Supplementary figure 1
|
|
|
- Ginger Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary figure 1 Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
2 CLUSTER BY SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS SELECTED PATHWAY ANALISYS TERMS Cluster : up-regulated genes in acute patients Cell cycle/dna repair Fatty acid metabolism/heme biosynthesis Signaling (IL-1, PI3K, MAPK) 1 Cluster 1: genes up-regulated in acute and down-regulated in chronic patients Class I PI3K signaling events mediated by AKT Regulation of actin cytoskeleton Endocytosis Oxidative phosphorylation/electron transport chain Proteasome/lysosome Protein proces. in endoplasmic reticulum/metabolism of proteins 2 Cluster 2: down-regulated genes in chronic patients Metabolism/Metabolism of vitamins and cofactors RNA transport Translation factors Integrin-linked kinase signaling Clusters 3 and : up-regulated genes in chronic patients 3 Krueppel-associated box/zinc-finger Hedgehog Glycine-serine-threonine metabolism Hypoxic and oxygen homeostasis regul. of HIF-1a Ribosome Mucin type O-glycan biosynthesis Cluster 5: down-regulated genes in acute patients 5 Ribosomal proteins LincRNA/Non-protein coding transcripts Signaling by GPCR ACUTE RESOLVED CHRONIC ACUTE/RESOLVED CHRONIC/RESOLVED Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
3 Supplementary figure 2 Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
4 a MITOCHONDRION ES = -.33 p =.9 ES = -.9 p <1 - PROTEASOME b PROTEASOME DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE P53 INDEPENDENT G1 S DNA DAMAGE CHECKPOINT PROTEASOME REGULATION ORNITHINE DECARBOX. ACTIVATION OF NF-KB IN B CELLS SIGNALING BY B CELL RECEPTOR BCR P53 DEPENDENT G1 DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE ER PHAGOSOME PATHWAY RNA POL I RNA POL III MITOCHONDRIAL SYSTEMIC LUPUS TRANSCRIPTION ERYTHEMATOSUS TRANSCRIPTION RNA POL I PROMOTER OPENING TRANSCRIPTION DEPOSITION OF NEW CENPA CONTAINING NUCLEOSOMES AT THE CENTROMERE RNA POL I TRANSCRIPTION MITOCHONDRION OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION PACKAGING OF TELOMERE ENDS RESPIRATORY ELECTRON TRANSPORT ENOS ACTIVATION AND REGULATION RESPIRATORY ELECTRON TRANSP. ATP SYNTHESIS BY CHEMIOSMOTIC COUPL. HEAT PRODUCTION BY UNCOUPLING PROT. DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE UP UP Node color DOWN Node border color DOWN Chr vs Res Chr vs FLUh ES = -.32 p =.3 TRANSCRIPTION ES = -.5 p = FLUh Chr Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
5 Supplementary figure 3 Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
6 Counts CD8 JC1 FL-2 Anti-CyC mab MFI Dextr+CD8+ cells Anti-ATP5O mab MFI Dextr+CD8+ cells Normalized to mode a Cytochrome c ATP5O 2,5 1, p=.3 p=.15 HC Res Chr 1,5 6 2 p=.5 p=.5 HC Res Chr Chr HC Chr Res Anti-CyC mab MFI Anti-ATP5O mab MFI b Valinomycin Unstimulated Stimulated Chr 1.5% 3% HC 2%.6% Dextramer JC1 FL-1 CCCP Unstimulated Stimulated Chr 99.9% 7.3% 23.% Res 99.9% 1.1%.8% DiOC6 Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
7 Supplementary figure Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
8 Ratio MFI stim./unstim. Dextr+CD8+ cells by Proteostat staining Counts Proteostat ratio no acute p= p= unstimulated anti-cd3 stimulated.5. HC n=15 Ratio Prot healthy Res n=7 Ratio Prot res Chr n=7 Ratio Prot cron Proteostat HC Res Chr Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
9 Supplementary figure 5 Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
10 ANNV MFI/ DEXTR+ CELLS % DEXTRAMER+ % ANNV+7AAD+ % DEXTRAMER+ % ANNV+7AAD+ % DEXTRAMER+ % ANNV+7AAD+ % DEXTRAMER+ % ANNV+7AAD+ % DEXTRAMER+ % ANNV+7AAD+ CD8 Dextramer CD8 Dextramer CD8 Dextramer a No antioxidant MitoQ MitoTempo Pt. n..9% 3.65% 2.39% 7.85% 1.9% 62.59% HBV-specific FLU-specific 1.65% 38.3% 2.% 3% 1 % 33% Pt. n.15 HBV-specific No expansion No IFN- detection.5% No IFN- detection.15% 67% FLU-specific 6.7% 62.2% 7.% 8.53% 8.51% 71.7% Pt. n.36 HBV-specific.19% 2.8%.21% 7.3% 1.8%.37% 62.8% 68.95% 7.2% 6.5% 6% 75% FLU-specific Dextramer IFN Dextramer IFN Dextramer IFN b Pt. n.25 c Pt. n.2 Pt. n.37 Pt. n.25 Pt. n.9 Pt. n No MTQ MTT antioxidant No MTQ MTT antioxidant No MTQ MTT antioxidant No MTQ MTT antioxidant No MTT antioxidant % DEXTRAMER+ % DEXTR+ANNV+7AAD+ Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
11 Supplementary figure 6 Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
12 a Fold change Chronic / Resolved b Fold change Chronic / Healthy PDCD CD CTLA PDCD1 CD2 KLRG BATF 3,5 3 2,5 2 1,5 1,5 EOMES BATF EOMES 1,8,6,,2 TBX21,5,,3,2,1 CD28 1,8,6,,2 -,2 TBX21 1,8,6,,2 -,2 CD28 qpcr Microarray Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
13 Supplementary figure 7 Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
14 Acute vs. Resolved NES = p <1 - FDR <1 - NES = 1.66 p <1 - FDR =.33 Kaech day8 effector vs memory CD8 T cell UP (Kaech SM et al, 22) Effector vs memory CD8 T cell UP (Wherry EJ et al, 27) Chronic vs. Resolved Chronic vs. Healthy NES = p <1 - FDR =.9 NES = p <1 - FDR =.19 Exhausted vs memory CD8 T cell DN (Wherry EJ et al, 27) Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
