06-2015-000434.R1
The gene expression profiling for hepatocellular carcinoma by network analysis approach shows a dominance of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDPs) between HUB nodes Journal: Manuscript ID: MB-ART-06-2015-000434.R1
Supplementary Information. PRC2 overexpression and PRC2-target gene repression relating to poorer prognosis in small
 Sato T, et al. Supplementary Information PRC2 overexpression and PRC2-target gene repression relating to poorer prognosis in small cell lung cancer Teruyuki Sato 1,2, Atsushi Kaneda 1,3,4 *, Shingo Tsuji
Sato T, et al. Supplementary Information PRC2 overexpression and PRC2-target gene repression relating to poorer prognosis in small cell lung cancer Teruyuki Sato 1,2, Atsushi Kaneda 1,3,4 *, Shingo Tsuji
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1- Differential expression of stress-related genes. Feature Number Probe Name Systematic Name Gene Name Description 30248 A_52_P342860 NM_007954 Es1 Mus musculus esterase 1 (Es1), mrna
Supplementary Table 1- Differential expression of stress-related genes. Feature Number Probe Name Systematic Name Gene Name Description 30248 A_52_P342860 NM_007954 Es1 Mus musculus esterase 1 (Es1), mrna
levels of genes were separated by their expression levels; 2,000 high, medium, and low
 Figure S1. Histone modification profiles near transcription start sites. The overall histone modification around transcription start sites (TSSs) was calculated. Histone modification levels of genes were
Figure S1. Histone modification profiles near transcription start sites. The overall histone modification around transcription start sites (TSSs) was calculated. Histone modification levels of genes were
Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death
 02.17.10 Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide The cell cycle may be divided into 4 phases The cell cycle triggers essential processes (DNA
02.17.10 Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide The cell cycle may be divided into 4 phases The cell cycle triggers essential processes (DNA
Cardiovascular Disease Products
 Cardiovascular Disease Products For more information, visit: www.bosterbio.com Cardiovascular Disease Research Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in developed nations. Boster Bio aims
Cardiovascular Disease Products For more information, visit: www.bosterbio.com Cardiovascular Disease Research Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in developed nations. Boster Bio aims
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle. 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
Comparison of prognostic signatures for ER positive breast cancer in TransATAC:
 Comparison of prognostic signatures for ER positive breast cancer in TransATAC: EndoPredict, a high performance test in node negative and node positive disease Ivana Sestak, PhD Centre for Cancer Prevention
Comparison of prognostic signatures for ER positive breast cancer in TransATAC: EndoPredict, a high performance test in node negative and node positive disease Ivana Sestak, PhD Centre for Cancer Prevention
Gene expression of muscular and neuronal pathways is cooperatively dysregulated in patients
 Gene expression of muscular and neuronal pathways is cooperatively dysregulated in patients with idiopathic achalasia Orazio Palmieri 1, Tommaso Mazza 2, Antonio Merla 1, Caterina Fusilli 2, Antonello
Gene expression of muscular and neuronal pathways is cooperatively dysregulated in patients with idiopathic achalasia Orazio Palmieri 1, Tommaso Mazza 2, Antonio Merla 1, Caterina Fusilli 2, Antonello
Molecular changes induced by the curcumin analogue D6 in human melanoma cells
 Rozzo et al. Molecular Cancer 213, 12:37 RESEARCH Molecular changes induced by the curcumin analogue D6 in human melanoma cells Open Access Carla Rozzo 1*, Manuela Fanciulli 2, Cristina Fraumene 2, Antonio
Rozzo et al. Molecular Cancer 213, 12:37 RESEARCH Molecular changes induced by the curcumin analogue D6 in human melanoma cells Open Access Carla Rozzo 1*, Manuela Fanciulli 2, Cristina Fraumene 2, Antonio
 Table S1. Metadata for transcriptome interaction network and pathway analysis of 5448 intracelluarly infected TEpi cells in comparison to mock TEpi cells. Gene symbol Full name Log2FC gene expression in
Table S1. Metadata for transcriptome interaction network and pathway analysis of 5448 intracelluarly infected TEpi cells in comparison to mock TEpi cells. Gene symbol Full name Log2FC gene expression in
Genomic Analyses across Six Cancer Types Identify Basal-like Breast Cancer as a Unique Molecular Entity
 Genomic Analyses across Six Cancer Types Identify Basal-like Breast Cancer as a Unique Molecular Entity Aleix Prat, Barbara Adamo, Cheng Fan, Vicente Peg, Maria Vidal, Patricia Galván, Ana Vivancos, Paolo
Genomic Analyses across Six Cancer Types Identify Basal-like Breast Cancer as a Unique Molecular Entity Aleix Prat, Barbara Adamo, Cheng Fan, Vicente Peg, Maria Vidal, Patricia Galván, Ana Vivancos, Paolo
Essential Questions. Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase?
