Supplemental Table 1: Enriched GO categories per cluster
|
|
|
- Frederica Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Table 1: Enriched GO categories per cluster Cluster Enriched with #genes Raw p-value Corrected p-value Frequency in set (%) Cluster 1 immune response - GO: E Cluster 1 cellular defense response - GO: E Cluster 1 defense response - GO: E Cluster 1 cell motility - GO: E Cluster 1 cytolysis - GO: E Cluster 1 leukocyte chemotaxis - GO: E Cluster 1 taxis - GO: E Cluster 1 viral genome replication - GO: E Cluster 1 cell adhesion - GO: E Cluster 1 extracellular space - GO: E Cluster 1 signal transducer activity - GO: E Cluster 1 antigen processing - GO: E Cluster 2 mitotic cell cycle - GO: E Cluster 2 cell cycle - GO: E Cluster 2 microtubule cytoskeleton - GO: E Cluster 2 cell cycle checkpoint - GO: E Cluster 2 microtubule-based process - GO: E Cluster 2 spindle organization and biogenesis - GO: E Cluster 2 establishment of organelle localization - GO: E Cluster 2 chromosome segregation - GO: E Cluster 3 regulation of metabolic process - GO: E Cluster 4 immune response - GO: E Each of the four clusters of Figure 1C was analyzed for enrichment of GO categories using the TANGO algorithm in Expander. Only GO categories are reported that are significant after correction for multiple testing (corrected P 0.05). # genes: number of genes that appear in the cluster and that are also annotated with the GO annotation. Raw P-value: hypergeometric enrichment P-value. Corrected P-value: significance level after the multiple testing correction performed by TANGO. Frequency in set: percentage of genes in a cluster that are annotated with the GO annotation.
2 Supplemental Table 2 Changes in expression of different categories of genes: Cell cycle Primary CMV infection Alias Accession Nr. Peak 1 year Latency TYMS NM_ CDCA7 JPO1 NM_ UHRF1 NM_ SAP30 NM_ NCAPG Condensin G NM_ MKI67 Ki67 NM_ RBBP8 CtIP NM_ CDCA5 NM_ CDC6 NM_ BIRC5 Survivin BC CEP55 NM_ TK1 NM_ MCM4 NM_ CENPF Mitosin NM_ G0S2 NM_ NUSAP1 NM_ CDC2 NM_ CDC7 NM_ DTYMK CDC8 AF MCM10 AB CDC50B AK TCEAL3 NM_ CSNK1D NM_ Numbers denote mean changes of replicate samples compared to the pool of purified naive CD8 + T cells. Fold changes < 2 are denoted in italics.
3 Supplemental Table 3 Changes in expression of different categories of genes: Metabolism Primary CMV infection Alias Accession Nr. Peak 1 year Latency HBB NM_ ATP2B4 AK SCD5 AL RRM2 BC SLC27A2 NM_ HBA2 NM_ SLC14A1 AF SLCO4C1 AF AYTL2 NM_ GFOD1 NM_ IDH2 NM_ RRM2 BC ENTPD1 NM_ AQP9 NM_ GLUL NM_ ACADM NM_ ADCY7 NM_ G6PD M EPHX2 NM_ SLC16A10 NM_ AK5 BC Numbers denote mean changes of replicate samples compared to the pool of purified naive CD8 + T cells. Fold changes < 2 are denoted in italics.
4 Supplemental Table 4 Changes in expression of different categories of genes: BCL-2 family members Primary CMV infection Alias Accession Nr. Peak 1 year Latency BAD NM_ BAK BC BAX NM_ BCL2 AK BCL2A1 NM_ BCL2L12 NM_ BCLG BCL2L14 NM_ BCL-RAMBO BCL2L13 NM_ BCL-W NM_ BCL-XL NM_ BCL-XS BCL2L1 NM_ BIK NM_ BIM BCL2L11 AF BOK NM_ DIVA BCL2L10 NM_ MCL1 NM_ Numbers denote mean changes of replicate samples compared to the pool of purified naive CD8 + T cells. Fold changes < 2 are denoted in italics.
5 Supplemental Table 5 Changes in expression of different categories of genes: Apoptosis Primary CMV infection Alias Accession Nr. Peak 1 year Latency ANXA2 NM_ ANXA4 NM_ BIRC4BP XAF-1 AK ANXA2P3 NR_ DIP AB ANXA5 NM_ UBE2C NM_ CASP1 NM_ TNFSF10 TRAIL NM_ FASLG TNFSF6 NM_ FAS CD95 AK ENC1 AY PMAIP1 NOXA BC TP53 p53 NM_ TP53I3 PIG3 NM_ TNFAIP3 M Numbers denote mean changes of replicate samples compared to the pool of purified naive CD8 + T cells. Fold changes < 2 are denoted in italics.
6 Supplemental Table 6 Changes in expression of different categories of genes: Transcription factors Primary CMV infection Alias Accession Nr. Peak 1 year Latency EOMES NM_ CEBPD NM_ CTBP2 NM_ ZC3HAV1L BC ZEB2 SIP1 BC MELK NM_ JAZF1 NM_ TBX21 T-bet NM_ ZNF683 NM_ RNF135 NM_ ASCL2 BC PRDM1 Blimp-1 NM_ BATF NM_ ZBTB32 NM_ E2F2 BC IRF4 NM_ MYBL1 X ZEB2 NM_ ZFHX1B SIP1 AK SMAD3 NM_ ZNF365 NM_ MYC NM_ MYB NM_ LEF1 AF ZNF165 NM_ ZNF395 PBF NM_ ZNF516 NM_ ZMAT1 AL BACH2 NM_ KLF7 NM_ ZSCAN18 NM_ ZNF238 NM_ PLAG1 NM_ ZNF516 BM NR3C2 NM_ SCML1 NM_ Numbers denote mean changes of replicate samples compared to the pool of purified naive CD8 + T cells. Fold changes < 2 are denoted in italics.