15 Supplementary figure 8 Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
16 Microarray Fold change Microarray Fold change Microarray Fold change Microarray Fold change Microarray Fold change Microarray Fold change Microarray Fold change Microarray Fold change Microarray Fold change a R 2 =.65 p= qpcr ATP5D expression Chr/Res Ac/Res PSMD expression 15 3, ,5 2 5 R 2 =.72 1,5 p=.2 1, qpcr Chr/Res Ac/Res b R 2 =.75 p= qpcr TIMM1 expression,15,1,5 Chr/Res 2 15 HSPA1A expression 1 5 R 2 =.91 p= qpcr Chr/Res 15 SUMO1 expression,93 15 HSPA1L expression R 2 =.57 p= qpcr,92,91,9,899 Chr/Res 1 5 R 2 =.72 p= qpcr Chr/Res 15 1 PSMB8 expression 5 R 2 =.75 p= qpcr,,3,2,1 Chr/Res 15 1 TIMM23 expression 5 R 2 =.56 p= qpcr,2,1 Chr/Res 15 NDUFA6 expression,2 1 5 R 2 =.59 p= qpcr,1 Chr/Res qpcr Microarray Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
17 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Pathway analysis of gene clusters differentially regulated in acute, resolved and chronic hepatitis B patients. Heat-map representation of differentially expressed genes identified by ANOVA in the three patient groups, subdivided into six expression patterns by self-organizing maps; up-regulated and down-regulated genes are shown in red and green, respectively. The barplots on the right compare mean gene expression levels in acute and chronic patients with those of resolved patients that served as a common reference. Selected pathway and gene ontology terms significantly associated (FDR.5) with misregulated transcripts in individual clusters are listed on the right-side of each gene cluster. Supplementary Figure 2. Comparison of exhausted HBV-specific CD8 cells from chronic patients with healthy subject FLUspecific CD8 cells. (a) Gene sets associated to the indicated processes, retrieved from GSEA comparison of chronic vs. resolved patients (see Fig. 3), are similarly enriched in the chronic patient vs. healthy subject comparison; enrichment values for each gene set are indicated on the left. FDR = false discovery rate. (b) Network (Cytoscape enrichment map) visualization of the concordance between the dysregulated (mainly down-regulated) gene sets and pathways revealed by GSEA comparison of exhausted CD8 cells with HBV- or FLUspecific CD8 cells from resolved and healthy subjects. The results of the chronic vs. resolved and the chronic vs. healthy comparisons are represented as red (up-regulated) to blue (down-regulated) colors in the center and the rim of each node, respectively, as indicated; a generalized and largely concordant downregulation is apparent. Supplementary Figure 3. Validation of mitochondrion-related gene dysregulation. (a) Expression levels of the electron transport chain proteins CyC (left) and ATP5O (right) represented as MFI values of target-specific mabs measured in FLU-specific cells from healthy controls (HC) and in HBV-specific cells from resolved (Res) and chronic patients (Chr). Representative examples of CyC and ATP5O electron transport chain protein expression in chronic patients (Chr) as compared to healthy controls (HC) and to resolved patients (Res) are also shown. (b) Dot-plots (top) and histograms (bottom) showing the fraction of stimulated cells undergoing MMP depolarization, determined on two representative CD8 cell samples by JC1 and DiOC6 staining, respectively. Cells treated with valinomycin or CCCP are shown as positive controls for MMP depolarization. Supplementary Figure. Functional validation of proteasome-related gene dysregulation. Aggresome quantification, expressed as the ratio of ProteoStat MFI measured in overnight anti-cd3-stimulated versus unstimulated dextramer+ cells from healthy controls (HC), resolved (Res) and chronic (Chr) patients. A representative example is illustrated on the right. Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
18 Supplementary Figure 5. Effect of MT-antioxidants on cytokine production, proliferation and viability of virus-specific CD8 cells. (a) PBMCs were stimulated with HLA-A2-restricted HBV or FLU peptides in the presence or absence of MitoQ or MitoTempo; T cells were stained with the corresponding HLA class-i dextramers prior to flow-cytometric analysis. The dot-plots represent IFNγ production by HBV-, or FLU-specific CD8 cells from three chronic hepatitis B patients. Preferential targeting of HBV-specific CD8 cells by MTantioxidants is apparent; of note, expansion of HBV-specific CD8 cells from patient (Pt) n. 15 was only observed in MT-antioxidanttreated cultures. (b) Ex-vivo annexin V staining, expressed as MFI, of unstimulated (left bar), anti-cd3-stimulated (middle bar) and MitoTempo-treated/anti-CD3 stimulated (right bar) HBV-specific CD8 cells from a chronic patient. (c) Frequencies of dextramer+ and annexin V+7AAD+/dextramer+ CD8 cells from chronic patients in untreated and antioxidant-treated T cell lines expanded in vitro by a 