 Essential Questions Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase? Cellular Growth Vocabulary Review selective permeability New cell cycle
Essential Questions Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase? Cellular Growth Vocabulary Review selective permeability New cell cycle
CPM (x 10-3 ) Tregs +Teffs. Tregs alone ICOS CLTA-4
 A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
EMT and ECM. Jesse Liang, Ph.D. Sample & Assay Technologies
 EMT and ECM Jesse Liang, Ph.D. 1 Epithelial Cells.1. Closely adjoined.2. Polarized.Epithelial Markers: E-Cadherin (adherens junctions) Claudins (tight junctions) Occludin (tight junctions) Desmoplakin
EMT and ECM Jesse Liang, Ph.D. 1 Epithelial Cells.1. Closely adjoined.2. Polarized.Epithelial Markers: E-Cadherin (adherens junctions) Claudins (tight junctions) Occludin (tight junctions) Desmoplakin
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT. Activity #3
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
Supplementary information. Dual targeting of ANGPT1 and TGFBR2 genes by mir-204 controls
 Supplementary information Dual targeting of ANGPT1 and TGFBR2 genes by mir-204 controls angiogenesis in breast cancer Ali Flores-Pérez, Laurence A. Marchat, Sergio Rodríguez-Cuevas, Verónica Bautista-Piña,
Supplementary information Dual targeting of ANGPT1 and TGFBR2 genes by mir-204 controls angiogenesis in breast cancer Ali Flores-Pérez, Laurence A. Marchat, Sergio Rodríguez-Cuevas, Verónica Bautista-Piña,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Late regulation of immune genes and micrornas in circulating leukocytes in a pig model of
 1 Supplementary material for: 2 3 4 5 6 Late regulation of immune genes and micrornas in circulating leukocytes in a pig model of influenza A (H1N2) infection Louise Brogaard, Peter M. H. Heegaard, Lars
1 Supplementary material for: 2 3 4 5 6 Late regulation of immune genes and micrornas in circulating leukocytes in a pig model of influenza A (H1N2) infection Louise Brogaard, Peter M. H. Heegaard, Lars
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.12 - CELL DIVISION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Oligo GEArray DNA Microarray:
 Oligo GEArray DNA Microarray: Rat Toxicology and Drug Resistance Catalog Number ORN-401 ERN-401 Format: HybTube (Standard protocol) HybPlate (Higher throughput protocol) Description The Oligo GEArray Rat
Oligo GEArray DNA Microarray: Rat Toxicology and Drug Resistance Catalog Number ORN-401 ERN-401 Format: HybTube (Standard protocol) HybPlate (Higher throughput protocol) Description The Oligo GEArray Rat
Numbers in a Cell Population
 B. Control of Cell Number 1. Review of the mitotic cell cycle and cell death 2. Regulation of cell number and quality during mitosis 3. Regulation of cell type during mitosis Numbers in a Cell Population
B. Control of Cell Number 1. Review of the mitotic cell cycle and cell death 2. Regulation of cell number and quality during mitosis 3. Regulation of cell type during mitosis Numbers in a Cell Population
RT 2 Profiler PCR Array:
 RT 2 Profiler PCR Array: Rat Cell Cycle Catalog Number For Real-Time Instruments: PARN-020A ABI Standard Blocks; Bio-Rad icycler, MyiQ, and (MJ Research) Chromo 4; and Stratagene Mx3005p, Mx3000p PARN-020C
RT 2 Profiler PCR Array: Rat Cell Cycle Catalog Number For Real-Time Instruments: PARN-020A ABI Standard Blocks; Bio-Rad icycler, MyiQ, and (MJ Research) Chromo 4; and Stratagene Mx3005p, Mx3000p PARN-020C
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of liver from a recipient mouse sacrificed after two rounds
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 Fah + hepatocytes in a Fah -/- mouse transplanted with sorted cells. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of liver from a recipient mouse sacrificed
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 Fah + hepatocytes in a Fah -/- mouse transplanted with sorted cells. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of liver from a recipient mouse sacrificed
5.1. KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 68 Reinforcement Unit 2 Resource Book
 5.1 THE CELL CYCLE KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Cells have a regular pattern of growth, DNA duplication, and division that is called the cell cycle.
