LGR5. Dnmt3b induced. Dnmt3b. Supplemental Figure 1
|
|
|
- Moses O’Brien’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Figure 1 LGR5 Control Dnmt3b LGR5 Dnmt3b induced Dnmt3b Supplemental Figure 1: Illustration of RNA FISH analysis of Lgr5 (left panel) and Dmnt3b expression (right panel) in colon crypts isolated from a wild- type (top row) and Dmnt3b induced (bottom row) mouse. Particulate signals represent individual LGR5 (left) or Dmnt3b (right) molecules. Nuclei stained with DAPI (purple). Lgr5 was used to identify crypt stem cells and Dmnt3b expression was quantifiedin Lgr5 positive cells. Dnmt3b expression in crypt stem cells of the dox inducedtransgenic mouse was on average ~ 2 fold higherthan in the littermatecontrol mouse.
2 Supplemental Figure 2 Supplemental Figure 2: Pairwise correlation of promoter methylation in colon epithelial cells +/- Dnmt3b transgene expression ( + = Dnmt3b transgene induction, - = no Dnmt3b induction). Promoter methylation fractions were calculated using reduced representation bisulfite sequencing data. The strong correlation of de novo methylation amongst samples with Dnmt3 inductionsupports the concept that Dnmt3b directly targets certain promoter regions.
3 Supplemental Table 1* Comparison of DNA methylation in colon epithelial cells of Dnmt3b overexpressing mice with DNA methylation of human colon cancer mouse data mouse data p value human (references) # p value human (references) # Alox < Apc Apba < Bcl < , 2 Boll 0.18 < Brca Cacna1g 0.42 < Cdh Cdkn2a 0.32 < Cdkn2b 0.02 < Efemp < Chfr Gad < Dapk Gata < Mgmt 0.03 < , 8 Gata < , 2 Mlh < Gata < Pten Gnb < Rb < < Socs Hic < Vhlh Hoxa < Hoxd < Lrp < Myod < , 4 Neurog < Nr3c < , 2 Otx < Rbp < Sfrp < Sfrp < Tert 0.21 < , 4 Thbs < Timp < , 4
4 *Supplemental Table 1: Comparison of DNA methylation in colon epithelial cells of Dnmt3b overexpressing mice with DNA methylation of human colon cancer. The mouse data show the absolute increase in DNA methylation caused by Dnmt3b overexpression (from 0 to 1) and the corresponding p value (comparison no dox versus plus dox, n = 5 each, t- test). Genes with an absolute increase ere defined as methylated and are colored in red, unmethylated genes are colored in blue. The column with human data shows the respective literature reference, red fields indicate genes that were reported as methylated in human colon cancer and blue fields indicate genes that were reported as unmethylated. In the case of Mgmt, labeled yellow, one reference indicates methylation and one reference indicates no methylation. To facilitate the comparison, genes with more than one promoter in human or mouse were not included in the analysis. # References Supplemental Table 1: (1), (2), (3), (4), (5), (6), (7), (8): 1. Widschwendter, M., Fiegl, H., Egle, D., Mueller- Holzner, E., Spizzo, G., Marth, C., Weisenberger, D. J., Campan, M., Young, J., Jacobs, I., and Laird, P. W. (2007) Nat Genet 39, Irizarry, R. A., Ladd- Acosta, C., Wen, B., Wu, Z., Montano, C., Onyango, P., Cui, H., Gabo, K., Rongione, M., Webster, M., Ji, H., Potash, J. B., Sabunciyan, S., and Feinberg, A. P. (2009) Nat Genet 41, Schuebel, K. E., Chen, W., Cope, L., Glockner, S. C., Suzuki, H., Yi, J. M., Chan, T. A., Van Neste, L., Van Criekinge, W., van den Bosch, S., van Engeland, M., Ting, A. H., Jair, K., Yu, W., Toyota, M., Imai, K., Ahuja, N., Herman, J. G., and Baylin, S. B. (2007) PLoS Genet 3, Shen, L., Toyota, M., Kondo, Y., Lin, E., Zhang, L., Guo, Y., Hernandez, N. S., Chen, X., Ahmed, S., Konishi, K., Hamilton, S. R., and Issa, J. P. (2007) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104, Toyota, M., Ahuja, N., Ohe- Toyota, M., Herman, J. G., Baylin, S. B., and Issa, J. P. (1999) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96, Zuo, X., Shen, L., Issa, J. P., Moy, O., Morris, J. S., Lippman, S. M., and Shureiqi, I. (2008) FASEB J 22, Xu, X. L., Yu, J., Zhang, H. Y., Sun, M. H., Gu, J., Du, X., Shi, D. R., Wang, P., Yang, Z. H., and Zhu, J. D. (2004) World J Gastroenterol 10, Kondo, Y., Shen, L., Cheng, A. S., Ahmed, S., Boumber, Y., Charo, C., Yamochi, T., Urano, T., Furukawa, K., Kwabi- Addo, B., Gold, D. L., Sekido, Y., Huang, T. H., and Issa, J. P. (2008) Nat Genet 40,
5 Supplemental Table 2* Dnmt3b methylates the same genes that are methylated in human colon cancer Gene Symbol Gata5 Dnmt3b Colon Cancer # Gene Symbol Dnmt3b Colon Cancer HoxA Sfrp Chfr Igf Sez6l Twist Mt Ebf Timp Hic Neurog Sfrp Rbp Sfrp Cdkn1c Neurod Epm2aip Gata Crabp Nr3c Bdnf Gata Cdh Tert Socs Itga Gabra Kl Esr Cacna1g Pgr Sfrp Cyp27B Bcl Mlh Tmeff Mgmt MyoD Drd Gad Gstp Gdnf Thbs # *Supplemental Table 2: The table shows a comparison of DNA methylation data from colon epithelial cells of Dnmt3b expressing mice as measured by RRBS with published DNA methylation data of human colon cancer (1). The mouse RRBS data are shown in the column Dnmt3b with numbers indicating the absolute methylation gain induced by Dnmt3b expression (0= no methylation, 1= complete methylation). Human colon cancer data are shown in the column colon cancer with numbers indicating percent of methylated reference (PMR, 0= no methylation, 100 = methylation equals methylated reference). The supplementary table S1 of Widschwendter et al. (1)lists 77 genes with a significant methylation increase in human colon cancer. For comparison with Dnmt3b data human genes with <0.1 absolute gain in human colon cancer (PMR gain in tumors < 10) or baseline methylation > 100% (PMR>100) were excluded. Based on these criteria 62 genes were eligible for the Dnmt3b/colon cancer comparison. Dnmt3b RRBS data were available for 44/62 eligible human genes. 37/44 (84%) of these genes were methylated both by Dnmt3b and in human colon cancer (red color), only 7/44 (16 %) were methylated in colon cancer and not methylated by Dnmt3b model. # Reference Supplemental Table 2: Widschwendter, M., Fiegl, H., Egle, D., Mueller- Holzner, E., Spizzo, G., Marth, C., Weisenberger, D.J., Campan, M., Young, J., Jacobs, I., et al Epigenetic stem cell signature in cancer. Nat Genet 39:
