Expression levels of b-pix mrna in ALS-MSCs and C-MSCs.
|
|
|
- Susan Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. The neurological functioning of ischemic rats depends on the origin of the transplanted MSCs. The scores of healthy rats in tests on forelimb placing, forelimb use asymmetry, and corner turn were 1.0, 0.0, and 0.5, respectively. No significant differences were observed between the 5 groups prior to implantation. However, the scores for forelimb use asymmetry and corner turn tests were significantly better in the C-MSC, huc-msc, and UCB-MSC groups (n = 10 in each group) than in the ALS-MSC group (n = 10) 21 days after implantation, and the scores on the forelimb placing test were significantly higher in the C-MSC, huc-msc, and UCB-MSC groups (n = 10 in each group) than in the ALS-MSC group (n = 10) 7 days after implantation. Data are means SD of 5 or more independent experiments. *P value < 0.05 compared with the PBS group. MSCs, mesenchymal stromal cells; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; huc, human umbilical cord; UCB, umbilical cord blood; C-MSCs, control healthy MSCs; MCAO, MCA occlusion.
2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Migratory abilities of ALS- MSCs and C-MSCs. In vitro cell migration assays show that the migratory capacity of ALS-MSCs (n = 7) is substantially lower than that of C-MSCs (n = 5). SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S3. Expression levels of b-pix mrna in ALS-MSCs and C-MSCs.
3 SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S4. Confirmation of the role of b-pix in neurological improvement by MSC implantation. To assess functional improvement by b-pix in vivo, post-msc-transplant stroke rats underwent neurological examination daily. Rats (n = 10) that received b-pix knockdown C-MSCs did not demonstrate any significant functional recovery, whereas rats (n = 10) that received control C-MSCs exhibited improvement (A). Rats (n = 10 in each group) that received b-pix overexpressing or control ALS-MSCs did not show any improvement of neurological function comparable (B). (*P < 0.05 compared with the group implanted with b-pix depleted C-MSCs).
4 SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S5. Comparison of the protein levels of several trophic factors in ALS-MSCs and C-MSCs. SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S6. mrna levels of several trophic factors in ALS-MSCs and C-MSCs.
5 SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S8. Levels of VEGF, IGF, and GDNF in ALS-MSCs and C-MSCs in infarcted hemispheres 3 days after direct injection of MSCs into the infarcted areas. Six additional rats were killed 3 days after the injection of ALS-MSCs (n = 3) or C-MSCs (n = 3), and the protein contents of homogenates taken from the hemispheres with ischemic infarcts were quantified with a BCA protein kit. Using commercially available kits for VEGF (Human VEGF Quantikine ELISA Kit; R&D Systems), IGF (Human IGF Quantikine ELISA Kit; R&D Systems), and GDNF (GDNF human ELISA Kit; Abcam), levels of VEGF, IGF, and GDNF were measured. All samples were tested in triplicate. The levels of VEGF, IGF, and GDNF, which were significantly higher in C-MSCs than in ALS-MSCs under in vitro condition, were also higher in the hemispheres injected with C-MSCs than with ALS-MSCs. [*P < 0.05; Wilcoxon Scores (rank sums)]. IGF, insulin-like growth factor. Reference: Pritchett J, C Wright, L Zeef and B Nadarajah. (2007). Stromal derived factor-1 exerts differential regulation on distinct cortical cell populations in vitro. BMC Dev Biol 7:31. SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S7. Effect of b-pix overexpression on neurotrophic factor secretion by MSCs. A total of ALS-MSCs or C-MSCs were plated in 96-well plates. After incubation for 24 h, culture supernatants were divided into triplicate 200 ml samples, and stromal cell derived factor-1a (SDF-1a) (A), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) (B), and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (C) levels were measured in the supernatants, with the appropriate ELISA kits (R&D Systems) [12]. [*P < 0.05 when compared with the C-MSCs, Wilcoxon Scores (rank sums)]. SDF-1a, stromal cell derived factor-1a. SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S9. Concentrations of SDF-1a in normal areas and periinfarct areas 2 weeks after infarct. Three additional rats were killed 2 weeks after the induction of infarcts, and the protein contents of homogenates of the periinfarct areas and the corresponding areas on the contralateral hemispheres were measured with a BCA protein kit (Pierce). Using a commercially available kit for rat SDF-1a (Quantikine Human SDF-1a; R&D Systems) [33], we measured the concentrations of SDF-1a. All samples were tested in triplicate. SDF-1a was significantly higher in the periinfarct areas than in the normal areas. [*P < 0.05, Wilcoxon Scores (rank sums)].