1-days stimulation with the HBV core peptide. An increase in the frequency of dextramer+ cells, associated with a reduction of annexin V+ expression upon MT-antioxidant treatment is apparent. Supplementary Figure 6. qpcr validation of selected genes previously associated to T cell exhaustion. (a) Upregulation of exhaustion-related inhibitory co-receptors and transcription factor genes 5 (Paley, M.A. et al. Science 338, (212); Quigley, M. et al. Nat Med 16, (21)) in HBV-specific CD8 cells from chronic HBV patients compared to patients with resolved infection. Relative mean expression levels (n=3) measured by qpcr or microarray are represented by white and grey bars, respectively. On the bottom, the same is shown for two genes (CD28 co-receptor and TBX21/T-bet transcription factor) which are down-regulated in CD8 cells from chronic HBV patients 5, (Paley, M.A. et al. Science 338, (212); Kurktschiev, P.D. et al. J Exp Med 211, (21)). (b) Same as (a) for the comparison between HBV-specific CD8 cells from chronic HBV patients and FLU-specific CD8 cells from healthy controls. Supplementary Figure 7. GSEA comparison of the chronic HBV transcript dataset with gene sets from the Immunologic signatures (MSigDB, C7) database. Dysregulated genes revealed by the acute HBV vs resolved patients comparison are significantly associated to the effector vs memory CD8 T cells gene sets identified in the LCMV-mouse model of chronic infection. Dysregulated genes that emerged from the comparison of chronic HBV vs. resolved patients (left) and chronic HBV patients vs. healthy subjects (right) are significantly associated to the previously published Exhausted vs memory CD8 T cell DN gene set. Enrichment values for each gene-set are indicated; FDR = false discovery rate. Supplementary Figure 8. Validation of selected genes dysregulated in CD8 cells from hepatitis B patients by Real-Time qpcr. (a) qpcr analysis of two genes (ATP5D and PSMD) up-regulated in acute vs. resolved and down-regulated in chronic vs. resolved comparisons. Spearman s correlation plots of expression levels derived from microarray (log 2 ) and qpcr (log Ct ) analyses are shown on the left. The bar-plots on the right show the ratios between mean expression levels derived from the chronic vs. resolved (Chr/Res) and the acute vs. resolved (Ac/Res) comparisons, measured by microarrays (grey bars) or Real-Time qpcr (white bars). (b) Same as (a) for a subset of genes down-regulated (TIMM1, SUMO1, PSMB8, NDUFA6 and TIMM23) or up-regulated (HSPA1A, HSPA1L) in the chronic vs. resolved (Chr/Res) comparison. Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
19 Supplementary Table Chronic patient clinical details Chronic HBV patients Gender (M/F) 27/15 Age* 2.5 (2-66) HBV-DNA * (IU/ml) 2.35x1 5 (.3 9.6x1 8 ) ALT * (U/L) 5.5 (11-351) HBV genotype 36 gen D 3 gen A 2 gen C 1 gen E eag neg HLA-A POS * Median and range shown Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275
20 Figure 3 statistical details. Panel C (left). Mann Whitney test: Chr vs HC, n1=7, n2=8, p=.3, U=.; Chr vs Res, n1=7, n2=7, p=.6. U=.; Chr vs Ac, n1=7, N2=3, p=.167, U=.. Panel C (right). Mann Whitney test: Chr vs HC, n1=9, n2=7, p=.2, U=.; Chr vs Res, n1=9, n2=6, p=., U=.; Chr PD1+ vs HC, n1=5, N2=7, p=.1,u=.; Chr PD1+ vs Res, n1=5,n2=6, p=., U=.. Panel D. Mann Whitney test: Chr vs HC, n1=16, n2=17, p<.1, U=2.; Chr vs Res, n1=16, n2=9, p=.55, U=22.5; Chr PD1+ vs HC, n1=9, n2=17, p=.15, U=2.; Chr PD1+ vs Res, n1=9, n2=9, p=., U=17.. Panel E (top). Wilcoxon signed rank test: Chr vs HC, number of pairs=1, p=.39, W=53; Chr vs Res, number of pairs=1, p=.371,w=1. Panel E. Wilcoxon signed rank test: (left) HC Unstimulated vs Stimulated, number of pairs=1, p=.2, W=55; (middle) Res Unstimulated vs Stimulated, number of pairs=1, p=.39, W=53; (right) Chr Unstimulated vs Stimulated, number of pairs=9, p=.6523, W=-9. Nature Medicine doi:1.138/nm.275
21 Figure statistical details. Panel A (top left). Wilcoxon signed rank test: %IFNg+ CD8+ MitoQ treated vs untreated, number of pairs=27, p<.1, W=-315; %TNFa+ CD8+ MitoQ treated vs untreated, number of pairs=27, p=.19, W=-235; %IFNg+ TNFa+ CD8+ MitoQ treated vs untreated, number of pairs=27, p<.1, W=-269. Panel A (top right). Wilcoxon signed rank test: fold increase %IFNg+ CD8+ MitoQ treated vs untreated, n=27, p<.1, W=299; fold increase %TNFa+ CD8+ MitoQ treated vs untreated, n=27, p=.2, W=275; fold increase %IFNg+ TNFa+ CD8+ MitoQ treated vs untreated, n=27, p<.1, W=233. Panel A (bottom left). Wilcoxon signed rank test: %IFNg+ CD8+ MitoTempo treated vs untreated, number of pairs=27, p<.1, W=-366; %TNFa+ CD8+ MitoTempo treated vs untreated, number of pairs=27, p<.1, W=-319; %IFNg+ TNFa+ CD8+ MitoTempo treated vs untreated, number of pairs=27, p<.1, W=-291. Panel A (bottom right). Wilcoxon signed rank test: fold increase %IFNg+ CD8+ MitoTempo treated vs untreated, n=27, p<.1, W=37; fold increase %TNFa+ CD8+ MitoTempo treated vs untreated, n=27, p<.1, W=36; fold increase %IFNg+ TNFa+ CD8+ MitoTempo treated vs untreated, n=27, p<.1, W=39. Panel B (top). Wilcoxon signed rank test: fold increase %IFNg+ CD3+ MitoQ treated vs untreated, n=27, p<.1, W=38; fold increase %TNFa+ CD3+ MitoQ treated vs untreated, n=27, p=.22, W=26; fold increase %IFNg+ TNFa+ CD3+ MitoQ treated vs untreated, n=27, p=.2, W=29. Panel B (bottom). Wilcoxon signed rank test: fold increase %IFNg+ CD3+ MitoTempo treated vs untreated, n=27, p<.1, W=317; fold increase %TNFa+ CD3+ MitoTempo treated vs untreated, n=27, p=.28, W=182; fold increase %IFNg+ TNFa+ CD3+ MitoTempo treated vs untreated, n=27, p=.2, W=259. Nature Medicine doi:1.138/nm.275