5.1 THE CELL CYCLE KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Cells have a regular pattern of growth, DNA duplication, and division that is called the cell cycle.
MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes
 1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
Table S4A- GOBP functional annotation of celecoxib-modulated genes common between CO
 Table S4A- GOBP functional annotation of celecoxib-modulated genes common between CO Terms ListHits ListTotal PopulationHits cell proliferation 44 228 1156 cell cycle 34 228 806 DNA replication and chromosome
Table S4A- GOBP functional annotation of celecoxib-modulated genes common between CO Terms ListHits ListTotal PopulationHits cell proliferation 44 228 1156 cell cycle 34 228 806 DNA replication and chromosome
Lecture 10. G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint
 Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
5/25/2015. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork
 Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Supplementary Figure S1. Supplementary Figure S1. Chemical structure of CH
 Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S1. Chemical structure of CH7057288. Supplementary Figure S2 Kinase % competition TRKA 99 TRKC 95 TRKB 92 MEK5 87 AXL 84 CLK1 82 MERTK 82 GCN2 (Kin.Dom.2,S808G)
Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S1. Chemical structure of CH7057288. Supplementary Figure S2 Kinase % competition TRKA 99 TRKC 95 TRKB 92 MEK5 87 AXL 84 CLK1 82 MERTK 82 GCN2 (Kin.Dom.2,S808G)
PROSTATE CANCER METRICS
 PROSTATE CANCER METRICS We examine the elements required in modeling cancer and we propose several variants. We focus primarily on intracellular models using a differential equation approach although questioning
PROSTATE CANCER METRICS We examine the elements required in modeling cancer and we propose several variants. We focus primarily on intracellular models using a differential equation approach although questioning
The expression of genes contributing to pancreatic adenocarcinoma progression is influenced by the respective environment Sagini et al
 The expression of genes contributing to pancreatic adenocarcinoma progression is influenced by the respective environment Sagini et al Supplementary Figure 1: Target genes regulated by TGM2. Figure represents
The expression of genes contributing to pancreatic adenocarcinoma progression is influenced by the respective environment Sagini et al Supplementary Figure 1: Target genes regulated by TGM2. Figure represents
Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion
 Probe Set ID RefSeq Transcript ID Gene Title Gene Symbol 205980_s_at NM_001017526 /// NM_181334 /// NM_181335 Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion ARHGAP8 /// LOC553158 FC ALK shrna
Probe Set ID RefSeq Transcript ID Gene Title Gene Symbol 205980_s_at NM_001017526 /// NM_181334 /// NM_181335 Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion ARHGAP8 /// LOC553158 FC ALK shrna
Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
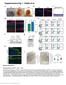 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of HPV Tg/+ ; Krt17 / mice. (a) Macroscopic images of HPV16 Tg/+ mouse ears at P40, P70 and P120. (b) Immunostaining of HPV16 Tg/+ ear tissue sections for K17 (red)
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of HPV Tg/+ ; Krt17 / mice. (a) Macroscopic images of HPV16 Tg/+ mouse ears at P40, P70 and P120. (b) Immunostaining of HPV16 Tg/+ ear tissue sections for K17 (red)
Supplemental Methods RNA sequencing experiment
 Supplemental Methods RNA sequencing experiment Mice were euthanized as described in the Methods and the right lung was removed, placed in a sterile eppendorf tube, and snap frozen in liquid nitrogen. RNA
Supplemental Methods RNA sequencing experiment Mice were euthanized as described in the Methods and the right lung was removed, placed in a sterile eppendorf tube, and snap frozen in liquid nitrogen. RNA
This is a free sample of content from Mitosis. Click here for more information on how to buy the book.