6 Supplemental Table 3* Gene Symbol Dnmt3b Colon Cancer # Gene Symbol Dnmt3b Colon Cancer Smad Prkar1a Apc Uqcrh Jup Cdk2ap Rpa Axin Grin2b Rb Smad Tgfbr Rpa App Stk Smad Xpa Faf Atm Tnfrsf10b Ercc Smad Ctnnb Xpc Ercc Rad23A Msh Xab Dph Atr Stat Pttg Ctsd Ercc Cxadr Hsd17b Pparg Mbd Clic Vdr Ncl Ercc Ung Ldlr Mbd Ccdn Ogg Psen Apex Psat Xrcc Cdkn2b Parp Dapk Parp Cdh Ercc Msh Ddb Erbb Brca Ptgs Pold Onecut Pten Dnajc Arpc1b Mthfr Vhl Sash Tgfvbr # *Supplemental Table 3: Genes not methylated in human colon cancer are also largely not methylated by Dnmt3b: The table shows a comparison of DNA methylation data from colon epithelial cells of Dnmt3b expressing mice as measured by RRBS with published DNA methylation data of human colon cancer (1). The mouse RRBS data are shown in the column Dnmt3b with numbers indicating the absolute methylation gain induced by Dnmt3b expression (0= no methylation, 1= complete methylation). Human colon cancer data are shown in the column colon cancer with
7 numbers indicating percent of methylated reference (PMR, 0= no methylation, 100 = methylation equals methylated reference). The supplementary table S1 of Widschwendter et al. (1) lists 100 genes with no significant methylation increase in human colon cancer. For comparison with Dnmt3b data human genes with baseline methylation > 100% (PMR>100) were excluded. Based on these criteria 94 genes were eligible for the Dnmt3b/colon cancer comparison. Dnmt3b RRBS data were available for 71/94 eligible human genes. 65/71 (92 %) of these genes were not methylated in colon cancer and also not methylated by Dnmt3b (blue color). Only 6/71 (8 %) genes were methylated by Dnmt3b (red) and not methylated in colon cancer. # Reference Supplemental Table 3: 1. Widschwendter, M., Fiegl, H., Egle, D., Mueller- Holzner, E., Spizzo, G., Marth, C., Weisenberger, D.J., Campan, M., Young, J., Jacobs, I., et al Epigenetic stem cell signature in cancer. Nat Genet 39:
8 Supplemental Methods Transgenic mice and transgene regulation All mice used in this study including the tetracycline inducible Dnmt3b transgenic mice and the genotyping protocol were described previously {Linhart, 2007 #227}. Briefly the tetracycline inducible transgene was targeted to the collagen I locus and the tetracycline sensitive transactivator M2-rtTA was targeted to the Rosa locus. Transgene induction was achieved by administering doxycycline (dox) in the drinking water (0.5g/liter). To test the stability of aberrant DNA methylation mice were first induced with dox for five months and a subset was then switched back to regular drinking water without dox for another four months: 5 months dox = On samples, n = 5; 4 months dox withdrawal = On/Off samples, n = 5; control mice with no transgene induction were age matched to On/Off samples (two Dnmt3b +/-, rtta +/- mice maintained without dox and two Dnmt3b -/-, rtta +/- mice exposed to dox in analogy to the On/Off samples). For the data shown in figures 1A-C mice were induced for four months. Tissue harvesting and DNA isolation Colon tumors from APC Min/+ mice were harvested under the dissecting microscope. Colon epithelial cells from tumor free colon samples of APC Min/+ mice and APC wild-type mice were harvested as described previously {Fujimoto, 2002 #118}. For DNA isolation tissue samples were digested with proteinase K (10mg/ml) in lysis buffer over night, treated with RNAse A, purified twice with Phenol/Chloroform, precipitated with isopropanol, washed in 70% EtOH and resuspended in water. Mouse embryonic fibroblasts
9 Double homozygous embryos (Dnmt3b transgene +/+ and Rosa-rtTA +/+) were harvested 12.5 days post conception. Cells were expanded for days in culture to generate two fully confluent 150 mm dishes per embryo. Production of gamma-irradiated samples: For each embryo ~ 70 % of two confluent 150 mm dishes with mouse embryonic fibroblasts were gamma-irradiated with 24 Gy. Following irradiation 8x10 6 cells were plated into each of two 100 mm dishes to generate two fully confluent 100 mm culture plates with growth arrested irradiated cells. Medium was replaced 12 hours after plating to remove non adherent cells. Production of mitomycin C treated samples: For each embryo two 150 mm culture plates were harvested and 8x10 6 cells were transferred into each of two 100 mm dishes. 12 hours after plating cells were treated with mitomycin C (5µg/ml, incubation 2.5 hours) and washed five times with PBS. Production of culture plates with untreated proliferating cells: For each embryo 2x10 6 untreated cells were transferred to each of two 100 mm plates. Plates with proliferating cells were constantly maintained at ~ 50% - 60% confluency. All cells received fresh medium simultaneously every two days. For transgene induction cells were cultured in the presence of 2µg/ml dox final concentration. After 14 days of dox treatment cells were harvested for DNA methylation analysis. Growth arrest by gamma-irradiation and mitomycin C treatment was evaluated by BrdU staining: For each sample cells were seeded into individual wells of a 24 well plate. To simulate the conditions of the experimental plates the seeding density in the 24 well plate was matched to the seeding density of the experimental plates: gamma-irradiated and mitomycin C treated samples were seeded at 2.8x10 5 /well and proliferating samples were seeded at 0.7x10 5 /well. Mitomycin C treatment in the 24 well plate was conducted in analogy to the experimental 100 mm plates. 24 hours after plating cells were incubated with 10µM BrdU for 4 hours and then subjected to immunostaining: Cells were fixed for 10 minutes in 4% paraformaldehyde, washed three times in PBS, then treated with 2N HCl for 10 minutes, neutralized in 0.1M borate for 10 minutes at RT, washed three times in PBS and blocked for 1 h with 1% BSA in PBS. Cells were then incubated with the