6 Supplementary Table S1. Median Values of Surface Antigen Expression in Various Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Patient no. CD29 + CD44 + CD73 + CD105 + CD34 + CD45 + HLA-DR + ALS-MSCs (Sporadic) A A A A A A ALS-MSCs (Familial) A C-MSCs C C C C C UCB-MSCs U U U U huc-mscs hu hu hu hu Value; %. Cells were labeled with the following antihuman antibodies: CD45-phycoerythrin (PE), CD44-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) (DakoCytomation), CD73-PE (BD Pharmingen), CD34-PE, CD29-FITC, CD49C-PE, CD54-FITC, CD105-FITC, CD106-FITC, HLA-DR-FITC, and PE- and FITC-conjugated isotype controls (Serotec). Labeled cells were analyzed by flow cytometry (Calibur) [8]. MSCs, mesenchymal stromal cells; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; huc, human umbilical cord; UCB, umbilical cord blood; C-MSCs, control healthy MSCs. Supplementary Table S2. Migration-Associated Genes No. Unigene GeneBank Symbol Description 1 Hs NM_ APC Adenomatous polyposis coli 2 Hs NM_ BRMS1 Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 3 Hs NM_ CCL7 Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 7 4 Hs NM_ CD44 CD44 molecule (Indian blood group) 5 Hs NM_ CDH1 Cadherin 1, type 1, E-cadherin (epithelial) 6 Hs NM_ CDH11 Cadherin 11, type 2, OB-cadherin (osteoblast) 7 Hs NM_ CDH6 Cadherin 6, type 2, K-cadherin (fetal kidney) 8 Hs NM_ CDKN2A Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (melanoma, p16, inhibits CDK4) 9 Hs NM_ CHD4 Chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 4 10 Hs NM_ COL4A2 Collagen, type IV, alpha 2 11 Hs NM_ CST7 Cystatin F (leukocystatin) 12 Hs NM_ CTBP1 C-terminal binding protein 1 13 Hs NM_ CTNNA1 Catenin (cadherin-associated protein), alpha 1, 102 kda 14 Hs NM_ CTSK Cathepsin K 15 Hs NM_ CTSL1 Cathepsin L1 16 Hs NM_ CXCL12 Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12 (stromal cell derived factor 1) 17 Hs NM_ CXCR4 Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 18 Hs NM_ DENR Density-regulated protein 19 Hs NM_ EPHB2 EPH receptor B2 20 Hs NM_ ETV4 Ets variant 4 21 Hs NM_ EWSR1 Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1 22 Hs NM_ FAT1 FAT tumor suppressor homolog 1 (Drosophila) 23 Hs NM_ FGFR4 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 24 Hs NM_ FLT4 Fms-related tyrosine kinase 4 25 Hs NM_ FN1 Fibronectin 1 26 Hs NM_ FXYD5 FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 5 27 Hs NM_ GNRH1 Gonadotropin-releasing hormone 1 (luteinizing-releasing hormone) 28 Hs NM_ KISS1R KISS1 receptor 29 Hs NM_ HGF Hepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor) (continued)
7 Supplementary Table S2. (Continued) No. Unigene GeneBank Symbol Description 30 Hs NM_ HPSE Heparanase 31 Hs NM_ HRAS V-Ha-ras Harvey rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog 32 Hs NM_ HTATIP2 HIV-1 Tat interactive protein 2, 30 kda 33 Hs NM_ IGF1 Insulin-like growth factor 1 (somatomedin C) 34 Hs NM_ IL18 Interleukin 18 (interferon-gamma-inducing factor) 35 Hs NM_ IL1B Interleukin 1, beta 36 Hs.846 NM_ IL8RB Interleukin 8 receptor, beta 37 Hs NM_ ITGA7 Integrin, alpha 7 38 Hs NM_ ITGB3 Integrin, beta 3 (platelet glycoprotein IIIa, antigen CD61) 39 Hs NM_ CD82 CD82 molecule 40 Hs NM_ KISS1 KiSS-1 metastasis-suppressor 41 Hs NM_ KRAS V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog 42 Hs NM_ RPSA Ribosomal protein SA 43 Hs NM_ MCAM Melanoma cell adhesion molecule 44 Hs NM_ MDM2 Mdm2 p53 binding protein homolog (mouse) 45 Hs NM_ MET Met protooncogene (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) 46 Hs NM_ METAP2 Methionyl aminopeptidase 2 47 Hs NM_ MGAT5 Mannosyl (alpha-1,6-)-glycoprotein beta-1,6-n-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 48 Hs.2258 NM_ MMP10 Matrix metallopeptidase 10 (stromelysin 2) 49 Hs NM_ MMP11 Matrix metallopeptidase 11 (stromelysin 3) 50 Hs.2936 NM_ MMP13 Matrix metallopeptidase 13 (collagenase 3) 51 Hs NM_ MMP2 Matrix metallopeptidase 2 (gelatinase A, 72 kda gelatinase, 72 kda type IV collagenase) 52 Hs NM_ MMP3 Matrix metallopeptidase 3 (stromelysin 1, progelatinase) 53 Hs.2256 NM_ MMP7 Matrix metallopeptidase 7 (matrilysin, uterine) 54 Hs NM_ MMP9 Matrix metallopeptidase 9 (gelatinase B, 92 kda gelatinase, 92 kda type IV collagenase) 55 Hs NM_ MTA1 Metastasis associated 1 56 Hs NM_ MTSS1 Metastasis suppressor 1 57 Hs NM_ MYC V-myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog (avian) 58 Hs NM_ MYCL1 V-myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog 1, lung carcinoma derived (avian) 59 Hs NM_ NF2 Neurofibromin 2 (merlin) 60 Hs NM_ NME1 Nonmetastatic cells 1, protein (NM23A) expressed in 61 Hs NM_ NME2 Nonmetastatic cells 2, protein (NM23B) expressed in 62 Hs.9235 NM_ NME4 Nonmetastatic cells 4, protein expressed in 63 Hs NM_ NR4A3 Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 3 64 Hs NM_ PLAUR Plasminogen activator, urokinase receptor 65 Hs NM_ PNN Pinin, desmosome associated protein 66 Hs NM_ PTEN Phosphatase and tensin homolog 67 Hs NM_ RB1 Retinoblastoma 1 68 Hs NM_ RORB RAR-related orphan receptor B 69 Hs NM_ SET SET nuclear oncogene 70 Hs NM_ SMAD2 SMAD family member 2 71 Hs NM_ SMAD4 SMAD family member 4 72 Hs NM_ SRC V-src sarcoma (Schmidt-Ruppin A-2) viral oncogene homolog (avian) 73 Hs NM_ SSTR2 Somatostatin receptor 2 74 Hs NM_ SYK Spleen tyrosine kinase 75 Hs NM_ TCF20 Transcription factor 20 (AR1) 76 Hs NM_ TGFB1 Transforming growth factor, beta 1 77 Hs NM_ TIMP2 TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2 78 Hs NM_ TIMP3 TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 3 79 Hs NM_ TIMP4 TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 4 80 Hs NM_ TNFSF10 Tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member Hs NM_ TP53 Tumor protein p53 82 Hs NM_ TRPM1 Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 1 83 Hs NM_ TSHR Thyroid stimulating hormone receptor 84 Hs NM_ VEGFA Vascular endothelial growth factor A 85 Hs NM_ B2M Beta-2-microglobulin 86 Hs NM_ HPRT1 Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 87 Hs NM_ RPL13A Ribosomal protein L13a (continued)
8 Supplementary Table S2. (Continued) No. Unigene GeneBank Symbol Description 88 Hs NM_ GAPDH Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 89 b-pix 90 Hs NM_ ACTB Actin, beta 91 N/A SA_00105 HGDC Human Genomic DNA Contamination 92 N/A SA_00104 RTC Reverse transcription control 93 N/A SA_00104 RTC Reverse transcription control 94 N/A SA_00104 RTC Reverse transcription control 95 N/A SA_00103 PPC Positive PCR control 96 N/A SA_00103 PPC Positive PCR control 97 N/A SA_00103 PPC Positive PCR control PCR, polymerase chain reaction. Supplementary Table S3. Body Weights of Groups of Sprague-Dawley Rats ALS-MSCs (n = 20) C-MSCs (n = 20) UCB-MSCs (n = 20) huc-mscs (n = 20) PBS (n = 10) Age (weeks) Body weight (g) Supplementary Table S4. Physiological Variables Before (Preischemia), During (Ischemia), and 30 min After Occlusion of the Middle Cerebral Arteries (Reperfusion) Group MABP (mmhg) ph PaCO 2 (mmhg) PaO 2 (mmhg) Haematocrit (%) CBF (% of preischemia of saline) Rectal temperature ( C) ALS-MSCs (n = 20) Preischemia Ischemia Reperfusion C-MSCs (n = 20) Preischemia Ischemia Reperfusion UCB-MSCs (n = 20) Preischemia Ischemia Reperfusion huc-mscs (n = 20) Preischemia Ischemia Reperfusion PBS (n = 10) Preischemia Ischemia Reperfusion Values are means SEM. MABP, mean arterial blood pressure; CBF, cerebral blood flow.