22 Figure 6 statistical details. Panel A (left). Wilcoxon signed rank test: fold increase %IFNg+ CD8+ HBV vs FLU MitoQ treated, n=9, p<.39, W=35.; fold increase %TNFa+ CD8+ HBV vs FLU MitoQ treated, n=9, p=.27, W=37.; fold increase %IFNg+ TNFa+ CD8+ HBV vs FLU MitoQ treated, n=9, p=.195, W=39.. Panel A (right). Wilcoxon signed rank test: fold increase %IFNg+ CD8+ HBV vs FLU MitoTempo treated, n=9, p<.195, W=39.; fold increase %TNFa+ CD8+ HBV vs FLU MitoTempo treated, n=9, p=.273, W=37.; fold increase %IFNg+ TNFa+ CD8+ HBV vs FLU MitoTempo treated, n=9, p=.5, W=33.. Nature Medicine doi:1.138/nm.275
HD1 (FLU) HD2 (EBV) HD2 (FLU)
 ramer staining + anti-pe beads ramer staining a HD1 (FLU) HD2 (EBV) HD2 (FLU).73.11.56.46.24 1.12 b CD127 + c CD127 + d CD127 - e CD127 - PD1 - PD1 + PD1 + PD1-1 1 1 1 %CD127 + PD1-8 6 4 2 + anti-pe %CD127
ramer staining + anti-pe beads ramer staining a HD1 (FLU) HD2 (EBV) HD2 (FLU).73.11.56.46.24 1.12 b CD127 + c CD127 + d CD127 - e CD127 - PD1 - PD1 + PD1 + PD1-1 1 1 1 %CD127 + PD1-8 6 4 2 + anti-pe %CD127
Supplemental Information. Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy. Induces Dynamic Changes. in PD-1 CD8 + Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells
 Immunity, Volume 50 Supplemental Information Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy Induces Dynamic Changes in PD-1 CD8 + Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells Sema Kurtulus, Asaf Madi, Giulia Escobar, Max Klapholz, Jackson
Immunity, Volume 50 Supplemental Information Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy Induces Dynamic Changes in PD-1 CD8 + Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells Sema Kurtulus, Asaf Madi, Giulia Escobar, Max Klapholz, Jackson
Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded
 Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded from TCGA and differentially expressed metabolic genes
Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded from TCGA and differentially expressed metabolic genes
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Supplementary Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs
 Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs.
 Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1. Enhanced detection of CTLA-4 on the surface of HIV-specific
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGEND Supplementary Figure 1. Enhanced detection of CTLA-4 on the surface of HIV-specific CD4 + T cells correlates with intracellular CTLA-4 levels. (a) Comparative CTLA-4 levels
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGEND Supplementary Figure 1. Enhanced detection of CTLA-4 on the surface of HIV-specific CD4 + T cells correlates with intracellular CTLA-4 levels. (a) Comparative CTLA-4 levels
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler
 Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler DR CALUX Boys Girls Database Systemic lupus erythematosus 4.4 0.0021 6.7
Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler DR CALUX Boys Girls Database Systemic lupus erythematosus 4.4 0.0021 6.7
Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to
 Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells.
 Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Lung Met 1 Lung Met 2 Lung Met Lung Met H3K4me1. Lung Met H3K27ac Primary H3K4me1
 a Gained Met-VELs 1.5 1.5 -.5 Lung Met 1 Lung Met Lung Met 3 1. Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K4me1 1 Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K7ac 1.5 Lung Met H3K7ac Lung Met H3K7ac.8 Primary H3K4me1 Primary H3K7ac
a Gained Met-VELs 1.5 1.5 -.5 Lung Met 1 Lung Met Lung Met 3 1. Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K4me1 1 Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K7ac 1.5 Lung Met H3K7ac Lung Met H3K7ac.8 Primary H3K4me1 Primary H3K7ac
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12
 1 Supplementary Data Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12 serum levels measured by multiplex ELISA (Luminex) in FL patients before
1 Supplementary Data Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12 serum levels measured by multiplex ELISA (Luminex) in FL patients before
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Department of Chemistry, Université de Montréal, C.P. 6128, Succursale centre-ville, Montréal, Québec, H3C 3J7, Canada.