10 primary antibody (rat anti BrdU from Axyll h7227, 1:150) for 30 minutes at RT, washed three times in PBS and then incubated with the FITC conjugated secondary antibody for 30 min at RT. Cells were counterstained with DAPI. For analysis of BrdU incorporation at least 100 cells were scored for each sample. Untreated proliferating cells: 32.4% BrdU positive, stdev = 7.04, n=5. Mitomycin C treated cells: 2.9% BrdU positive, stdev = 1.7, n = 3. Irradiated cells: 5.8% BrdU positive, stdev = 0.9, n =2. Lgr5 and Dnmt3b mrna quantification by fluorescence in situ hybridization We used 4 micron sections from frozen circular wrapped colon samples, which were stored on coverglass coated with poly-l-lysine at -80C. The sections were fixed for 10 minutes in 4% formaldehyde at room temperature, followed by 3 washes with PBS. The sections were then permeabilized in 70% EtOH at 4C for at least 4 hours, after which the sections were prehybridized, hybridized and imaged as described {Raj, 2008 #279}. We used probes targeting Lgr5 and Dmnt3b, with Lgr5 coupled to tetramethylrhodamine and Dmnt3b coupled to Cy5. We acquired stacks of images spanning the entire height of the section and then located individual mrna molecules using the semi-automated method described in {Raj, 2008 #279}. We then manually identified Lgr5 positive cells and found the density of Dmnt3b mrnas present in those cells in a total of 19 wild-type Lgr5 positive areas and 49 overexpressor Lgr5 positive areas. We obtained errors in the density measurements by bootstrap resampling. To compute the p-value for the difference in density between the two strains, we computed the fraction of the time that the null hypothesis (no difference) would be satisfied given a random resampling of the dataset. A list of probes used for RNA FISH is shown at the end of supplemental methods.
11 cdna and quantitative PCR cdna production and quantitative PCR was conducted as described previously {Linhart, 2007 #227}. Briefly, cdna was prepared from total RNA using oligo-dt primers. For each sample, a minus-rt reaction was generated, and pooled minus-rt reactions were used as negative controls for quantitative PCR reactions (SYBR Green, Invitrogen). For quantitation, standard dilution curves were included on each plate. All samples were analyzed in triplicate, ß-Actin was used as an endogenous control. Individual data were converted to relative values based on the standard curve and then normalized to the ß-Actin values of the same sample. For Dnmt3b quantification we used primers Dnmt3b forward: GTTCGAGCTGGCAAGACCTT and Dnmt3b reverse: TGGTCCTCCAGTGACTCTCCA and for ß-Actin we used primers ß- Actin forward: TGAACCCTAAGGCCAACCG and ß-Actin reverse: AGGTCTCAAACATGATCTGGGTC DNA Methylation Analysis (Mass Array Platform) Genomic DNA sodium bisulfite conversion was performed using EZ-96 DNA Methylation Kit (Zymo Research, Orange County, CA). The manufacturer s protocol was followed using 1ug of genomic DNA and the alternative conversion protocol (a two temperature DNA denaturation). Sequenom s MassARRAY platform was used to perform quantitative methylation analysis. This system utilizes matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-offlight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry in combination with RNA base specific cleavage (MassCLEAVE). A detectable pattern is then analyzed for methylation status. PCR primers were designed using Methprimer ( and Epidesigner (epidesigner.com). When it was feasible, amplicons were designed to cover CpG islands in the same region as the 5`UTR. For each reverse primer an additional T7 promoter tag for in-
12 vitro transcription was added, as well as a 10mer tag on the forward primer to adjust for melting temperature differences. The MassCLEAVE biochemistry was performed as previously described {Ehrich, 2005 #122}. Mass spectra were acquired using a MassARRAY Compact MALDI-TOF (Sequenom, San Diego) and spectra s methylation ratios were generated by the Epityper software v1.0 (Sequenom, San Diego). A list of all primers is provided at the end of supplemental methods. DNA Methylation Analysis (Reduced Representation Bisulphite Sequencing) RRBS methylation analysis was conducted as described previously {Meissner, 2008 #272}. The library was constructed with the DNA sample kit (Illumina, IP ). Mouse genomic DNA was digested wit MspI. A small and a large size fragment band were isolated from a 3% Nusieve gel, bp and bp fragments respectively. Isolated and phenol:chloroform purified DNA was end-repaired and adenylated. The fragments were ligated to the 3 T-overhang methylated-cytosine-containing adapters. After adapter ligation DNA was bisulfite treated with Qiagen s Epitect bisulfite kit with modification of the manufacturers protocol by adding two additional bisulfite conversion cycles. After bisulfite treatment DNA was PCR amplified for 24 cycles. Small and large library fragments (with adapters) were size selected on a 3% Nusieve gel, and bp respectively. Libraries were sequenced on the genome Analyzer II (Ilumina). For sequence analysis the mouse genome (NCBI Build 37) was in silico digested with MspI and fractionated into fragments with ranges of ("short") or nt ("long"). Tags representing 36 nt at both ends of each fragment were extracted and every C was converted to T to generate the RRBS library. A bisulphite-aware short-read aligner{gu, #308} was used to align each set of Illumina 36 nt reads to the appropriate RRBS library, allowing up to 2 mismatches. Reads mapped to a library were intersected with genome locations representing promoters (defined
13 as 2 kb up- and downstream of the transcription start site) derived from NCBI Refseq transcripts (with coordinates from UCSC Bioinformatics) for further analysis. A CpG was defined as scorable if it was assayed by at least 5 reads, and a promoter with least 5 scorable CpGs was itself defined as scorable. In each sample, the methylation fraction of a promoter was calculated as the mean of scorable CpGs. After grouping methylation fractions for short and long fragment sets, differential methylation was assayed by a moderated t-test as implemented in the R package "limma".