9 Supplementary Table S5. Surface Marker Expression on ALS-MSCs and C-MSCs After Genetic Modification Vehicle C-MSCs Vehicle ALS-MSCs b-pix knockdown C-MSCs b-pix overexpressed ALS-MSCs CD CD CD CD CD CD CD49C CD CD HLA-DR Cells were labeled with the following antihuman antibodies: CD45-PE, CD44-FITC (DakoCytomation), CD73-PE (BD Pharmingen), CD34- PE, CD29-FITC, CD49C-PE, CD54-FITC, CD105-FITC, CD106-FITC, HLA-DR-FITC, and PE- and FITC-conjugated isotype controls (Serotec). Labeled cells were analyzed by flow cytometry (Calibur) [8]. ALS-MSCs and C-MSCs have the same CD45 - CD34 - CD29 + CD73 + CD105 + CD44 + HLA-DR - phenotype. This phenotype was not altered by b-pix knockdown in C-MSCs or b-pix overexpression in ALS-MSCs.
Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No.
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array.
 Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
HCMV Promotes Breast Cancer Metastasis: Impacts of CMVIL-10 in the Tumor Microenvironment
 The University of San Francisco USF Scholarship: a digital repository @ Gleeson Library Geschke Center Master's Theses Theses, Dissertations, Capstones and Projects Summer 8-13-2013 HCMV Promotes Breast
The University of San Francisco USF Scholarship: a digital repository @ Gleeson Library Geschke Center Master's Theses Theses, Dissertations, Capstones and Projects Summer 8-13-2013 HCMV Promotes Breast
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20
 Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Long-term protection studies. 45 minutes of ischemia was induced in wild type (S1pr2 +/+ ) and S1pr2 -/- by MCAO. A) 5 days later brains were harvested
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Long-term protection studies. 45 minutes of ischemia was induced in wild type (S1pr2 +/+ ) and S1pr2 -/- by MCAO. A) 5 days later brains were harvested
U118MG. Supplementary Figure 1 U373MG U118MG 3.5 A CCF-SSTG
 A172 CCF-SSTG1 15 - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10101112131617192022-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22 T98G U373MG - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7
A172 CCF-SSTG1 15 - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10101112131617192022-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22 T98G U373MG - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p <0.01 for 0.01 mm NS-398, 0.1mM ibuprofen and COX-2 RNAi.
 Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Applied Biosystems models 7500 (Fast block), 7900HT (Fast block), StepOnePlus, ViiA 7 (Fast block)
 RT² Profiler PCR Array (96-Well Format and 384-Well [4 x 96] Format) Human HIV Infection and Host Response Cat. no. 330231 PAHS-051YA For pathway expression analysis Format Format A Format C Format D Format
RT² Profiler PCR Array (96-Well Format and 384-Well [4 x 96] Format) Human HIV Infection and Host Response Cat. no. 330231 PAHS-051YA For pathway expression analysis Format Format A Format C Format D Format
1. The metastatic cascade. 3. Pathologic features of metastasis. 4. Therapeutic ramifications. Which malignant cells will metastasize?