 Phosphoproteome dynamics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under heat shock and cold stress Evgeny Kanshin 1,5, Peter Kubiniok 1,2,5, Yogitha Thattikota 1,3, Damien D Amours 1,3 and Pierre Thibault 1,2,4 * 1
Phosphoproteome dynamics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under heat shock and cold stress Evgeny Kanshin 1,5, Peter Kubiniok 1,2,5, Yogitha Thattikota 1,3, Damien D Amours 1,3 and Pierre Thibault 1,2,4 * 1
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a
 Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
CD25-PE (BD Biosciences) and labeled with anti-pe-microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec) for depletion of CD25 +
 Supplements Supplemental Materials and Methods Depletion of CD25 + T-cells from PBMC. Fresh or HD precultured PBMC were stained with the conjugate CD25-PE (BD Biosciences) and labeled with anti-pe-microbeads
Supplements Supplemental Materials and Methods Depletion of CD25 + T-cells from PBMC. Fresh or HD precultured PBMC were stained with the conjugate CD25-PE (BD Biosciences) and labeled with anti-pe-microbeads
Generation of ST2-GFP reporter mice and characterization of ILC1 cells following infection
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of ST2-GFP reporter mice and characterization of ILC1 cells following infection with influenza virus. (a) ST2-GFP reporter mice were generated as described in Methods.
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of ST2-GFP reporter mice and characterization of ILC1 cells following infection with influenza virus. (a) ST2-GFP reporter mice were generated as described in Methods.
Therapeutic PD L1 and LAG 3 blockade rapidly clears established blood stage Plasmodium infection
 Supplementary Information Therapeutic PD L1 and LAG 3 blockade rapidly clears established blood stage Plasmodium infection Noah S. Butler, Jacqueline Moebius, Lecia L. Pewe, Boubacar Traore, Ogobara K.
Supplementary Information Therapeutic PD L1 and LAG 3 blockade rapidly clears established blood stage Plasmodium infection Noah S. Butler, Jacqueline Moebius, Lecia L. Pewe, Boubacar Traore, Ogobara K.
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS
 1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS Figure S1 Cumulative ZIKV production by testis explants over a 9 day-culture period. Viral titer values presented in Figure 1B (viral release over a 3 day-culture period measured
1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS Figure S1 Cumulative ZIKV production by testis explants over a 9 day-culture period. Viral titer values presented in Figure 1B (viral release over a 3 day-culture period measured
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection
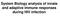 System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers and recovery of antigen specificity
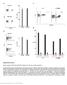 Supplementary Figure 1 Binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers and recovery of antigen specificity (a, b) Fluorescent-based determination of the binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers (+barcode)
Supplementary Figure 1 Binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers and recovery of antigen specificity (a, b) Fluorescent-based determination of the binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers (+barcode)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from
 Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Expanded View Figures
 Molecular Systems iology Tumor CNs reflect metabolic selection Nicholas Graham et al Expanded View Figures Human primary tumors CN CN characterization by unsupervised PC Human Signature Human Signature
Molecular Systems iology Tumor CNs reflect metabolic selection Nicholas Graham et al Expanded View Figures Human primary tumors CN CN characterization by unsupervised PC Human Signature Human Signature
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3218
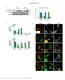 Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous EGFR trafficking and responses depend on biased ligands. (a) Lysates from HeLa cells stimulated for 2 min. with increasing concentration of ligands were immunoblotted
Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous EGFR trafficking and responses depend on biased ligands. (a) Lysates from HeLa cells stimulated for 2 min. with increasing concentration of ligands were immunoblotted
Expanded View Figures
 Solip Park & Ben Lehner Epistasis is cancer type specific Molecular Systems Biology Expanded View Figures A B G C D E F H Figure EV1. Epistatic interactions detected in a pan-cancer analysis and saturation
Solip Park & Ben Lehner Epistasis is cancer type specific Molecular Systems Biology Expanded View Figures A B G C D E F H Figure EV1. Epistatic interactions detected in a pan-cancer analysis and saturation
Spleen. mlns. E Spleen 4.1. mlns. Spleen. mlns. Mock 17. Mock CD8 HIV-1 CD38 HLA-DR. Ki67. Spleen. Spleen. mlns. Cheng et al. Fig.