14 List of primers used for MALDI- TOF methylation analysis AmpliconNamGeneName LeftPrimer RightPrimer Chr targetstart targetend SQ00001_Esr1Esr1 TTTGAGGTAG TAATACCAAAAchr SQ00002_Esr1Esr1 TAAGGTTGTTGTTTTTCAACCAchr SQ00003_Esr1Esr1 GAAGGTTTATAAAAATAACCTTchr SQ00004_Esr1Esr1 TGGATTAGAGCCTTCTATAAAchr SQ00005_MyoMyod1 GTGGTTATTTTAACTCCATATCchr SQ00006_MyoMyod1 GATTTAGGAA CCTTACAAACCchr SQ00007_MyoMyod1 TTGTTTGTTGTAATATAAAAAAchr SQ00008_MyoMyod1 GTTTGAGTAAATCTAAATATAAchr SQ00009_MyoMyod1 GGTTTTAGGA ACTTTCTTCAC chr SQ00010_Tus Tusc1 TTTGTATAAGTTCCTACAACTAchr SQ00011_Tus Tusc1 GGAAAGTTTT AAAACCTCATAchr SQ00012_Tus Tusc1 GGTTAGAGAATTACTTCTCTTTchr SQ00013_AloxAlox15 GTTTTTAGTAATAAAAATTTCTchr SQ00014_AloxAlox15 GGTAGAAGGGCCATCTTACAAchr SQ00015_AloxAlox15 GGTATGGGAAAAAACCCCCAAchr SQ00016_AloxAlox15 TTGGATGTTTTAACATCTAATCchr SQ00017_AloxAlox15 GGAGTAAGGGCATCACAAATAchr SQ00018_TertTert GGTTGGAGTATACTTAAAAAAchr SQ00019_TertTert ATTTTTAGTGGACCACCAACTCchr SQ00020_TertTert GGTGTTATTTTACAAAAAAAA chr SQ00021_TertTert GAGGTTTGGGAACCACTAAAAchr SQ00022_GadGad1 TGTTGAGTGTAATCACCCCAAAchr SQ00023_GadGad1 TGTAAGTAAG ATCACTTCAACchr SQ00024_GadGad1 GGTTTTTTTATACTAAAATAACchr SQ00025_GadGad1 GTTAATTTTTT AACAAACACCAchr SQ00026_GadGad1 GGAGATAGAATTCTTTCCAAAchr SQ00027_GadGad1 GGAATTTGGA TACCCTTAATCchr SQ00028_Gat Gata3_01 AGGAGGGAGTCCTAAATAAAAchr SQ00029_Gat Gata3_01 AGGATGAGGTAACATCACAAAchr SQ00030_Gat Gata3_01 GGTTAGGTAA AAAAAATCCTCchr SQ00031_Gat Gata3_02 GTTTGTTTTGTCTAAATAAACCchr SQ00032_Gat Gata3_02 AGATTTTGGTTAAATATACCTAchr SQ00033_Gat Gata3_02 TTAGGAGTTTTACTCTCCTTTT chr SQ00034_Gat Gata3_03 TAAATAGTTTTAATTTCAAAAAchr SQ00035_Gat Gata3_03 AGGGAATGTACTACCTATCCCchr SQ00036_Gat Gata3_03 GGTTGTAGTTTATCACAAATCAchr SQ00037_Gat Gata3_03 TGGAAATTAGTCCTCAACACAchr SQ00038_HoxHoxa1 TTAAGGATGGCTTTAATCCCAchr SQ00039_HoxHoxa1 TAGAGGATTGCCCTTCTAAAAchr SQ00040_HoxHoxa1 ATTATTATTAGAATATACCAACchr SQ00041_HoxHoxa1 TTTGGAATATTACTATACCCCCchr SQ00042_HoxHoxa1 GTAGGAATTA ACCCAACCCAAchr SQ00043_WntWnt7a_01 GTTTTTAGTGACAACCCCACCTchr SQ00044_WntWnt7a_01 TATTAAAGATTAAACCTCCCTCchr SQ00045_WntWnt7a_01 TGGGAAGAATCCCCTACTCCAchr SQ00046_WntWnt7a_02 TATGTTTAGGTCTCTAAAACAAchr SQ00047_WntWnt7a_02 GTAGTGGGAGTCCCTAACTCTchr
15 SQ00048_WntWnt7a_02 GTTTTGGGATATATACCCTCAAchr SQ00049_WntWnt7a_02 GAAGGATGTT CTAAACACTAAchr SQ00050_WntWnt7a_03 GAAGGAAGTTTCTACTCTTCT chr SQ00051_WntWnt7a_03 TGTTTTTGTTACAATATCCTCCchr SQ00052_Bcl2Bcl2_01 ATTTTGGATTTCTTCCAACCTAchr SQ00053_Bcl2Bcl2_01 TGGATTATAG ACAAAACACA chr SQ00054_Bcl2Bcl2_01 AATTTTTTAGGAACCTTAAAATchr SQ00055_Bcl2Bcl2_02 TTGTAAATGTTAATTTCCAAATchr SQ00056_Bcl2Bcl2_02 TAGTTATTTTT TCAATCCAACAchr SQ00057_Bcl2Bcl2_02 GAGGTGTTTA AAATCCTCTTCchr SQ00058_Nr3 Nr3c1 GAGAGGATAAATTATCAAATAchr SQ00059_Nr3 Nr3c1 AGATGATTTATCCTTAACACCTchr SQ00060_Nr3 Nr3c1 