 1. The metastatic cascade 3. Pathologic features of metastasis 4. Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of Paget s disease of the nipple (intraductal
1. The metastatic cascade 3. Pathologic features of metastasis 4. Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of Paget s disease of the nipple (intraductal
Diagnostic test Suggested website label Description Hospitals available
 Diagnostic test Suggested website label Description Hospitals available Abbott Molecular Inc, PATHVYSION HER-2 DNA Probe Kit (FISH) PathVysion kit A diagnostic tool used to determine whether a particular
Diagnostic test Suggested website label Description Hospitals available Abbott Molecular Inc, PATHVYSION HER-2 DNA Probe Kit (FISH) PathVysion kit A diagnostic tool used to determine whether a particular
1.The metastatic cascade. 2.Pathologic features of metastasis. 3.Therapeutic ramifications
 Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Supplementary Material Correlation matrices on FP and FN profiles
 Supplementary Material Correlation matrices on FP and FN profiles The following two tables give the correlation coefficients for the FP profiles and the FN profiles of a single tagging solutions against
Supplementary Material Correlation matrices on FP and FN profiles The following two tables give the correlation coefficients for the FP profiles and the FN profiles of a single tagging solutions against
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer genetics
 Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Gene Expression Analysis To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and mice given renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), ncounter
Supplementary Materials and Methods Gene Expression Analysis To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and mice given renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), ncounter
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber
 Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma plasma B cell.
 Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Supplementary Table 1: Motor-clutch gene mrna expression Myosin Motors
 Supplementary Table 1: Motor-clutch gene mrna expression Myosin Motors Symbol Description Expression Rank MYL6 myosin, light chain 6, alkali, smooth muscle and non-muscle 11903 79 MYH9 myosin, heavy chain
Supplementary Table 1: Motor-clutch gene mrna expression Myosin Motors Symbol Description Expression Rank MYL6 myosin, light chain 6, alkali, smooth muscle and non-muscle 11903 79 MYH9 myosin, heavy chain
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Supplementary Figure 1: Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points
 A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
Effects of Ole e 1 allergen on human bronchial epithelial cells cultured at air-liquid interface (No. JIACI-D )
 1 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLES Effects of Ole e 1 allergen on human bronchial epithelial cells cultured at air-liquid interface (No. JIACI-D-17-00149) Juan C. López-Rodríguez 1, Guillermo Solís-Fernández 1, Rodrigo
1 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLES Effects of Ole e 1 allergen on human bronchial epithelial cells cultured at air-liquid interface (No. JIACI-D-17-00149) Juan C. López-Rodríguez 1, Guillermo Solís-Fernández 1, Rodrigo
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 21 Done by Ahmad Rawajbeh Corrected by Omar Sami Doctor Maha Shomaf Ability to Invade and Metastasize The metastatic cascade can be subdivided into two phases: 1-invasion of ECM and vascular dissemination:
number 21 Done by Ahmad Rawajbeh Corrected by Omar Sami Doctor Maha Shomaf Ability to Invade and Metastasize The metastatic cascade can be subdivided into two phases: 1-invasion of ECM and vascular dissemination:
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer
 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto Apr 2010 Skin tumor in a 10-year-old Rottweiler. Considering the external appearance and
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto Apr 2010 Skin tumor in a 10-year-old Rottweiler. Considering the external appearance and
In vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was performed to analyze cell
 Supplementary Methods BrdU incorporation in vivo In vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was performed to analyze cell proliferation in the heart. Mice were subjected to LI-TAC, and 5 days later
Supplementary Methods BrdU incorporation in vivo In vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was performed to analyze cell proliferation in the heart. Mice were subjected to LI-TAC, and 5 days later
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 a Percent of body weight! (%) 4! 3! 1! Epididymal fat Subcutaneous fat Liver SD Percent of body weight! (%) ** 3! 1! SD Percent of body weight! (%) 6! 4! SD ** b Blood glucose (mg/dl)!