 C D E F Mock 17 Mock 4.1 CD38 57 CD8 23.7 HLA-DR Ki67 G H I Cheng et al. Fig.S1 Supplementary Figure 1. persistent infection leads to human T cell depletion and hyper-immune activation. Humanized mice
C D E F Mock 17 Mock 4.1 CD38 57 CD8 23.7 HLA-DR Ki67 G H I Cheng et al. Fig.S1 Supplementary Figure 1. persistent infection leads to human T cell depletion and hyper-immune activation. Humanized mice
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment. Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein
 Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/264/rs4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A Systems Approach for Decoding Mitochondrial Retrograde Signaling Pathways Sehyun Chae, Byung Yong Ahn, Kyunghee Byun,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/264/rs4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A Systems Approach for Decoding Mitochondrial Retrograde Signaling Pathways Sehyun Chae, Byung Yong Ahn, Kyunghee Byun,
Expanded View Figures
 EMO Molecular Medicine Proteomic map of squamous cell carcinomas Hanibal ohnenberger et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. Technical reproducibility. Pearson s correlation analysis of normalised SILC
EMO Molecular Medicine Proteomic map of squamous cell carcinomas Hanibal ohnenberger et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. Technical reproducibility. Pearson s correlation analysis of normalised SILC
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.3957
 Supplementary Fig. 1. p38 alternative activation, IL-21 expression, and T helper cell transcription factors in PDAC tissue. (a) Tissue microarrays of pancreatic tissue from 192 patients with pancreatic
Supplementary Fig. 1. p38 alternative activation, IL-21 expression, and T helper cell transcription factors in PDAC tissue. (a) Tissue microarrays of pancreatic tissue from 192 patients with pancreatic
IgG3 regulates tissue-like memory B cells in HIV-infected individuals
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-018-0180-5 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. IgG3 regulates tissue-like memory B cells in HIV-infected individuals Lela
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-018-0180-5 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. IgG3 regulates tissue-like memory B cells in HIV-infected individuals Lela
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy
 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy Legend Supplementary Figure 1: First, gating is performed to include only single cells (singlets) (A) and CD3+ cells (B). After gating on the lymphocyte
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy Legend Supplementary Figure 1: First, gating is performed to include only single cells (singlets) (A) and CD3+ cells (B). After gating on the lymphocyte
Supplementary Figure 1. Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints
 Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
AbSeq on the BD Rhapsody system: Exploration of single-cell gene regulation by simultaneous digital mrna and protein quantification
 BD AbSeq on the BD Rhapsody system: Exploration of single-cell gene regulation by simultaneous digital mrna and protein quantification Overview of BD AbSeq antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates. High-throughput
BD AbSeq on the BD Rhapsody system: Exploration of single-cell gene regulation by simultaneous digital mrna and protein quantification Overview of BD AbSeq antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates. High-throughput
REACTOME: Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) REACTOME:72764 Eukaryotic Translation Termination. REACTOME:72737 Cap dependent Translation Initiation
 A REACTOME:975957 Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) REACTOME:975956 Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) REACTOME:927802
A REACTOME:975957 Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) REACTOME:975956 Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) REACTOME:927802
Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x
 Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x magnification). B: Second HC skin stained for TSLP receptor in brown
Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x magnification). B: Second HC skin stained for TSLP receptor in brown
chapter 1 - fig. 2 Mechanism of transcriptional control by ppar agonists.
 chapter 1 - fig. 1 The -omics subdisciplines. chapter 1 - fig. 2 Mechanism of transcriptional control by ppar agonists. 201 figures chapter 1 chapter 2 - fig. 1 Schematic overview of the different steps
chapter 1 - fig. 1 The -omics subdisciplines. chapter 1 - fig. 2 Mechanism of transcriptional control by ppar agonists. 201 figures chapter 1 chapter 2 - fig. 1 Schematic overview of the different steps
Supplementary Materials
 1 Supplementary Materials Rotger et al. Table S1A: Demographic characteristics of study participants. VNP RP EC CP (n=6) (n=66) (n=9) (n=5) Male gender, n(%) 5 (83) 54 (82) 5 (56) 3 (60) White ethnicity,
1 Supplementary Materials Rotger et al. Table S1A: Demographic characteristics of study participants. VNP RP EC CP (n=6) (n=66) (n=9) (n=5) Male gender, n(%) 5 (83) 54 (82) 5 (56) 3 (60) White ethnicity,
Muse Assays for Cell Analysis
 Muse Assays for Cell Analysis Multiple Assay Outputs for Cell Analysis Cell Health Cell Signalling Immunology Muse Count & Viability Kit Muse Cell Cycle Kit Muse Annexin V & Dead Cell Kit Muse Caspase
Muse Assays for Cell Analysis Multiple Assay Outputs for Cell Analysis Cell Health Cell Signalling Immunology Muse Count & Viability Kit Muse Cell Cycle Kit Muse Annexin V & Dead Cell Kit Muse Caspase
pplementary Figur Supplementary Figure 1. a.