 Index A Actomyosin, cleavage furrow ingression, 150 153 AICAR. See Aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide ALIX, 157 Aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR), 179 Ana2, 74 76, 89 Anaphase chromosome
Index A Actomyosin, cleavage furrow ingression, 150 153 AICAR. See Aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide ALIX, 157 Aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR), 179 Ana2, 74 76, 89 Anaphase chromosome
103.5 Membrane metalloendopeptidase TGA GGG GTC ACG ATT TTA GG ATG ATG GTG AGG AGC AGG AC
 Supplementary Table SA Primers used for real-time RT-PCR gene regulation and their confirmation Gene Name Accession no Size Region Forward Primer Reverse Primer Efficiency% AKT v-akt oncogene homolog NM_00563
Supplementary Table SA Primers used for real-time RT-PCR gene regulation and their confirmation Gene Name Accession no Size Region Forward Primer Reverse Primer Efficiency% AKT v-akt oncogene homolog NM_00563
15. Supplementary Figure 9. Predicted gene module expression changes at 24hpi during HIV
 Supplementary Information Table of content 1. Supplementary Table 1. Summary of RNAseq data and mapping statistics 2. Supplementary Table 2. Biological functions enriched in 12 hpi DE genes, derived from
Supplementary Information Table of content 1. Supplementary Table 1. Summary of RNAseq data and mapping statistics 2. Supplementary Table 2. Biological functions enriched in 12 hpi DE genes, derived from
The Cell Life Cycle. S DNA replication, INTERPHASE. G 2 Protein. G 1 Normal THE CELL CYCLE. Indefinite period. synthesis. of histones.
 Mitosis & Meiosis The Cell Life Cycle INTERPHASE G 1 Normal cell functions plus cell growth, duplication of organelles, protein synthesis S DNA replication, synthesis of histones THE CELL CYCLE M G 2 Protein
Mitosis & Meiosis The Cell Life Cycle INTERPHASE G 1 Normal cell functions plus cell growth, duplication of organelles, protein synthesis S DNA replication, synthesis of histones THE CELL CYCLE M G 2 Protein
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall Cell Cycle Effects of Radiation
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
Fig. 3 Terms and their Frequencies across documents
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS Application Notes Supplemental Materials Data and text mining NLPCORE Computer Aided Discovery of Annotations of Bioentities and their Relationships in Articles Varun Mittal, Alexander
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS Application Notes Supplemental Materials Data and text mining NLPCORE Computer Aided Discovery of Annotations of Bioentities and their Relationships in Articles Varun Mittal, Alexander
Supplemental Table 1. List of genes and mature shrna sequences identified from the shrna screen in BRCA2-mutant PEO1 cells.