GGGGAATGATTCAACAAATCTchr SQ00061_Nr3 Nr3c1 GGATTTGTATACTATAAATAACchr SQ00062_Nr3 Nr3c1 GAATTATTTTTAAAACCTTAACchr SQ00063_Nr3 Nr3c1 TAGAGAGGAAAATAAAAAAC chr SQ00064_CldnCldn5 GGGTTGTTTATCAAAATAACAAchr SQ00065_CldnCldn5 GGGTTTTGTTTTCCTTTAATTC chr SQ00066_CldnCldn5 TGTAAGGTGT CCCTTAAACATchr SQ00067_CldnCldn5 GATAAGAAGATTAAAACAACAchr SQ00068_PtenPten TAGTTTAGGG AACCCATAAAAchr SQ00069_PtenPten GGTTTTTTGGTCCTAAAACAAAchr SQ00070_PtenPten GGGGATTAAGAACCAAACTCAchr SQ00071_PtenPten GGGGTTTAGT CAAAAAACAC chr SQ00072_PtenPten TTTGTTTAATT ACCTCAAAAACchr SQ00073_PtenPten GGAAGTTGTA TCCCAACCCTAchr SQ00074_PtenPten TTTGTTATTAT AAACTTCTTCTchr SQ00075_PtenPten GAAATTTAGG ACCTCAAAAACchr SQ00076_PtenPten GGAAGGATAACTCAACTCTCAchr SQ00077_PtenPten GTTTTTTGTTT CAACCAAAAA chr SQ00078_Peg Peg1 ATATGTTGGG CAACAAAAAC chr SQ00079_Peg Peg1 TTTATTAGAATCAACAAAAAC chr SQ00080_Peg Peg1 TTATTGATGATCTAAAACACACchr SQ00081_Peg Peg1 TGAAGAAAGTTCTTCCAAAATchr SQ00082_Peg Peg1 GAGTTGTTGTTTAAATTACTTCchr SQ00083_Igf2 Igf2r AGGTTTTAGG CTAACTTACCTchr SQ00084_Igf2 Igf2r AGATATTTTGGCAAAACACTAAchr SQ00085_Igf2 Igf2r GAGGATTTTA ATCCTCCCCTT chr SQ00086_Igf2 Igf2r GGTGTAAATT CCTTCATATACchr SQ00087_Igf2 Igf2r GATAGGAGGAAACCCCATTATchr SQ00088_Igf2 Igf2r TTGTAGATAATCCCAAAATATAchr SQ00089_Igf2 Igf2r GGATTTTGTAGCCCCTCCCTTC chr SQ00090_Igf2 Igf2r GTTAGTAAGA CCTCCTTATACchr SQ00091_Boll Boll TGGAGTTAGGCTAACTAACCTchr SQ00092_Boll Boll TAAAGATAAA ACTAAAACCTAchr SQ00093_Boll Boll GGGAGGGAAAACTAAAACCTAchr SQ00094_Boll Boll GTTGGAAAGAATAAAAACCCCchr SQ00095_Boll Boll GGAAGTTTTTACTCCAAAATCCchr SQ00096_EfemEfemp1 GAAGTAATTG AAACTCATATTchr SQ00097_EfemEfemp1 TAGTTATAGGAAACACCTAACAchr
16 SQ00098_EfemEfemp1 TAGTTATAGGAAATAACTAAACchr SQ00099_EfemEfemp1 TTTGTGAATTATCCACCTCCATchr SQ00100_GnbGnb4 TGGTTTGGGTTAACTTCAAATTchr SQ00101_GnbGnb4 GTTTTGTGTGGCCAAACTTTAAchr SQ00102_GnbGnb4 TGTGGTTTTTTACCACACCCAAchr SQ00103_Dlk1Dlk1- Gtl2 ATAGGTTTTTAACTCCATAATAchr SQ00104_Dlk1Dlk1- Gtl2 TTTATTAGGGACACCTAACCTAchr SQ00105_Dlk1Dlk1- Gtl2 TTATGGTATAAACATCCATATAchr SQ00106_Dlk1Dlk1- Gtl2 ATAGTATTGGTCCATAACATAAchr SQ00107_Dlk1Dlk1- Gtl2 TTTGGTATAGACCACAACACTTchr SQ00108_Dlk1Dlk1- Gtl2 GATGTGTTGTGATCCCCTATACchr SQ00109_Dlk1Dlk1- Gtl2 GGAGAATGTT TCCACAATCTAchr SQ00110_Otx Otx1 GGTAGGGATTTTTACCAACCTchr SQ00111_Otx Otx1 ATTGAGTGATATACTAAAACCCchr SQ00112_Otx Otx1 TTGGTTGTTTTAAATAAAACTAchr SQ00113_Otx Otx1 GAGGTTAGGTCTAAAATCCCCchr SQ00114_Otx Otx1 GAGGGTAGTAATTACAAAATCchr SQ00115_Otx Otx1 GAATATTTTTGAAATTACTAACchr SQ00116_Otx Otx1 TTTATTAAATTCACTATAAAAAchr SQ00117_Irx2 Irx2 GGGTAGTTTTATCACCCTAAAAchr SQ00118_Irx2Irx2 TAGAGGATTGAAAACCCAAC chr SQ00119_Irx2 Irx2 TTGTAGGAGGCACACTCTCATchr SQ00120_Irx2 Irx2 AGTAGGAAAGCTTTTATTCCTTchr SQ00121_Irx2 Irx2 GAAGGAGAATAAAAACTAAA chr SQ00122_Irx2 Irx2 TTTAAGAAAG ATTAATCCAAAchr SQ00123_Irx2 