Supplementary Figure 1 a Percent of body weight! (%) 4! 3! 1! Epididymal fat Subcutaneous fat Liver SD Percent of body weight! (%) ** 3! 1! SD Percent of body weight! (%) 6! 4! SD ** b Blood glucose (mg/dl)!
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Supplementary Figure (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes ~ 4.6 -
 Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Subject Index. Bcl-2, apoptosis regulation Bone marrow, polymorphonuclear neutrophil release 24, 26
 Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Seeds and soil theory by Stephen Paget at the end of the XIX century.
 Seeds and soil theory by Stephen Paget at the end of the XIX century. In The Distribution Of Secondary Growths In Cancer Of The Breast Paget presents and analyzes 735 fatal cases of breast cancer, complete
Seeds and soil theory by Stephen Paget at the end of the XIX century. In The Distribution Of Secondary Growths In Cancer Of The Breast Paget presents and analyzes 735 fatal cases of breast cancer, complete
B16F1 B16F10 Supplemental Figure S1
 B16F1 B16F1 Supplemental Figure S1 Representative microangiography images of B16F1 and B16F1 tumors grown in the cranial windows. FITC-dextran (2 million MW) was injected systemically to visualize blood
B16F1 B16F1 Supplemental Figure S1 Representative microangiography images of B16F1 and B16F1 tumors grown in the cranial windows. FITC-dextran (2 million MW) was injected systemically to visualize blood
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers. A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs
 Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Cancer Biology Course. Invasion and Metastasis
 Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Hepatocyte toxicity assay. Freshly isolated hepatocytes were incubated for overnight with varying concentrations (-25 µm) of sodium glycochenodeoxycholate (GCDC) or
Supplementary Materials and Methods Hepatocyte toxicity assay. Freshly isolated hepatocytes were incubated for overnight with varying concentrations (-25 µm) of sodium glycochenodeoxycholate (GCDC) or
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis
 Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
TNFSF13B tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b NF-kB pathway cluster, Enrichment Score: 3.57
 Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Figure 1. Possible role of oncogene activation, receptor, G-protein mutation, or tumor
 Figures Part of introduction Figure 1. Possible role of oncogene activation, receptor, G-protein mutation, or tumor supressor gene deletion in the induction of thyroid carcinoma. ( by James A Fagin, M.D.)
Figures Part of introduction Figure 1. Possible role of oncogene activation, receptor, G-protein mutation, or tumor supressor gene deletion in the induction of thyroid carcinoma. ( by James A Fagin, M.D.)
Karyotype analysis reveals transloction of chromosome 22 to 9 in CML chronic myelogenous leukemia has fusion protein Bcr-Abl
 Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Assessment of cell survival (MTT) Assessment of early apoptosis and cell death
 Overexpression of a functional calcium-sensing receptor dramatically increases osteolytic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells in a mouse model of bone metastasis through epiregulinmediated osteoprotegerin downregulation
Overexpression of a functional calcium-sensing receptor dramatically increases osteolytic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells in a mouse model of bone metastasis through epiregulinmediated osteoprotegerin downregulation
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
RT 2 Profiler PCR Array:
 RT 2 Profiler PCR Array: Rat Cell Cycle Catalog Number For Real-Time Instruments: PARN-020A ABI Standard Blocks; Bio-Rad icycler, MyiQ, and (MJ Research) Chromo 4; and Stratagene Mx3005p, Mx3000p PARN-020C
RT 2 Profiler PCR Array: Rat Cell Cycle Catalog Number For Real-Time Instruments: PARN-020A ABI Standard Blocks; Bio-Rad icycler, MyiQ, and (MJ Research) Chromo 4; and Stratagene Mx3005p, Mx3000p PARN-020C
OncoMir Library Cancer Type Target Gene
 OncoMir Library Cancer Type Target Gene hsa-let-7a-1 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-2 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-3 Breast Cancer, Lung
OncoMir Library Cancer Type Target Gene hsa-let-7a-1 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-2 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-3 Breast Cancer, Lung
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier
 Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Growth Factors. BIT 230 Walsh Chapter 7
 Growth Factors BIT 230 Walsh Chapter 7 3 Definitions Autocrine: a mode of hormone action in which a hormone affects the function of the cell type that produced it. Paracrine: Relating to the release of
Growth Factors BIT 230 Walsh Chapter 7 3 Definitions Autocrine: a mode of hormone action in which a hormone affects the function of the cell type that produced it. Paracrine: Relating to the release of
Basic tumor nomenclature
 Jonas Nilsson jonas.a.nilsson@surgery.gu.se Sahlgrenska Cancer Center Bilder gjorda av Per Holmfeldt och Jonas Nilsson Benign tumor Basic tumor nomenclature Malignant tumor = cancer Metastasis Carcinoma:
Jonas Nilsson jonas.a.nilsson@surgery.gu.se Sahlgrenska Cancer Center Bilder gjorda av Per Holmfeldt och Jonas Nilsson Benign tumor Basic tumor nomenclature Malignant tumor = cancer Metastasis Carcinoma:
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
CURRENT AND EMERGING CANCER DIAGNOSTIC TESTS Emerging Assays, and Companies Developing New Technologies and Products.