7 Supplemental Table 7 Changes in expression of different categories of genes: Adhesion and migration Alias Accession Nr. Primary CMV infection Peak 1 year Latency ITGAD CD11D I_ CX3CR1 NM_ CCR1 NM_ CCR5 NM_ VCAM1 NM_ CXCR6 I_ CD36 NM_ ADAM8 CD156 NM_ ITGB2 LFA-1 NM_ Tetraspan 2 I_ VCL Vinculin I_ ITGAL LFA-1 NM_ ITGB1 NM_ PECAM1 NM_ L-selectin, SELL CD62L BC ITGA6 CD49f NM_ AMIGO1 AB NRCAM NM_ JAM3 NM_ ROBO1 NM_ CCR7 NM_ Numbers denote mean changes of replicate samples compared to the pool of purified naive CD8 + T cells. Fold changes < 2 are denoted in italics.
8 Supplemental Table 8 Changes in expression of different categories of genes: Cytokine receptors Primary CMV infection Alias Accession Nr. Peak 1 year Latency IL28RA NM_ IL2RB CD122 NM_ IL2RG CD132 NM_ IL18R1 NM_ IL6R X IL7RA I_ Numbers denote mean changes of replicate samples compared to the pool of purified naive CD8 + T cells. Fold changes < 2 are denoted in italics.
9 Supplemental Table 9 Changes in expression of different categories of genes: Exhaustion and differentiation Primary CMV infection Alias Accession Nr. Peak 1 year Latency CD38 NM_ F2R NM_ SLAMF7 NM_ LAG3 NM_ VSTM3 NM_ PDGFD NM_ TSPAN5 NM_ CD160 NM_ CD244 2B4 NM_ TSPAN2 NM_ EDG8 AK HAVCR2 TIM3 BC SLAMF6 NM_ CD70 NM_ KLRG1 NM_ KLRC1 NKG2A NM_ TGFBR3 BC PTGER2 NM_ TMEM49 NM_ PDCD1 PD-1 NM_ CTLA4 AY CD27 NM_ PLXND1 NM_ CD28 NM_ SERINC5 TPO1 NM_ TGFBR2 NM_ SNN Stannin AL NT5E CD73 NM_ KCNQ1 NM_ TMEPAI NM_ VIPR1 NM_ MAL NM_ Numbers denote mean changes of replicate samples compared to the pool of purified naive CD8 + T cells. Fold changes < 2 are denoted in italics.
10 Supplemental Table 10 Changes in expression of different categories of genes: molecules Cytokines Primary CMV infection Alias Accession Nr. Peak 1 year Latency IL32 NM_ IL1B NM_ IL23A NM_ Chemokines IL8 CXCL8 NM_ CCL4 Mip-1β NM_ CCL5 Rantes NM_ CKLF NM_ XCL1 NM_ CXCL7 NM_ CCL3 Mip-1α NM_ CCL3L1 NM_ XCL2 NM_ CMTM1 NM_ CXCL4 NM_ CXCL10 IP10 NM_ CCL23 NM_ CXCL2 NM_ CMTM8 NM_ molecules GZMA I_ S100A8 NM_ GZMB NM_ LYZ NM_ GZMH NM_ GNLY NM_ SPON2 NM_ CKLF NM_ S100A9 NM_ FGFBP2 NM_ GZMK NM_ PRF1 NM_ PROK2 NM_ TGFB1 NM_ LTB NM_ SECTM1 NM_ BTBD11 NM_ PCSK5 AK NELL2 NM_ TANC2 AB SCGB3A1 NM_ SPINK2 NM_ CA6 NM_ Numbers denote mean changes of replicate samples compared to the pool of purified naive CD8 + T cells. Fold changes < 2 are denoted in italics.
11 Supplemental Table 11 Changes in expression of different categories of genes: s regulated by IFNγ Primary CMV infection Accession Nr. Peak 1 year Latency IFNG NM_ IFI27 NM_ IFI16 I_ OAS1 NM_ IFI44L NM_ IFI30 J IRF4 NM_ ISG15 NM_ IFIT1 NM_ IFIT3 NM_ MX1 NM_ ISG20 NM_ OASL NM_ IFIT2 NM_ IFIT2 BC IFNAR1 NM_ IFNGR2 NM_ Numbers denote mean changes of replicate samples compared to the pool of purified naive CD8 + T cells. Fold changes < 2 are denoted in italics.
12 Supplemental Table 12: s with similar fold change between latent HCMV and exhausted LCMV CD8 + T cells Agilent ID Symbol Affymetrix ID HCMV LCMV A_23_P CCR _at A_24_P20630 LEF _g_at A_23_P LEF _g_at A_23_P SELL _at A_23_P KLRD _at A_23_P ACTN _f_at A_23_P93348 LTB _at A_23_P68601 CST _at A_24_P KLRG _at A_23_P LAG _at A_23_P F2R 95474_at A_23_P PRDM _at A_23_P GPR _at A_23_P CCL _at A_23_P CD _at A_23_P IFNG 99334_at A_24_P97374 EOMES _at A_24_P CCL3L _at A_23_P GZMA _s_at A_23_P GZMB _at A_23_P CCL _at Numbers denote mean changes of replicate samples compared to the pool of purified naive CD8 + T cells.
13 Supplemental Figure 1 A B CMV pp65 CD HLA-DR CD Peak 1-year and Latency Sort windows of microarray samples. (A) To obtain HCMV-specific cells for RNA isolation, at the peak of the HCMV infection all highly activated cells were sorted (CD8 + CD38 + HLA-DR + ). (B) Cells at 1-year and latency were sorted with HCMV-pp65 tetramers. (C) Sort windows for naive (CD8 + CD45RA + CD27 + ), effector- (CD8 + CD45RA + CD27 ), and memory- cells (CD8 + CD45RA CD27 + ). C CD Naive CD45RA 22.3 Naive,, and CD8 + cells during latency 30.3 CD27
14 Supplemental Figure 2 Consensus matrix for the hierarchical clustering of Figure 1A. The consensus matrix is a visual representation of the clustering results and the stability of the sample clusters across 200 bootstrap samples. Samples that remain consistently clustered together across different bootstrap samples have a high consensus. Blue indicates no consensus, yellow indicates maximal consensus across bootstrap samples from the original data. Note that the clustering in three groups (naive), (peak, 1-year), (latency, effector) is highly stable.
15 Supplemental Figure weeks after Tx CD45RA CD27 EBV-reactive cells during the primary HCMV infection have a memory pheno. At the timepoints pre and during HCMV infection (weeks 5, 9, and 49) EBV tetramer + cells express markers indicating a stable predominantly memory (CD8 + CD45RA CD27 + ) pheno.