Irx2 GTATTGGTTTTAATAACAACTCchr SQ00124_Irx2 Irx2 TTTGGTTTTTATACCCAAACCTchr SQ00125_Irx2 Irx2 ATAAGGTTAG AAATTCCCTAAchr SQ00126_Irx2 Irx2 GGGTTTAAGT AATACCCCTACchr SQ00127_Irx2 Irx2 GTTTGTAGTGGAACCTCAAACAchr SQ00128_Irx2 Irx2 GTAGTTAGGA CCCAATTTAACchr SQ00129_Irx2 Irx2 GAGTAGGTTGTTCCTCAACTCchr SQ00130_Irx2 Irx2 GTGTTGGTGA CCCACCAACCCchr SQ00131_Ghs Ghsr GGAGGATTTT CCACCAACATAchr SQ00132_Ghs Ghsr GGTTAAGGTGATATCAAAACTchr SQ00133_Ghs Ghsr TTTTATATGTT CAATAAATCACchr SQ00134_GhsGhsr TTGATAAATTGCTAAAAAAAC chr SQ00135_Ghs Ghsr TTTTTATTGTTTTCTACAAACTCchr SQ00136_LmtLmtk3_01 GTTTTTATGGTACAAAACCTCAchr SQ00137_LmtLmtk3_01 GGGGAGGAGGATACCTCCTCAchr SQ00138_LmtLmtk3_01 GGGGTTGTTTACCCCTCCAAAAchr SQ00139_LmtLmtk3_01 GTATTTTGTTTAATATCAAAACchr SQ00140_LmtLmtk3_01 ATTTGAGGGA TCCCCATAACTchr SQ00141_LmtLmtk3_02 AGAGTTTTGG AACTAACCAAAchr SQ00142_LmtLmtk3_02 GGGTTTTGAG CTCCTCTATTA chr SQ00143_LmtLmtk3_02 GTTTGGAGAT CCTAACTCTTCchr SQ00144_RbpRbp1 GAAGGTTTGA TAAATTCCAAAchr SQ00145_RbpRbp1 GGGTTTTGTGTTCCACAAACATchr SQ00146_RbpRbp1 AGTTTGTTTTACAAACTAACAAchr SQ00147_Thb Thbs2 TTAGTATTTTGCAAAATAAAA chr
17 SQ00148_Thb Thbs2 AGATTGGTTG ACTAAATTTCTchr SQ00149_Thb Thbs2 GATTGATAGG CCACTAAACTAchr SQ00150_Thb Thbs2 TGGGGAGTTT CAAAAAACCTAchr SQ00151_Tim Timp3 TTATTATGATTCTACAAAACATchr SQ00152_Tim Timp3 TTTTATAGGGATCTTACTCCCT chr SQ00153_Tim Timp3 TTTAGGGTTGTAAAACTTCCTTchr SQ00154_Tim Timp3 GTAGAAGGTACCCCTATATCAchr SQ00155_Tim Timp3 TTTAGGGTTGTAAAACTTCCTTchr SQ00156_HoxHoxd1 ATTTAGTTAAATCCCCTCAAAAchr SQ00157_HoxHoxd1 GGTGGTTAGGTCAACCACTTTchr SQ00158_HoxHoxd1 GGGGATATAGTAAACTACCTAchr SQ00159_HoxHoxd1 GGGTTTTGATTAACCCTTTCAAchr SQ00160_Lrp2Lrp2 GGATAATTTGAACCAAAACCTCchr SQ00161_Lrp2Lrp2 GTTTTGGGTAGCCCTCAAAACTchr SQ00162_Lrp2Lrp2 GTTTTATTTTGTAACCCCAAAAchr SQ00163_Lrp2Lrp2 GGTTTGGTTTACTACAATCATCchr SQ00164_Lrp2Lrp2 TTGTGTTTTTGCTCCAAACAATchr SQ00165_Lrp2Lrp2 GGGAATTTAG CTTACTCCCCT chr SQ00166_Lrp2Lrp2 AGTGATTGAA TACATAAAACCchr SQ00167_mmmmu_mir_34aGTTGTGAGTA CCCATACCCACchr SQ00168_miRmiR34- a TGGTTTTATTTACAAAAACAT chr SQ00169_miRmiR34- a AAGATTGAGGCCAAAATAAA chr SQ00170_miRmiR34- a TAGGGGTGTT CAAAAACTTAAchr SQ00171_miRmiR34- a GTTTAAGATGAAATCACCTAACchr SQ00172_miRmiR34- a GTGTTAATAG CAACCTAAACTchr SQ00173_miRmiR34- a TTAGGGATTAAAAAATCATTTCchr SQ00174_miRmiR34- a GGTTTTTTTGTATAACTCTATCchr SQ00175_miRmiR34- a GTGGGGTTGGCAAAATCCCACchr SQ00176_miRmiR34- a TGAGTTTAGG AACAAAAAAA chr SQ00177_miRmiR34- a TGAGAGATGTAAATCCTTCACchr SQ00178_miRmiR34- a TATTGGTTTAGAACCTAAATTAchr SQ00179_miRmiR34- a GTTGTTTTATAAACTCTAACACchr SQ00180_miRmiR34- a GATGAGGGTGATACAACAATAchr SQ00181_miRmiR34- a GGATGGGGAGCAACATCCCATchr SQ00182_miRmiR34- a TGGGGAGGTTACCAACAAAC chr SQ00183_miRmiR34- a TGTTTATATTT ACCCTAAACCCchr SQ001_Cdkn2 Cdkn2a AGTAAATAGGCTAAACCAAATchr SQ002_Cdkn2 Cdkn2a GTAAATAGGT