 CURRENT AND EMERGING CANCER DIAGNOSTIC TESTS Emerging Assays, and Companies Developing New Technologies and Products Table of Contents Major Current And Emerging Cancer Diagnostic Tests 1. Introduction
CURRENT AND EMERGING CANCER DIAGNOSTIC TESTS Emerging Assays, and Companies Developing New Technologies and Products Table of Contents Major Current And Emerging Cancer Diagnostic Tests 1. Introduction
Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ).
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
An Estrogen-Related Receptor α-specific Antagonist Inhibits Breast Tumor Growth in Both ER-positive and ER-negative Mouse Xenografts
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA An Estrogen-Related Receptor α-specific Antagonist Inhibits Breast Tumor Growth in Both ER-positive and ER-negative Mouse Xenografts Michael J. Chisamore 1,2, Hilary A. Wilkinson 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA An Estrogen-Related Receptor α-specific Antagonist Inhibits Breast Tumor Growth in Both ER-positive and ER-negative Mouse Xenografts Michael J. Chisamore 1,2, Hilary A. Wilkinson 1,
Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 9th Edition by Kumar
 Link full download:https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-robbinsand-cotran-pathologic-basis-of-disease-9th-edition-by-kumar Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 9th
Link full download:https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-robbinsand-cotran-pathologic-basis-of-disease-9th-edition-by-kumar Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 9th
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
qpcr-array Analysis Service
 qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia
 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 3 Rate of growth, local invasion, and metastasis. Molecular basis of cancer (normal cell-cycle and cellular proliferation). Enrique
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 3 Rate of growth, local invasion, and metastasis. Molecular basis of cancer (normal cell-cycle and cellular proliferation). Enrique
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
ulcer healing role 118 Bicarbonate, prostaglandins in duodenal cytoprotection 235, 236
 Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Targeted Agent and Profiling Utilization Registry (TAPUR ) Study. February 2018
 Targeted Agent and Profiling Utilization Registry (TAPUR ) Study February 2018 Precision Medicine Therapies designed to target the molecular alteration that aids cancer development 30 TARGET gene alterations
Targeted Agent and Profiling Utilization Registry (TAPUR ) Study February 2018 Precision Medicine Therapies designed to target the molecular alteration that aids cancer development 30 TARGET gene alterations
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Pleiotrophin Regulates the Expansion and Regeneration of Hematopoietic Stem Cells Heather A Himburg 1, Garrett G Muramoto 1 *, Pamela Daher 1*, Sarah K Meadows 1, J. Lauren Russell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Pleiotrophin Regulates the Expansion and Regeneration of Hematopoietic Stem Cells Heather A Himburg 1, Garrett G Muramoto 1 *, Pamela Daher 1*, Sarah K Meadows 1, J. Lauren Russell
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
Tissue repair. (3&4 of 4)
 Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Bihong Zhao, M.D, Ph.D Department of Pathology
 Bihong Zhao, M.D, Ph.D Department of Pathology 04-28-2009 Is tumor self or non-self? How are tumor antigens generated? What are they? How does immune system respond? Introduction Tumor Antigens/Categories
Bihong Zhao, M.D, Ph.D Department of Pathology 04-28-2009 Is tumor self or non-self? How are tumor antigens generated? What are they? How does immune system respond? Introduction Tumor Antigens/Categories
7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions
 Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed
Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA
 PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA Department of Pathology Gadjah Mada University School of Medicine dr. Harijadi Blok Biomedis, 6 Maret 2009 [12] 3/17/2009 1 The pathobiology of neoplasia Normal cells Malignant
PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA Department of Pathology Gadjah Mada University School of Medicine dr. Harijadi Blok Biomedis, 6 Maret 2009 [12] 3/17/2009 1 The pathobiology of neoplasia Normal cells Malignant
Upcoming Webinars. Profiling genes by pathways and diseases. Sample & Assay Technologies -1-