16 Supplemental Figure 4 A Fold change compared to naive N E M LEF-1 RNA and protein levels. (A) qpcr of sorted effector and memory CD8 + cells in latency. Expression is measured as fold change compared to a pool of naive CD8 + cells. (B) Western blot showing low amounts of LEF-1 protein in effector and memory CD8 + cells B Naive
17 Supplemental Figure 5 Comparison of expression of genes regulated in latent HCMV-specific cells with exhausted murine LCMV-specific CD8 + cells. Scatterplot for genes that were up- or downregulated significantly (corrected P ) and 10-fold or greater in the latent HCMV-specific CD8 + T cells and that could be mapped to Affymetrix mouse probesets (n = 73) versus the orthologous mouse genes in exhausted LCMV-reactive cells.
Molecular profiling of cytomegalovirus-induced human CD8 + T cell differentiation
 Molecular profiling of cytomegalovirus-induced human CD8 + T cell differentiation Kirsten M.L. Hertoghs,, Ineke J.M. ten Berge, René A.W. van Lier J Clin Invest. 2010;120(11):4077-4090. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci42758.
Molecular profiling of cytomegalovirus-induced human CD8 + T cell differentiation Kirsten M.L. Hertoghs,, Ineke J.M. ten Berge, René A.W. van Lier J Clin Invest. 2010;120(11):4077-4090. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci42758.
HTG EdgeSeq Immuno-Oncology Assay Gene List
 A2M ABCB1 ABCB11 ABCC2 ABCG2 ABL1 ABL2 ACTB ADA ADAM17 ADGRE5 ADORA2A AICDA AKT3 ALCAM ALO5 ANA1 APAF1 APP ATF1 ATF2 ATG12 ATG16L1 ATG5 ATG7 ATM ATP5F1 AL BATF BA BCL10 BCL2 BCL2L1 BCL6 BID BIRC5 BLNK
A2M ABCB1 ABCB11 ABCC2 ABCG2 ABL1 ABL2 ACTB ADA ADAM17 ADGRE5 ADORA2A AICDA AKT3 ALCAM ALO5 ANA1 APAF1 APP ATF1 ATF2 ATG12 ATG16L1 ATG5 ATG7 ATM ATP5F1 AL BATF BA BCL10 BCL2 BCL2L1 BCL6 BID BIRC5 BLNK
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4+ T cells
 Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Effect of Cytomegalovirus Infection on Immune Responsiveness. Rene van Lier Sanquin Blood Supply Foundation
 Effect of Cytomegalovirus Infection on Immune Responsiveness Rene van Lier Sanquin Blood Supply Foundation OUTLINE CMV infection and vaccination responses Effects of CMV infection on CD8 + T cell numbers
Effect of Cytomegalovirus Infection on Immune Responsiveness Rene van Lier Sanquin Blood Supply Foundation OUTLINE CMV infection and vaccination responses Effects of CMV infection on CD8 + T cell numbers
BD Rhapsody Immune Response Panel Hs
 Doc ID: 55665 Rev. 2.0 PRODUCT INSERT BD Rhapsody Immune Response Panel Hs BD Biosciences Kit Part Number: 633750 Purpose The BD Rhapsody Immune Response Panel Hs is a set of ready-to-use primer pools
Doc ID: 55665 Rev. 2.0 PRODUCT INSERT BD Rhapsody Immune Response Panel Hs BD Biosciences Kit Part Number: 633750 Purpose The BD Rhapsody Immune Response Panel Hs is a set of ready-to-use primer pools
4. Th1-related gene expression in infected versus mock-infected controls from Fig. 2 with gene annotation.
 List of supplemental information 1. Graph of mouse weight loss during course of infection- Line graphs showing mouse weight data during course of infection days 1 to 10 post-infections (p.i.). 2. Graph
List of supplemental information 1. Graph of mouse weight loss during course of infection- Line graphs showing mouse weight data during course of infection days 1 to 10 post-infections (p.i.). 2. Graph
CPM (x 10-3 ) Tregs +Teffs. Tregs alone ICOS CLTA-4
 A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
qpcr-array Analysis Service
 qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
TNFSF13B tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b NF-kB pathway cluster, Enrichment Score: 3.57
 Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Dynamic Changes in Chromatin Accessibility Occur in CD8 + T Cells Responding to Viral Infection
 Resource Dynamic Changes in Chromatin Accessibility Occur in CD8 + T Cells Responding to Viral Infection Highlights d Examined chromatin accessibility in endogenous CD8 + T cells during viral infection
Resource Dynamic Changes in Chromatin Accessibility Occur in CD8 + T Cells Responding to Viral Infection Highlights d Examined chromatin accessibility in endogenous CD8 + T cells during viral infection
To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Gene Expression Analysis To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and mice given renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), ncounter
Supplementary Materials and Methods Gene Expression Analysis To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and mice given renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), ncounter
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs
 Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
An integrated transcriptomic and functional genomic approach identifies a. type I interferon signature as a host defense mechanism against Candida
 Supplementary information for: An integrated transcriptomic and functional genomic approach identifies a type I interferon signature as a host defense mechanism against Candida albicans in humans Sanne
Supplementary information for: An integrated transcriptomic and functional genomic approach identifies a type I interferon signature as a host defense mechanism against Candida albicans in humans Sanne
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Kennedy GA, Varelias A, Vuckovic S, et al.
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Kennedy GA, Varelias A, Vuckovic S, et al.