 Guillemette_Supplemental Table 1 Gene Mature Sequence Gene Mature Sequence ATTCATAGGATGTCAGCAG LOC157193 TATGCGTAAGTAATAAATTGCT TTAGTTCTGTCTTGGAGG LOC152225 CGCATATATGTTCTGACTT ALDH2 CACTTCAGTGTATGCCT
Guillemette_Supplemental Table 1 Gene Mature Sequence Gene Mature Sequence ATTCATAGGATGTCAGCAG LOC157193 TATGCGTAAGTAATAAATTGCT TTAGTTCTGTCTTGGAGG LOC152225 CGCATATATGTTCTGACTT ALDH2 CACTTCAGTGTATGCCT
Prentice Hall. Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6th Edition (Campbell, et al) High School
 Prentice Hall Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6th Edition (Campbell, et al) 2009 High School C O R R E L A T E D T O Biology I Students should understand that scientific knowledge is gained from observation
Prentice Hall Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6th Edition (Campbell, et al) 2009 High School C O R R E L A T E D T O Biology I Students should understand that scientific knowledge is gained from observation
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
BIOH111. o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Chromosomes
 & Karyotypes The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Homologous Chromosomes Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape,
& Karyotypes The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Homologous Chromosomes Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape,
Gene Expression Multiplexing Menu
 Gene Expression Multiplexing Menu Mouse Rat Human Table of CONTENTS Mouse Inflammatory Plex 2 Rat Stress Plex 3 Growth Regulation Plex 4 Multitox Plex 5 Pharma III Plex 6 Reference Plex 7 Human Transporter
Gene Expression Multiplexing Menu Mouse Rat Human Table of CONTENTS Mouse Inflammatory Plex 2 Rat Stress Plex 3 Growth Regulation Plex 4 Multitox Plex 5 Pharma III Plex 6 Reference Plex 7 Human Transporter
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
The Cell Cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
Statistical Issues in Translational Cancer Research
 Statistical Issues in Translational Cancer Research Martin Bøgsted Department of Haematology Aalborg University Hospital and Department of Clinical Medicine Aalborg University The only useful function
Statistical Issues in Translational Cancer Research Martin Bøgsted Department of Haematology Aalborg University Hospital and Department of Clinical Medicine Aalborg University The only useful function
Supplementary Figures and Tables. An inflammatory gene signature distinguishes neurofibroma Schwann cells and
 Supplementary Figures and Tables An inflammatory gene signature distinguishes neurofibroma Schwann cells and macrophages from cells in the normal peripheral nervous system Kwangmin Choi 1, Kakajan Komurov
Supplementary Figures and Tables An inflammatory gene signature distinguishes neurofibroma Schwann cells and macrophages from cells in the normal peripheral nervous system Kwangmin Choi 1, Kakajan Komurov
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE. In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for..
 Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
TNFSF13B tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b NF-kB pathway cluster, Enrichment Score: 3.57
 Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
The Avatar System TM Yields Biologically Relevant Results
 Application Note The Avatar System TM Yields Biologically Relevant Results Liquid biopsies stand to revolutionize the cancer field, enabling early detection and noninvasive monitoring of tumors. In the
Application Note The Avatar System TM Yields Biologically Relevant Results Liquid biopsies stand to revolutionize the cancer field, enabling early detection and noninvasive monitoring of tumors. In the
For focused group profiling of human HIV infection and host response genes expression
 ExProfile TM Human HIV Infection and Host Response Related Gene qpcr Array For focused group profiling of human HIV infection and host response genes expression Cat. No. QG023-A (1 x 96-well plate, Format
ExProfile TM Human HIV Infection and Host Response Related Gene qpcr Array For focused group profiling of human HIV infection and host response genes expression Cat. No. QG023-A (1 x 96-well plate, Format
Name. A.P. Biology Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
 A.P. Biology Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Name Living species MUST possess the ability to r if they are to flourish. The Cell Cycle follows the life of a cell from its o until its d. The Key Roles Of Cell
A.P. Biology Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Name Living species MUST possess the ability to r if they are to flourish. The Cell Cycle follows the life of a cell from its o until its d. The Key Roles Of Cell
Additional Data File 1
 Additional Data File 1 Detailed text profiles for clusters {B, C, D, E, F, G, H, J, and K} in Eisen M, Spellman P, Brown P, Botstein D: Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns.
Additional Data File 1 Detailed text profiles for clusters {B, C, D, E, F, G, H, J, and K} in Eisen M, Spellman P, Brown P, Botstein D: Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns.