 pplementary Figur Supplementary Figure 1. a. Quantification by RT-qPCR of YFV-17D and YFV-17D pol- (+) RNA in the supernatant of cultured Huh7.5 cells following viral RNA electroporation of respective
pplementary Figur Supplementary Figure 1. a. Quantification by RT-qPCR of YFV-17D and YFV-17D pol- (+) RNA in the supernatant of cultured Huh7.5 cells following viral RNA electroporation of respective
Will Antigen Depletion Restore HBVspecific
 Will Antigen Depletion Restore HBVspecific Immunity? Adam J. Gehring, Ph.D. Biology Lead Toronto Centre for Liver Disease University Health Network (UHN) Assistant Professor Department of Immunology University
Will Antigen Depletion Restore HBVspecific Immunity? Adam J. Gehring, Ph.D. Biology Lead Toronto Centre for Liver Disease University Health Network (UHN) Assistant Professor Department of Immunology University
CPM (x 10-3 ) Tregs +Teffs. Tregs alone ICOS CLTA-4
 A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads
 Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads Representative example of comparative ex vivo tetramer enrichment performed in three independent experiments with either conventional
Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads Representative example of comparative ex vivo tetramer enrichment performed in three independent experiments with either conventional
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information High fat diet-induced changes of mouse hepatic transcription and enhancer activity can be reversed by subsequent weight loss Majken Siersbæk, Lyuba Varticovski, Shutong Yang,
Supplementary information High fat diet-induced changes of mouse hepatic transcription and enhancer activity can be reversed by subsequent weight loss Majken Siersbæk, Lyuba Varticovski, Shutong Yang,
SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Experimental design and workflow utilized to generate the WMG Protein Atlas.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental design and workflow utilized to generate the WMG Protein Atlas. (a) Illustration of the plant organs and nodule infection time points analyzed. (b) Proteomic workflow
Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental design and workflow utilized to generate the WMG Protein Atlas. (a) Illustration of the plant organs and nodule infection time points analyzed. (b) Proteomic workflow
Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer
 Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer Results Presented by Stacey Lin Lloyd Lab http://www.amsbio.com/expression-ready-lentiviral-particles.aspx Overview
Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer Results Presented by Stacey Lin Lloyd Lab http://www.amsbio.com/expression-ready-lentiviral-particles.aspx Overview
Tbk1-TKO! DN cells (%)! 15! 10!
 a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Metabolic ER stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) of mice with dietary obesity.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Metabolic ER stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) of mice with dietary obesity. Male C57BL/6J mice were fed a normal chow (NC, 10% fat) or a high-fat diet (HFD,
Supplementary Figure 1 Metabolic ER stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) of mice with dietary obesity. Male C57BL/6J mice were fed a normal chow (NC, 10% fat) or a high-fat diet (HFD,
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
c Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (8 w) Supplementary Figure bp 300 bp Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (4 h) Dox 20 mg/kg i.p.
 a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice.
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice. Twelve week old mice were subjected to ad libitum (AL) or dietary restriction (DR) regimens for three months. (A) Body
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice. Twelve week old mice were subjected to ad libitum (AL) or dietary restriction (DR) regimens for three months. (A) Body
Nature Getetics: doi: /ng.3471
 Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of exome sequencing data. ( a ) Exome tumor normal sample sizes for bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer (BRCA), carcinoid (CARC), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLLX), colorectal
Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of exome sequencing data. ( a ) Exome tumor normal sample sizes for bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer (BRCA), carcinoid (CARC), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLLX), colorectal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune
 Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune System to Inhibit Tumor Growth Alyssa K. Kosmides, John-William Sidhom, Andrew Fraser, Catherine A. Bessell, Jonathan P. Schneck * Supplemental Figure
Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune System to Inhibit Tumor Growth Alyssa K. Kosmides, John-William Sidhom, Andrew Fraser, Catherine A. Bessell, Jonathan P. Schneck * Supplemental Figure
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary. presence of the. (c) mrna expression. Error. in naive or
 Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-10. Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald,
 Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-1 Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald, James A. Dromey, Bo Han Lee, Junyan Qian, Ralph M Böhmer and Leonard
Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-1 Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald, James A. Dromey, Bo Han Lee, Junyan Qian, Ralph M Böhmer and Leonard
a 10 4 Link et al. Supplementary Figure 1 Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.1842 Cells per mouse ( 10 5 ) TRPV2KO anti-gr1 anti-gr anti-f4/80
 a 10 4 WT 10 4 TRPV2KO 10 3 10 3 anti-gr1 10 2 10 1 anti-gr1 10 2 10 1 10 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 anti-f4/80 42.3 45.2 10 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 anti-f4/80 10 4 10 4 40 42.5 anti-cd11b 10 3 10 2
a 10 4 WT 10 4 TRPV2KO 10 3 10 3 anti-gr1 10 2 10 1 anti-gr1 10 2 10 1 10 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 anti-f4/80 42.3 45.2 10 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 anti-f4/80 10 4 10 4 40 42.5 anti-cd11b 10 3 10 2
W/T Itgam -/- F4/80 CD115. F4/80 hi CD115 + F4/80 + CD115 +
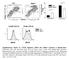 F4/8 % in the peritoneal lavage 6 4 2 p=.15 n.s p=.76 CD115 F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + MHCII MHCII Supplementary Figure S1. CD11b deficiency affects the cellular responses