Functional classification of memory CD8 þ T cells by CX 3 CR1 expression
 Received 26 Apr 21 Accepted 6 Aug 21 Published 2 Sep 21 DOI: 1.138/ncomms936 OPEN Functional classification of memory CD8 þ T cells by CX 3 CR1 expression Jan P. Böttcher 1,w, *, Marc Beyer 2, *, Felix
Received 26 Apr 21 Accepted 6 Aug 21 Published 2 Sep 21 DOI: 1.138/ncomms936 OPEN Functional classification of memory CD8 þ T cells by CX 3 CR1 expression Jan P. Böttcher 1,w, *, Marc Beyer 2, *, Felix
T cell memory Friday, February 10, 17
 T cell memory 2-10-2017 expansion contraction memory recall EFFECTORS 10 6 pathogen load secondary challenge MEMORY 10 2 NAIVE 2 7-8 30 >1 year days post-infection In mouse, ~100 naïve, CD8s become ~3x10
T cell memory 2-10-2017 expansion contraction memory recall EFFECTORS 10 6 pathogen load secondary challenge MEMORY 10 2 NAIVE 2 7-8 30 >1 year days post-infection In mouse, ~100 naïve, CD8s become ~3x10
Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 *** Nature Medicine: doi: /nm Pten pc-/- ;Zbtb7a pc-/- Pten pc-/- ;Pml pc-/- Pten pc-/- ;Trp53 pc-/-
 Gr-1 Gr-1 Gr-1 Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 a Gr1-CD11b 3 months Spleen T cells 3 months Spleen B cells 3 months Spleen Macrophages 3 months Spleen 15 4 8 6 c CD11b+/Gr1+ cells [%] 1 5 b T cells
Gr-1 Gr-1 Gr-1 Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 a Gr1-CD11b 3 months Spleen T cells 3 months Spleen B cells 3 months Spleen Macrophages 3 months Spleen 15 4 8 6 c CD11b+/Gr1+ cells [%] 1 5 b T cells
CD Marker Antibodies. atlasantibodies.com
 CD Marker Antibodies atlasantibodies.com CD Marker Antibodies Product Name Product Number Validated Applications Anti-ACE HPA029298 IHC,WB Anti-ACKR1 HPA016421 IHC Anti-ACKR1 HPA017672 IHC Anti-ADAM17
CD Marker Antibodies atlasantibodies.com CD Marker Antibodies Product Name Product Number Validated Applications Anti-ACE HPA029298 IHC,WB Anti-ACKR1 HPA016421 IHC Anti-ACKR1 HPA017672 IHC Anti-ADAM17
Cancer, inflammation, and immunity crosstalk
 Contact Technical Support BRCsupport@QIAGEN.COM 1-800-362-7737 Cancer, inflammation, and immunity crosstalk Jesse Liang, Ph.D. Legal disclaimer QIAGEN products shown here are intended for molecular biology
Contact Technical Support BRCsupport@QIAGEN.COM 1-800-362-7737 Cancer, inflammation, and immunity crosstalk Jesse Liang, Ph.D. Legal disclaimer QIAGEN products shown here are intended for molecular biology
Genomic Analyses across Six Cancer Types Identify Basal-like Breast Cancer as a Unique Molecular Entity
 Genomic Analyses across Six Cancer Types Identify Basal-like Breast Cancer as a Unique Molecular Entity Aleix Prat, Barbara Adamo, Cheng Fan, Vicente Peg, Maria Vidal, Patricia Galván, Ana Vivancos, Paolo
Genomic Analyses across Six Cancer Types Identify Basal-like Breast Cancer as a Unique Molecular Entity Aleix Prat, Barbara Adamo, Cheng Fan, Vicente Peg, Maria Vidal, Patricia Galván, Ana Vivancos, Paolo
1,000 in silico simulated alpha, beta, gamma and delta TCR repertoires were created.
 938 939 940 941 942 Figure S1 Schematic of the in silico TCRminer and MiXCR validation. 1,000 in silico simulated alpha, beta, gamma and delta TCR repertoires were created. Then, 100,000 simulated 80 bp
938 939 940 941 942 Figure S1 Schematic of the in silico TCRminer and MiXCR validation. 1,000 in silico simulated alpha, beta, gamma and delta TCR repertoires were created. Then, 100,000 simulated 80 bp
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY. CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells. Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation
 IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Supplementary Table S1: Gene expression targets
 Supplementary Table S1: Gene expression targets Probe ID Gene ID Gene Descriptions Cell type Antigen-dependent activation MmugDNA.32422.1.S1_at CD180 CD180 molecule B 1 MmugDNA.18254.1.S1_at CD19 CD19
Supplementary Table S1: Gene expression targets Probe ID Gene ID Gene Descriptions Cell type Antigen-dependent activation MmugDNA.32422.1.S1_at CD180 CD180 molecule B 1 MmugDNA.18254.1.S1_at CD19 CD19
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Immunological characterization of a recipient of a cross-match positive. Thet Su Win, Naoka Murakami, Thiago J. Borges, Anil Chandraker, George
 Supplementary Materials Immunological characterization of a recipient of a cross-match positive face transplant Thet Su Win, Naoka Murakami, Thiago J. Borges, Anil Chandraker, George Murphy, Christine
Supplementary Materials Immunological characterization of a recipient of a cross-match positive face transplant Thet Su Win, Naoka Murakami, Thiago J. Borges, Anil Chandraker, George Murphy, Christine
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS
 1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS Figure S1 Cumulative ZIKV production by testis explants over a 9 day-culture period. Viral titer values presented in Figure 1B (viral release over a 3 day-culture period measured
1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS Figure S1 Cumulative ZIKV production by testis explants over a 9 day-culture period. Viral titer values presented in Figure 1B (viral release over a 3 day-culture period measured
Moyamoya disease susceptibility gene RNF213 links inflammatory and angiogenic
 Supplementary Information for Moyamoya disease susceptibility gene RNF213 links inflammatory and angiogenic signals in endothelial cells Kazuhiro Ohkubo 1,, Yasunari Sakai 1,*,, Hirosuke Inoue 1, Satoshi
Supplementary Information for Moyamoya disease susceptibility gene RNF213 links inflammatory and angiogenic signals in endothelial cells Kazuhiro Ohkubo 1,, Yasunari Sakai 1,*,, Hirosuke Inoue 1, Satoshi
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection
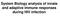 System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
CD80 and PD-L2 define functionally distinct memory B cell subsets that are. Griselda V Zuccarino-Catania, Saheli Sadanand, Florian J Weisel, Mary M
 Supplementary Figures CD8 and PD-L define functionally distinct memory B cell subsets that are independent of antibody isotype Running title: Memory B Cell Subset Function Griselda V Zuccarino-Catania,
Supplementary Figures CD8 and PD-L define functionally distinct memory B cell subsets that are independent of antibody isotype Running title: Memory B Cell Subset Function Griselda V Zuccarino-Catania,
Figure 1: Effects of cisplatin on survival of lung cancer cells.