CAAATTCTTAAchr SQ003_Cdkn2 Cdkn2a TTATTTATAAACTAAACCCCAAchr SQ004_Cdkn2 Cdkn2a TAAGAGAGGGCCCCTCCCCCAchr SQ005_Apba1Apba1 TTGGAAGATTTATCCTCTATCCchr SQ006_Apba1Apba1 GTTAGGGATT CCAAACCTAAAchr SQ007_Apba1Apba1 TGGAGAGTAGTACCACCTCCAchr SQ008_Apba1Apba1 GGGTTTTTTTGTACCACCTCCAchr SQ009_Apba1Apba1 GATTTTTGGAAACAACTTTATTchr SQ010_Apba1Apba1 GGTTTGAAAG AATCCCTAATAchr SQ011_Apba2Apba2 GATTGATTGTGCCCCTTAAAAAchr SQ012_Apba2Apba2 TTTAGTTTATT TTAAAAAATCAchr SQ013_Apba2Apba2 TTTTGATTTTTTATACCCCTCTAchr SQ014_Apba2Apba2 TTTGGGTAGG CCCCTCAAAAAchr
18 SQ015_Apba2Apba2 GGGATTTGGACCTTATAAAACchr SQ016_Apba2Apba2 TTTTGTTTTTTTAAATCCCTTAAchr SQ017_Apba2Apba2 TTTAAAGAGATCCAAAAACCCAchr SQ018_Mlh1_Mlh1 AATTTAGAAG CCAAACTAATTchr SQ019_Mlh1_Mlh1 AATTTAGAAG CCAAACTAATTchr SQ020_Mlh1_Mlh1 GGTAAGTGTT TTCCCTCAACTchr SQ021_Mlh1_Mlh1 TTTATTTTTGAACCAAAAACA chr SQ022_Mlh1_Mlh1 TTAGTGTATGGCCACAAAAAC chr SQ023_Mlh1_Mlh1 GTTTTTAGAAAATTAAACAACAchr SQ024_Mlh1_Mlh1 TGGTATTTATGTTTCTATCATC chr SQ025_Mlh1_Mlh1 TAATGTTATTATAAACCTAAAAchr SQ026_Cacna Cacna1g TTTAGGTTTATACTCAACAAACchr SQ027_Cacna Cacna1g GGGGGTTTTA AACCCCTTAAAchr SQ028_Cacna Cacna1g GGTGGGGGTTATAACTCTCCCchr SQ029_Cacna Cacna1g TTTAGTTGGTTATTCACAATCCchr SQ030_Cacna Cacna1g TTGATTTTTTA CCCCTACCCTCchr SQ031_Cacna Cacna1g GTTTGAAGTTGAAAAAAATCTCchr SQ032_Neuro Neurog1 TTTTTGGGTAGACACCAAACTCchr SQ033_Neuro Neurog1 AGGTGGAGGTAACCAAACCCAchr SQ034_Neuro Neurog1 GGGTTGGTTTTCACTTTCTACCchr SQ035_Neuro Neurog1 GTTTTAATTTT CCCTTTAAAAAchr SQ036_Neuro Neurog1 GAGGAGGATTAATATCTCAACchr SQ037_Runx3 Runx3 TGGGTTTGAA ACTACCACTATchr SQ038_Runx3 Runx3 TTTGAGGTTTAAACCAAATAAAchr SQ039_Socs1_Socs1 GGAGGATTAGAAAAAAACCT chr SQ040_Socs1_Socs1 ATTTTTTTATA AAACCCAAAC chr SQ041_Socs1_Socs1 GAGTGAGTTT CAAACAACTCCchr SQ042_Socs1_Socs1 GATTTTGGTAGCACCTTCCCACchr SQ043_Apc_0 Apc AGGTGAGTAGCTAAAAAAAC chr SQ044_Apc_0 Apc GGTGGAGTGACAAACAATCCTchr SQ045_Apc_0 Apc TTGGAAGGGTAAAATCTACCAchr SQ047_Sfrp2_Sfrp2 TGGTTGGGTTTACTCCAACACCchr SQ048_Sfrp2_Sfrp2 GTAGTGTTGA CCAACCAAAATchr SQ049_Sfrp2_Sfrp2 AGGGGGAGTAAAAAAAACCC chr SQ050_Sfrp2_Sfrp2 GGTTGGATGGAACCCCAACCTchr SQ051_Sfrp4_Sfrp4 AGAATTATGG AACTTTCCTACchr SQ052_Sfrp4_Sfrp4 GGGTAGTGGACACAAACTTTTchr SQ053_Rb1_0Rb1 GTAGAGATGGAACTACCCCTAchr SQ054_Rb1_0Rb1 GGTTTTTTGGAAAAACTACCATchr SQ055_Rb1_0Rb1 GGGTTTTTTTGAAACAAAACT chr SQ056_Rb1_0Rb1 TTTTTTGTTAGCCAAAATAAAAchr SQ057_Vhlh_0Vhlh TTAATTGTAGGCCTCCTCTAAAchr SQ058_Vhlh_0Vhlh GGAAGGTAGTCCTCCAAATTAchr SQ059_Vhlh_0Vhlh ATAGGTTGGT ACCCTCTCAAAchr SQ060_Vhlh_0Vhlh GGTTGTAGAA AAAAAAAACA chr SQ061_Brca1_Brca1 TTTAAGAGAG CCCACCCTTTAchr SQ062_Brca1_Brca1 GAAGGGGTTGCTCAAAACTATchr SQ063_Gata4_Gata4 GGGGAATTTT ATTTTAATACCchr SQ064_Gata4_Gata4 GGAGAGGGTTTCATCCTTTTA chr SQ065_Gata4_Gata4 GGTTTTAGTGTACCCTACCTAAchr