 Upcoming Webinars -1- Keep up to date: Follow Pathway focused biology on Facebook www.facebook.com/pathwaycentral Latest information on, pathway focused research and demos. -2- Understanding Gene Expression
Upcoming Webinars -1- Keep up to date: Follow Pathway focused biology on Facebook www.facebook.com/pathwaycentral Latest information on, pathway focused research and demos. -2- Understanding Gene Expression
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER
 THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID
 Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID Pathway ID Pathway name # components # enriched GO terms a4b1_paxdep_pathway Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 20 179 a4b1_paxindep_pathway Paxillin-independent
Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID Pathway ID Pathway name # components # enriched GO terms a4b1_paxdep_pathway Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 20 179 a4b1_paxindep_pathway Paxillin-independent
Mechanisms of Gene Regulation and Signal! Transduction in Hypoxia!
 Mechanisms of Gene Regulation and Signal! Transduction in Hypoxia! Lorenz Poellinger! Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology! Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden! Normoxia - O 2 availability is in balance
Mechanisms of Gene Regulation and Signal! Transduction in Hypoxia! Lorenz Poellinger! Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology! Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden! Normoxia - O 2 availability is in balance
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained jejunum sections ( 200 magnification;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained jejunum sections ( 200 magnification;
Src-INACTIVE / Src-INACTIVE
 Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Emerging" hallmarks of cancer, a. Reprogramming of energy metabolism b. Evasion of the immune system, Enabling characteristics, a.
 HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
Eosinophils! 40! 30! 20! 10! 0! NS!
 A Macrophages Lymphocytes Eosinophils Neutrophils Percentage (%) 1 ** 4 * 1 1 MMA SA B C Baseline FEV1, % predicted 15 p = 1.11 X 10-9 5 CD4:CD8 ratio 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Cellular infiltrate in the
A Macrophages Lymphocytes Eosinophils Neutrophils Percentage (%) 1 ** 4 * 1 1 MMA SA B C Baseline FEV1, % predicted 15 p = 1.11 X 10-9 5 CD4:CD8 ratio 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Cellular infiltrate in the
Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 9th Edition by Kumar
 Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-robbins-cotran-pathologic-basis-of-disease-9th-edition-bykumar-abbas-and-aster Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease
Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-robbins-cotran-pathologic-basis-of-disease-9th-edition-bykumar-abbas-and-aster Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease
The Role of Microenvironment in the Control of Tumor Angiogenesis
 The Role of Microenvironment in the Control of Tumor Angiogenesis Domenico Ribatti The Role of Microenvironment in the Control of Tumor Angiogenesis Domenico Ribatti Department of Basic Medical Sciences,
The Role of Microenvironment in the Control of Tumor Angiogenesis Domenico Ribatti The Role of Microenvironment in the Control of Tumor Angiogenesis Domenico Ribatti Department of Basic Medical Sciences,
Wnt signaling. Ramray Bhat.
 Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4324
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Supplementary Figure 1. Kinetics of SnCs development in surgically-induced OA and effect of GCV-induced SnC clearance on OA disease progression
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Supplementary Figure 1. Kinetics of SnCs development in surgically-induced OA and effect of GCV-induced SnC clearance on OA disease progression
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice
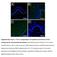 Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples. Major Principles:
 Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
General Pathology VPM 152. Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer
 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto http://people.upei.ca/eaburto Winter 2015 Molecular Basis of Cancer Fundamental principles
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto http://people.upei.ca/eaburto Winter 2015 Molecular Basis of Cancer Fundamental principles
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2)
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