 Figure 1 Figure 1: Effects of cisplatin on survival of lung cancer cells. To determine the IC 50 concentration of cisplatin, cells were treated with various concentrations of cisplatin and cell survival
Figure 1 Figure 1: Effects of cisplatin on survival of lung cancer cells. To determine the IC 50 concentration of cisplatin, cells were treated with various concentrations of cisplatin and cell survival
T Cell Activation. Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009
 T Cell Activation Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009 Phases of Adaptive Immune Responses Phases of T cell responses IL-2 acts as an autocrine growth factor Fig. 11-11 Clonal Expansion of T cells
T Cell Activation Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009 Phases of Adaptive Immune Responses Phases of T cell responses IL-2 acts as an autocrine growth factor Fig. 11-11 Clonal Expansion of T cells
Supplemental Figure 1. IL-3 blockade with Fab CSL362 depletes plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pdcs), but not basophils, at higher doses.
 Supplemental Figure 1. IL-3 blockade with Fab CSL362 depletes plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pdcs), but not basophils, at higher doses. Percentage of viable (A) pdcs (Sytox Blue-, Lin1-, HLADR+, BDCA2++)
Supplemental Figure 1. IL-3 blockade with Fab CSL362 depletes plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pdcs), but not basophils, at higher doses. Percentage of viable (A) pdcs (Sytox Blue-, Lin1-, HLADR+, BDCA2++)
% of Cells A B C. Proliferation Index. T cell count (10 6 ) Division Index. % of Max CFSE. %Ki67+ cells. Supplementary Figure 1.
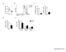 A B C T cell count (1 6 ) 3. 2. 1.. * % of Max CFSE ormoxia ypoxia o Stim. Proliferation Index 2.5 2. 1.5 1. * Division Index 2. 1.5 1..5. D E %Ki67+ cells 1 8 6 4 2 % of Cells 8 ormoxia 6 ypoxia 4 2 *
A B C T cell count (1 6 ) 3. 2. 1.. * % of Max CFSE ormoxia ypoxia o Stim. Proliferation Index 2.5 2. 1.5 1. * Division Index 2. 1.5 1..5. D E %Ki67+ cells 1 8 6 4 2 % of Cells 8 ormoxia 6 ypoxia 4 2 *
Supplementary Figures and Tables. An inflammatory gene signature distinguishes neurofibroma Schwann cells and
 Supplementary Figures and Tables An inflammatory gene signature distinguishes neurofibroma Schwann cells and macrophages from cells in the normal peripheral nervous system Kwangmin Choi 1, Kakajan Komurov
Supplementary Figures and Tables An inflammatory gene signature distinguishes neurofibroma Schwann cells and macrophages from cells in the normal peripheral nervous system Kwangmin Choi 1, Kakajan Komurov
Immune reprogramming via PD-1 inhibition enhances early-stage lung cancer survival
 Immune reprogramming via PD-1 inhibition enhances early-stage lung cancer survival Geoffrey J. Markowitz, 1,2,3 Lauren S. Havel, 1,2,3 Michael J.P. Crowley, 3,4 Yi Ban, 1,2,3 Sharrell B. Lee, 1,3 Jennifer
Immune reprogramming via PD-1 inhibition enhances early-stage lung cancer survival Geoffrey J. Markowitz, 1,2,3 Lauren S. Havel, 1,2,3 Michael J.P. Crowley, 3,4 Yi Ban, 1,2,3 Sharrell B. Lee, 1,3 Jennifer
Subject Index. Bcl-2, apoptosis regulation Bone marrow, polymorphonuclear neutrophil release 24, 26
 Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Eosinophils! 40! 30! 20! 10! 0! NS!
 A Macrophages Lymphocytes Eosinophils Neutrophils Percentage (%) 1 ** 4 * 1 1 MMA SA B C Baseline FEV1, % predicted 15 p = 1.11 X 10-9 5 CD4:CD8 ratio 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Cellular infiltrate in the
A Macrophages Lymphocytes Eosinophils Neutrophils Percentage (%) 1 ** 4 * 1 1 MMA SA B C Baseline FEV1, % predicted 15 p = 1.11 X 10-9 5 CD4:CD8 ratio 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Cellular infiltrate in the
Statistical Issues in Translational Cancer Research
 Statistical Issues in Translational Cancer Research Martin Bøgsted Department of Haematology Aalborg University Hospital and Department of Clinical Medicine Aalborg University The only useful function
Statistical Issues in Translational Cancer Research Martin Bøgsted Department of Haematology Aalborg University Hospital and Department of Clinical Medicine Aalborg University The only useful function
Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Distinct Features in Human Breast Cancer
 Resource Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Distinct Features in Human Breast Cancer Graphical Abstract Authors George Plitas, Catherine Konopacki, Kenmin Wu,..., Ekaterina V. Putintseva, Dmitriy M. Chudakov,
Resource Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Distinct Features in Human Breast Cancer Graphical Abstract Authors George Plitas, Catherine Konopacki, Kenmin Wu,..., Ekaterina V. Putintseva, Dmitriy M. Chudakov,
ACE ImmunoID Biomarker Discovery Solutions ACE ImmunoID Platform for Tumor Immunogenomics
 ACE ImmunoID Biomarker Discovery Solutions ACE ImmunoID Platform for Tumor Immunogenomics Precision Genomics for Immuno-Oncology Personalis, Inc. ACE ImmunoID When one biomarker doesn t tell the whole
ACE ImmunoID Biomarker Discovery Solutions ACE ImmunoID Platform for Tumor Immunogenomics Precision Genomics for Immuno-Oncology Personalis, Inc. ACE ImmunoID When one biomarker doesn t tell the whole
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection. C57BL/6 mice were (a) treated intravaginally with 20 µl of PBS or infected with 6.7x10 4 pfu of HSV-2 in the
Supplementary Figure 1 Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection. C57BL/6 mice were (a) treated intravaginally with 20 µl of PBS or infected with 6.7x10 4 pfu of HSV-2 in the
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs.
 Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
Supplementary information CD4 T cells are required for both development and maintenance of disease in a new model of reversible colitis
 Supplementary information CD4 T cells are required for both development and maintenance of disease in a new model of reversible colitis rasseit and Steiner et al. .. Supplementary Figure 1 % of initial
Supplementary information CD4 T cells are required for both development and maintenance of disease in a new model of reversible colitis rasseit and Steiner et al. .. Supplementary Figure 1 % of initial
Follicular Lymphoma. ced3 APOPTOSIS. *In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans 131 of the organism's 1031 cells die during development.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
The epigenetic landscape of T cell subsets in SLE identifies known and potential novel drivers of the autoimmune response
 Abstract # 319030 Poster # F.9 The epigenetic landscape of T cell subsets in SLE identifies known and potential novel drivers of the autoimmune response Jozsef Karman, Brian Johnston, Sofija Miljovska,
Abstract # 319030 Poster # F.9 The epigenetic landscape of T cell subsets in SLE identifies known and potential novel drivers of the autoimmune response Jozsef Karman, Brian Johnston, Sofija Miljovska,
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment Alex Chenchik, Ph.D. Cellecta, Inc.
 Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment Alex Chenchik, Ph.D. Cellecta, Inc. Cellecta, Inc. Founded: April 2006 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA 12 SBIR Grants Custom Service Provider for Functional
Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment Alex Chenchik, Ph.D. Cellecta, Inc. Cellecta, Inc. Founded: April 2006 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA 12 SBIR Grants Custom Service Provider for Functional
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3745
 Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental settings. (a) Experimental setup and bioinformatic data analysis of transcriptomic changes induced in neonatal and adult monocytes by stimulation with 10 ng/ml LPS for
Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental settings. (a) Experimental setup and bioinformatic data analysis of transcriptomic changes induced in neonatal and adult monocytes by stimulation with 10 ng/ml LPS for
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
A bioinformatics driven cancer study
 The 11th China-Japan-Korea Bioinformatics Training Course & Symposium, June 16-18, Suzhou, China A bioinformatics driven cancer study Chao Li and Yixue Li yxli@sibs.ac.cn Shanghai Institutes for Bio-Medicine
The 11th China-Japan-Korea Bioinformatics Training Course & Symposium, June 16-18, Suzhou, China A bioinformatics driven cancer study Chao Li and Yixue Li yxli@sibs.ac.cn Shanghai Institutes for Bio-Medicine
For focused group profiling of human HIV infection and host response genes expression
 ExProfile TM Human HIV Infection and Host Response Related Gene qpcr Array For focused group profiling of human HIV infection and host response genes expression Cat. No. QG023-A (1 x 96-well plate, Format
ExProfile TM Human HIV Infection and Host Response Related Gene qpcr Array For focused group profiling of human HIV infection and host response genes expression Cat. No. QG023-A (1 x 96-well plate, Format
Late regulation of immune genes and micrornas in circulating leukocytes in a pig model of
 1 Supplementary material for: 2 3 4 5 6 Late regulation of immune genes and micrornas in circulating leukocytes in a pig model of influenza A (H1N2) infection Louise Brogaard, Peter M. H. Heegaard, Lars
1 Supplementary material for: 2 3 4 5 6 Late regulation of immune genes and micrornas in circulating leukocytes in a pig model of influenza A (H1N2) infection Louise Brogaard, Peter M. H. Heegaard, Lars
Deconvolution of Heterogeneous Wound Tissue Samples into Relative Macrophage Phenotype Composition via Models based on Gene Expression
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information for: Deconvolution of Heterogeneous Wound Tissue Samples into
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information for: Deconvolution of Heterogeneous Wound Tissue Samples into
Micro 204. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier
 Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
HARNESS THE POWER OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM TO FIGHT CANCER
 OncoPept TM HARNESS THE POWER OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM TO FIGHT CANCER OncoPept identifies and delivers priortized T-cell neo-epitopes from the patient's tumor mutanome 2 What is OncoPept? OncoPept is an integrated
OncoPept TM HARNESS THE POWER OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM TO FIGHT CANCER OncoPept identifies and delivers priortized T-cell neo-epitopes from the patient's tumor mutanome 2 What is OncoPept? OncoPept is an integrated
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information An orally available, small-molecule interferon inhibits viral replication Hideyuki Konishi 1, Koichi Okamoto 1, Yusuke Ohmori 1, Hitoshi Yoshino 2, Hiroshi Ohmori 1, Motooki Ashihara
Supplementary Information An orally available, small-molecule interferon inhibits viral replication Hideyuki Konishi 1, Koichi Okamoto 1, Yusuke Ohmori 1, Hitoshi Yoshino 2, Hiroshi Ohmori 1, Motooki Ashihara
Prepared by Cyrus H. Nozad, MD, University of Tennessee and John Seyerle, MD, Ohio State University
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 21 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, Seventh Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 21: Antigen-Presenting Dendritic Cells (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 21 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, Seventh Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 21: Antigen-Presenting Dendritic Cells (Pages
Tissue-resident memory features are linked to the magnitude of cytotoxic T cell responses in human lung cancer
 Tissue-resident memory features are linked to the magnitude of cytotoxic T cell responses in human lung cancer 21 Nature America, Inc., part of Springer Nature. All rights reserved. Anusha-Preethi Ganesan
Tissue-resident memory features are linked to the magnitude of cytotoxic T cell responses in human lung cancer 21 Nature America, Inc., part of Springer Nature. All rights reserved. Anusha-Preethi Ganesan
Venky Ramakrishna PhD Celldex Therapeutics, Hampton NJ, USA
 Antibody Targeting of Human CD27 with Varlilumab (CDX-1127) identifies genes and pathways related to inflammation Venky Ramakrishna PhD Celldex Therapeutics, Hampton NJ, USA www.celldextherapeutics.com
Antibody Targeting of Human CD27 with Varlilumab (CDX-1127) identifies genes and pathways related to inflammation Venky Ramakrishna PhD Celldex Therapeutics, Hampton NJ, USA www.celldextherapeutics.com
U118MG. Supplementary Figure 1 U373MG U118MG 3.5 A CCF-SSTG