F4/8 % in the peritoneal lavage 6 4 2 p=.15 n.s p=.76 CD115 F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + MHCII MHCII Supplementary Figure S1. CD11b deficiency affects the cellular responses
Venky Ramakrishna PhD Celldex Therapeutics, Hampton NJ, USA
 Antibody Targeting of Human CD27 with Varlilumab (CDX-1127) identifies genes and pathways related to inflammation Venky Ramakrishna PhD Celldex Therapeutics, Hampton NJ, USA www.celldextherapeutics.com
Antibody Targeting of Human CD27 with Varlilumab (CDX-1127) identifies genes and pathways related to inflammation Venky Ramakrishna PhD Celldex Therapeutics, Hampton NJ, USA www.celldextherapeutics.com
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Honegger et al. /pnas.0 HCV proteins Core E E P NS NS NSA NSB NSA NSB HCV peptide pools 9 Fig. S. HCV proteins represented in the nine peptide pool arrays used for the IFN-γ ELISpot
Supporting Information Honegger et al. /pnas.0 HCV proteins Core E E P NS NS NSA NSB NSA NSB HCV peptide pools 9 Fig. S. HCV proteins represented in the nine peptide pool arrays used for the IFN-γ ELISpot
HARNESS THE POWER OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM TO FIGHT CANCER
 OncoPept TM HARNESS THE POWER OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM TO FIGHT CANCER OncoPept identifies and delivers priortized T-cell neo-epitopes from the patient's tumor mutanome 2 What is OncoPept? OncoPept is an integrated
OncoPept TM HARNESS THE POWER OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM TO FIGHT CANCER OncoPept identifies and delivers priortized T-cell neo-epitopes from the patient's tumor mutanome 2 What is OncoPept? OncoPept is an integrated
Loss of CD96 Expression as a New Biomarker for T-cell Senescence in HIV-1 Infection
 Loss of CD96 Expression as a New Biomarker for T-cell Senescence in HIV-1 Infection Mohamed El-Far, PhD CHUM research center (CRCHUM) University of Montreal, QC Canada 6th International Workshop on HIV
Loss of CD96 Expression as a New Biomarker for T-cell Senescence in HIV-1 Infection Mohamed El-Far, PhD CHUM research center (CRCHUM) University of Montreal, QC Canada 6th International Workshop on HIV
EXPression ANalyzer and DisplayER
 EXPression ANalyzer and DisplayER Tom Hait Aviv Steiner Igor Ulitsky Chaim Linhart Amos Tanay Seagull Shavit Rani Elkon Adi Maron-Katz Dorit Sagir Eyal David Roded Sharan Israel Steinfeld Yossi Shiloh
EXPression ANalyzer and DisplayER Tom Hait Aviv Steiner Igor Ulitsky Chaim Linhart Amos Tanay Seagull Shavit Rani Elkon Adi Maron-Katz Dorit Sagir Eyal David Roded Sharan Israel Steinfeld Yossi Shiloh
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis
 Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
ankylosing spondylitis Department of Clinical Immunology, Xijing Hospital, The Fourth Military
 Functional defects in CD4 + CD25 high FoxP3 + regulatory cells in ankylosing spondylitis Huifang Guo 1, 2, 3, Ming Zheng 1, 2, 3, Kui Zhang 1, 3, Fengfan Yang 1, 3, Xin Zhang 1, 3, Qing Han 1, 3, Zhi-Nan
Functional defects in CD4 + CD25 high FoxP3 + regulatory cells in ankylosing spondylitis Huifang Guo 1, 2, 3, Ming Zheng 1, 2, 3, Kui Zhang 1, 3, Fengfan Yang 1, 3, Xin Zhang 1, 3, Qing Han 1, 3, Zhi-Nan
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of liver from a recipient mouse sacrificed after two rounds
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 Fah + hepatocytes in a Fah -/- mouse transplanted with sorted cells. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of liver from a recipient mouse sacrificed
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 Fah + hepatocytes in a Fah -/- mouse transplanted with sorted cells. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of liver from a recipient mouse sacrificed
Supplementary Figure 1: Additional metabolic parameters of obesity mouse models and controls. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose and (c) insulin
 Supplementary Figure 1: Additional metabolic parameters of obesity mouse models and controls. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose and (c) insulin resistance index of homeostatic model assessment (HOMA IR)
Supplementary Figure 1: Additional metabolic parameters of obesity mouse models and controls. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose and (c) insulin resistance index of homeostatic model assessment (HOMA IR)
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with
 Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation
 Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks
 Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks Analyzing 24 Proteomes Per Day by Microflow SWATH Acquisition and Spectronaut Pulsar Analysis Jan Muntel 1, Nick Morrice 2, Roland M. Bruderer 1, Lukas
Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks Analyzing 24 Proteomes Per Day by Microflow SWATH Acquisition and Spectronaut Pulsar Analysis Jan Muntel 1, Nick Morrice 2, Roland M. Bruderer 1, Lukas
p.r623c p.p976l p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r2922w p.r2370h p.c1201y p.a868v p.s952* RING_C BP PHD Cbp HAT_KAT11
 ARID2 p.r623c KMT2D p.v650fs p.p976l p.r2922w p.l1212r p.d1400h DNA binding RFX DNA binding Zinc finger KMT2C p.a51s p.d372v p.c1103* p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r4586h PHD/ RING DHHC/ PHD PHD FYR N
ARID2 p.r623c KMT2D p.v650fs p.p976l p.r2922w p.l1212r p.d1400h DNA binding RFX DNA binding Zinc finger KMT2C p.a51s p.d372v p.c1103* p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r4586h PHD/ RING DHHC/ PHD PHD FYR N
B220 CD4 CD8. Figure 1. Confocal Image of Sensitized HLN. Representative image of a sensitized HLN
 B220 CD4 CD8 Natarajan et al., unpublished data Figure 1. Confocal Image of Sensitized HLN. Representative image of a sensitized HLN showing B cell follicles and T cell areas. 20 µm thick. Image of magnification
B220 CD4 CD8 Natarajan et al., unpublished data Figure 1. Confocal Image of Sensitized HLN. Representative image of a sensitized HLN showing B cell follicles and T cell areas. 20 µm thick. Image of magnification
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2419
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
2.28E E AKT/CAT P-3-4:
 Supplemental Table 1: IPA network analysis of the microarray data presented in Figure 6 showing the most significant molecular and cellular function classifications along with the respective number of
Supplemental Table 1: IPA network analysis of the microarray data presented in Figure 6 showing the most significant molecular and cellular function classifications along with the respective number of