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, sensitizes lung cancer cells to treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary
PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, sensitizes lung cancer cells to treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary
An Introduction to Genetics. 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid
 An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Supplementary Information. Deciphering the Venomic Transcriptome of Killer- Wasp Vespa velutina
 Supplementary Information Deciphering the Venomic Transcriptome of Killer- Wasp Vespa velutina Zhirui Liu, Shuanggang Chen, You Zhou, Cuihong Xie, Bifeng Zhu, Huming Zhu, Shupeng Liu, Wei Wang, Hongzhuan
Supplementary Information Deciphering the Venomic Transcriptome of Killer- Wasp Vespa velutina Zhirui Liu, Shuanggang Chen, You Zhou, Cuihong Xie, Bifeng Zhu, Huming Zhu, Shupeng Liu, Wei Wang, Hongzhuan
Editorial Type 2 Diabetes and More Gene Panel: A Predictive Genomics Approach for a Polygenic Disease
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DIABETES AND METABOLIC RESEARCH Editorial Type 2 Diabetes and More Gene Panel: A Predictive Genomics Approach for a Polygenic Disease Amr TM Saeb* University Diabetes Center, College
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DIABETES AND METABOLIC RESEARCH Editorial Type 2 Diabetes and More Gene Panel: A Predictive Genomics Approach for a Polygenic Disease Amr TM Saeb* University Diabetes Center, College
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
The Cell Cycle 4/10/12. Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences
 SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER April 2013 Vol.56 No.4: 1 7 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4460-x Table S1 Human paired-end RNA-Seq data sets from the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database Experiment
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER April 2013 Vol.56 No.4: 1 7 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4460-x Table S1 Human paired-end RNA-Seq data sets from the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database Experiment
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1 33,312. Aire rep 1. Aire rep 2 # 44,325 # 44,055. Aire rep 1. Aire rep 2.
 a 33,312 b rep 1 rep 1 # 44,325 rep 2 # 44,055 [0-84] rep 2 [0-84] 1810043G02Rik Pfkl Dnmt3l Icosl rep 1 [0-165] rep 2 [0-165] Rps14 Cd74 Mir5107 Tcof1 rep 1 [0-69] rep 2 [0-68] Id3 E2f2 Asap3 rep 1 [0-141]
a 33,312 b rep 1 rep 1 # 44,325 rep 2 # 44,055 [0-84] rep 2 [0-84] 1810043G02Rik Pfkl Dnmt3l Icosl rep 1 [0-165] rep 2 [0-165] Rps14 Cd74 Mir5107 Tcof1 rep 1 [0-69] rep 2 [0-68] Id3 E2f2 Asap3 rep 1 [0-141]
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
ShinyGO: a web application for in-depth analysis of gene sets
 ShinyGO: a web application for in-depth analysis of gene sets Steven Xijin Ge 1,*, and Dongmin Jung 1,2 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Box 2225, Brookings, SD, USA 57007 2 Avison Biomedical
ShinyGO: a web application for in-depth analysis of gene sets Steven Xijin Ge 1,*, and Dongmin Jung 1,2 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Box 2225, Brookings, SD, USA 57007 2 Avison Biomedical
Eosinophils! 40! 30! 20! 10! 0! NS!
 A Macrophages Lymphocytes Eosinophils Neutrophils Percentage (%) 1 ** 4 * 1 1 MMA SA B C Baseline FEV1, % predicted 15 p = 1.11 X 10-9 5 CD4:CD8 ratio 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Cellular infiltrate in the
A Macrophages Lymphocytes Eosinophils Neutrophils Percentage (%) 1 ** 4 * 1 1 MMA SA B C Baseline FEV1, % predicted 15 p = 1.11 X 10-9 5 CD4:CD8 ratio 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Cellular infiltrate in the
Genomic Medicine for Physical and Mental Health
 Genomic Medicine for Physical and Mental Health Transform your health and mood with DNA-directed healthcare Learn about your DNA and what makes you unique Have you been trying to lose weight and gain muscle
Genomic Medicine for Physical and Mental Health Transform your health and mood with DNA-directed healthcare Learn about your DNA and what makes you unique Have you been trying to lose weight and gain muscle
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