 A172 CCF-SSTG1 15 - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10101112131617192022-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22 T98G U373MG - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7
A172 CCF-SSTG1 15 - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10101112131617192022-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22 T98G U373MG - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7
Activated mast cells promote differentiation of B cells into effector cells
 Supplementary,information, Activated mast cells promote differentiation of B cells into effector cells Anna-Karin E. Palm 1, Gianni Garcia Faroldi 2, Marcus Lundberg 1, Gunnar Pejler 3, 2 and Sandra Kleinau
Supplementary,information, Activated mast cells promote differentiation of B cells into effector cells Anna-Karin E. Palm 1, Gianni Garcia Faroldi 2, Marcus Lundberg 1, Gunnar Pejler 3, 2 and Sandra Kleinau
15. Supplementary Figure 9. Predicted gene module expression changes at 24hpi during HIV
 Supplementary Information Table of content 1. Supplementary Table 1. Summary of RNAseq data and mapping statistics 2. Supplementary Table 2. Biological functions enriched in 12 hpi DE genes, derived from
Supplementary Information Table of content 1. Supplementary Table 1. Summary of RNAseq data and mapping statistics 2. Supplementary Table 2. Biological functions enriched in 12 hpi DE genes, derived from
CD4 + follicular helper T cell infiltration predicts breast cancer survival
 Research article CD4 + follicular helper T cell infiltration predicts breast cancer survival Chunyan Gu-Trantien, 1 Sherene Loi, 2 Soizic Garaud, 1 Carole Equeter, 1,2 Myriam Libin, 1 Alexandre de Wind,
Research article CD4 + follicular helper T cell infiltration predicts breast cancer survival Chunyan Gu-Trantien, 1 Sherene Loi, 2 Soizic Garaud, 1 Carole Equeter, 1,2 Myriam Libin, 1 Alexandre de Wind,
An epithelial circadian clock controls pulmonary inflammation and glucocorticoid action
 An epithelial circadian clock controls pulmonary inflammation and glucocorticoid action Supplementary Figure : Expression levels of toll-like receptor 4 (Tlr4) in muse lung does not change throughout the
An epithelial circadian clock controls pulmonary inflammation and glucocorticoid action Supplementary Figure : Expression levels of toll-like receptor 4 (Tlr4) in muse lung does not change throughout the
Department of International Health (Vaccine science track) Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health
 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome is a TH17 and Treg immune disease By Wan-Jiung Hu Postdoctorate Genomics Research Center Academia Sinica No 128 Academia Road section2 Nangang 115, Taipei, Taiwan Previous
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome is a TH17 and Treg immune disease By Wan-Jiung Hu Postdoctorate Genomics Research Center Academia Sinica No 128 Academia Road section2 Nangang 115, Taipei, Taiwan Previous
ACE ImmunoID. ACE ImmunoID. Precision immunogenomics. Precision Genomics for Immuno-Oncology
 ACE ImmunoID ACE ImmunoID Precision immunogenomics Precision Genomics for Immuno-Oncology Personalis, Inc. A universal biomarker platform for immuno-oncology Patient response to cancer immunotherapies
ACE ImmunoID ACE ImmunoID Precision immunogenomics Precision Genomics for Immuno-Oncology Personalis, Inc. A universal biomarker platform for immuno-oncology Patient response to cancer immunotherapies
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Fluorochrome Panel 1 Panel 2 Panel 3 Panel 4 Panel 5 CTLA-4 CTLA-4 CD15 CD3 FITC. Bio) PD-1 (MIH4, BD) ICOS (C398.4A, Biolegend) PD-L1 (MIH1, BD)
 Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
OncoMir Library Cancer Type Target Gene
 OncoMir Library Cancer Type Target Gene hsa-let-7a-1 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-2 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-3 Breast Cancer, Lung
OncoMir Library Cancer Type Target Gene hsa-let-7a-1 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-2 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-3 Breast Cancer, Lung
Effector Mechanisms of Cell-Mediated Immunity
 Effector Mechanisms of Cell-Mediated Immunity Dr. Julia Rempel Section of Hepatology 789-3825 jdrempel@cc.umanitoba.ca 804D JBRC Topics: I. Types of Cell-Mediated Immunity II. Migration of Effector T Lymphocytes
Effector Mechanisms of Cell-Mediated Immunity Dr. Julia Rempel Section of Hepatology 789-3825 jdrempel@cc.umanitoba.ca 804D JBRC Topics: I. Types of Cell-Mediated Immunity II. Migration of Effector T Lymphocytes
Experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) presents a histopathologic
 Differentially Expressed Genes in MHC-Compatible Rat Strains That Are Susceptible or Resistant to Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis Mary J. Mattapallil, 1 Andrea Augello, 2 Chris Cheadle, 3 Diane Teichberg,
Differentially Expressed Genes in MHC-Compatible Rat Strains That Are Susceptible or Resistant to Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis Mary J. Mattapallil, 1 Andrea Augello, 2 Chris Cheadle, 3 Diane Teichberg,
MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR REJECTION IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION AN OVERVIEW
 MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR REJECTION IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION AN OVERVIEW YVON LEBRANCHU Service Néphrologie et Immunologie Clinique CHU TOURS ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELL CD4 + T CELL CYTOKINE PRODUCTION CLONAL
MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR REJECTION IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION AN OVERVIEW YVON LEBRANCHU Service Néphrologie et Immunologie Clinique CHU TOURS ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELL CD4 + T CELL CYTOKINE PRODUCTION CLONAL
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Engineered T cells: Next-generation cancer immunotherapy
 Engineered T cells: Next-generation cancer immunotherapy Rahul Purwar, Assistant Professor Department of Biosciences & Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay) Mumbai, India, 400076
Engineered T cells: Next-generation cancer immunotherapy Rahul Purwar, Assistant Professor Department of Biosciences & Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay) Mumbai, India, 400076
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment. Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein
 Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
TGF-β receptor maintains CD4 T helper cell identity during chronic viral infections
 TGF-β receptor maintains CD4 T helper cell identity during chronic viral infections Gavin M. Lewis, 1 Ellen J. Wehrens, 1 Lara Labarta-Bajo, 1 Hendrik Streeck, 2 and Elina I. Zuniga 1 1 Division of Biological
TGF-β receptor maintains CD4 T helper cell identity during chronic viral infections Gavin M. Lewis, 1 Ellen J. Wehrens, 1 Lara Labarta-Bajo, 1 Hendrik Streeck, 2 and Elina I. Zuniga 1 1 Division of Biological
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementary figure 1 Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275 CLUSTER BY SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS SELECTED PATHWAY ANALISYS TERMS Cluster : up-regulated genes in acute patients Cell cycle/dna repair Fatty acid
Supplementary figure 1 Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275 CLUSTER BY SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS SELECTED PATHWAY ANALISYS TERMS Cluster : up-regulated genes in acute patients Cell cycle/dna repair Fatty acid
Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation. Thursday Jan 26th, 2017
 Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation Thursday Jan 26th, 2017 Topics The life of immune cells Where are they born? Where are they educated? Where do they function? How do they get there? The
Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation Thursday Jan 26th, 2017 Topics The life of immune cells Where are they born? Where are they educated? Where do they function? How do they get there? The
Supplement Results, Figures and Tables
 Supplement Results, Figures and Tables Results PET imaging The SUV was significantly higher in tumours of the parental HSC-3 cell line than tumours of the EV and the MMP-8 overexpressing cell lines (Figure
Supplement Results, Figures and Tables Results PET imaging The SUV was significantly higher in tumours of the parental HSC-3 cell line than tumours of the EV and the MMP-8 overexpressing cell lines (Figure
Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and Tissues of the Immune System. Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
A fresh approach to Immuno-oncology: Ex vivo analysis of drug efficacy in fresh patient tumortissue
 A fresh approach to Immuno-oncology: Ex vivo analysis of drug efficacy in fresh patient tumortissue Soner Altiok, MD, PhD Chief Scientific Officer Nilogen Oncosystems Tampa, Florida - Nilogen Oncosystems,
A fresh approach to Immuno-oncology: Ex vivo analysis of drug efficacy in fresh patient tumortissue Soner Altiok, MD, PhD Chief Scientific Officer Nilogen Oncosystems Tampa, Florida - Nilogen Oncosystems,
DEVELOPMENT AND REVERSAL
 DEVELOPMENT AND REVERSAL OF T CELL EXHAUSTION E. John Wherry Institute for Immunology University of Pennsylvania IAS 2016 Towards an HIV Cure Symposium Durban, South Africa www.iasociety.org T cell exhaustion
DEVELOPMENT AND REVERSAL OF T CELL EXHAUSTION E. John Wherry Institute for Immunology University of Pennsylvania IAS 2016 Towards an HIV Cure Symposium Durban, South Africa www.iasociety.org T cell exhaustion
The quest for the identification of the genetic determinants of cancer immune responsiveness
 2015 Sidra Medical and Research Center The quest for the identification of the genetic determinants of cancer immune responsiveness Francesco M Marincola - Chief Research Officer Sidra Medical and Research
2015 Sidra Medical and Research Center The quest for the identification of the genetic determinants of cancer immune responsiveness Francesco M Marincola - Chief Research Officer Sidra Medical and Research
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation
 Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid analysis showed increased eosinophil in 30% of subjects with IrIa BAL
 Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid analysis showed increased eosinophil in 30% of subjects with IrIa BAL UBC Chan-Yeung Centre for Occupational and Environmental Respiratory Disease Understanding exposure effects
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid analysis showed increased eosinophil in 30% of subjects with IrIa BAL UBC Chan-Yeung Centre for Occupational and Environmental Respiratory Disease Understanding exposure effects
Supplementary. presence of the. (c) mrna expression. Error. in naive or
 Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
* Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
 Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Supplemental Information. High-Throughput Microfluidic Labyrinth for the. Label-free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells
 Cell Systems, Volume 5 Supplemental Information High-Throughput Microfluidic Labyrinth for the Label-free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells Eric Lin, Lianette Rivera-Báez, Shamileh Fouladdel, Hyeun
Cell Systems, Volume 5 Supplemental Information High-Throughput Microfluidic Labyrinth for the Label-free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells Eric Lin, Lianette Rivera-Báez, Shamileh Fouladdel, Hyeun
Cellular biomarkers of T lymphocyte func6on. Michael Be9s University of Pennsylvania Department of Microbiology
 Cellular biomarkers of T lymphocyte func6on Michael Be9s University of Pennsylvania Department of Microbiology What T cell response parameters could be important for an effec6ve T cell based product? Specificity
Cellular biomarkers of T lymphocyte func6on Michael Be9s University of Pennsylvania Department of Microbiology What T cell response parameters could be important for an effec6ve T cell based product? Specificity
Welcome. Nanostring Immuno-Oncology Summit. September 21st, FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
 Welcome Nanostring Immuno-Oncology Summit September 21st, 2017 1 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Agenda 4:00-4:30
Welcome Nanostring Immuno-Oncology Summit September 21st, 2017 1 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Agenda 4:00-4:30
Detection of immune cell checkpoint and functional markers in the tumor microenvironment by the RNA in situ hybridization RNAscope assay
 pplication Note Immunotherapy Detection of immune cell checkpoint and functional markers in the tumor microenvironment by the RN in situ hybridization RNscope assay Ming-Xiao He, Na Li, Courtney nderson,
pplication Note Immunotherapy Detection of immune cell checkpoint and functional markers in the tumor microenvironment by the RN in situ hybridization RNscope assay Ming-Xiao He, Na Li, Courtney nderson,
OVARIAN CANCER POSSIBLE TUMOR-SUPPRESSIVE ROLE OF BATF2 IN OVARIAN CANCER
 POSSIBLE TUMOR-SUPPRESSIVE ROLE OF BATF2 IN OVARIAN CANCER Rissa Fedora, OMS-III OVARIAN CANCER 5 th leading cause of death among American women Risk factors: Age Gender female Greater lifetime ovulations
POSSIBLE TUMOR-SUPPRESSIVE ROLE OF BATF2 IN OVARIAN CANCER Rissa Fedora, OMS-III OVARIAN CANCER 5 th leading cause of death among American women Risk factors: Age Gender female Greater lifetime ovulations
Supplementary Material. Table S1. Summary of mapping results
 Supplementary Material Table S1. Summary of mapping results Sample Total reads Mapped (%) HNE0-1 99687516 80786083 (81.0%) HNE0-2 94318720 77047792 (81.7%) HNE0-3 104033900 84348102 (81.1%) HNE15-1 94426598
Supplementary Material Table S1. Summary of mapping results Sample Total reads Mapped (%) HNE0-1 99687516 80786083 (81.0%) HNE0-2 94318720 77047792 (81.7%) HNE0-3 104033900 84348102 (81.1%) HNE15-1 94426598
5/1/13. The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age. The cellular organization of the thymus
 T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology
 Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