19 SQ066_Gata4_Gata4 GATTTTGTTTGCTACCTAACCAchr SQ067_Gata5_Gata5 TTTTTGGGTGGTCAAAAAAAC chr SQ068_Gata5_Gata5 GGATTAGGTA CTCCAACTAAAchr SQ069_Gata5_Gata5 TTAGAGTTGTTCTAAACCCCCTchr SQ070_Hic1_0Hic1 TAGGTTGGGT TACTTCCTACCchr SQ071_Hic1_0Hic1 GGGTTTTTTTTCCAACTACCTAchr SQ072_Hic1_0Hic1 TTTGGGGTTTTCCCCCAATTTCchr SQ073_Hic1_0Hic1 GTTTTTGTTTT CAACAACCACCchr SQ074_Cdkn2 Cdkn2b TAGTATTAGAGAAAAACCATTTchr SQ075_Cdkn2 Cdkn2b GGTTTGTGGTAATTCCAAACTAchr SQ076_Cdkn2 Cdkn2b TTATTGGGTTTCACACAACCAAchr SQ077_Cdkn2 Cdkn2b TTTGTTGAGTGTCCCCTCTAAAchr SQ078_Rassf1Rassf1 TAGTAGTGGT CAAAAACAAA chr SQ079_Rassf1Rassf1 GGTTGGAGAATAAAAATTAACchr SQ080_Rassf1Rassf1 TTTTATTTTTTTCCTAAAACAACchr SQ081_Rassf1Rassf1 AATTGATTATTCCCAACAAATAchr SQ082_Dapk1Dapk1 GGGTGTGGGGCCCCTTCCTAAchr SQ083_Dapk1Dapk1 TTTTTGGGTTTTCTAAACTAAAchr SQ084_Dapk1Dapk1 TTAGAGAAGGCCCCAACCTAAchr SQ085_Dapk1Dapk1 AGTTTAGGTTGAATCCTTAAATchr SQ086_Cdh1_ Cdh1 TTAATTATAGACCCTCCACATAchr SQ087_Cdh1_ Cdh1 TGTTTTTGTTGACCTTCTACAAchr SQ088_Cdh1_ Cdh1 GGATATTTGG CCTTCTTCCAAchr SQ089_Cdh1_ Cdh1 TTTAATTTTTTTCCTACAATTCCchr SQ090_Mgmt Mgmt AGTTTTAGGTTCAATACCCCAAchr SQ091_Mgmt Mgmt TGTTTGAGTATTCTAAAATAAAchr SQ092_Chfr_0Chfr TTTTGGGTTTTTTTAAATCCCTchr SQ093_Chfr_0Chfr GAAGAAGTTT CAACAAAATA chr SQ094_Nespa Nespas DMR TTGGATTTTTTAAAACCTCCAAchr SQ095_Nespa Nespas DMR GGTGTGAGAGAACCCCCATAAchr SQ096_Nespa Nespas DMR TGGGGGTTTTTTAAATCTCAACchr SQ097_Nespa Nespas DMR GTGGGTTAGT ATCTAACATATchr SQ098_Nespa Nespas DMR TTTTTTTTAGGCCCCTCCTCCT chr SQ099_Nespa Nespas DMR GGGATTTGTA TTTTCTCAAAAchr SQ100_Nespa Nespas DMR GGGTATATTG ACCCCAACCCAchr SQ101_Nespa Nespas DMR TAGGTTAGTTAAAAATCCCTAAchr SQ102_Nespa Nespas DMR GTTAAGGTAA AAACAAAAAA chr SQ103_Nespa Nespas DMR GAGAAGGTTT AAAAAAAACA chr SQ104_Peg3.DPeg3 DMR GGTGTATGTTGAAAAACCCTAAchr SQ105_Peg3.DPeg3 DMR TTTTTTGTTAGAAACTACATCCchr SQ106_Peg3.DPeg3 DMR GGGTGTATGT TCCCCCTTTTC chr SQ107_Peg3.DPeg3 DMR GGAGAGATGTACCTTATCAATchr SQ108_Peg3.DPeg3 DMR AGAGGATTTT CATACTACAAAchr SQ109_Peg3.DPeg3 DMR GATTTTGTTTGCCACCAACCCAchr SQ110_H19.D H19 DMR AGTTTTAAGGTAACTCATAAATchr SQ111_H19.D H19 DMR TGAAGGAGTTCCCAAAATCACchr SQ112_H19.D H19 DMR TTTTGGGATATCCAAAAACAA chr SQ113_H19.D H19 DMR GGGGTTTGAGTAAAAACACCTchr SQ114_H19.D H19 DMR TTATGATTATGCCCAAATTCAAchr SQ115_H19.D H19 DMR ATAAGGGTTA TTAAAAAATCCchr
20 SQ116_H19.D H19 DMR GAGGGGGTTTCAAAAATACA chr SQ117_H19.D H19 DMR GTGGTAGGATAACCCCCTCCAchr SQ118_H19.D H19 DMR TTGGAATTTATCATAAACCCCTchr SQ119_H19.D H19 DMR TAAGGAGATT AAAAAAACTCAchr
21 List of probes used for RNA FISH analysis of Dnmt3b mrna expression Probes are numbered according to their position on the Dnmt3b mrna starting at the 5 position. The second number indicates the CG content of the probe in %. The third number indicates the position of the probe on the target mrna. 1,45,8,attcagatgtctgctgtctc 2,45,46,ataatgcactcctcataccc 3,45,69,ggtcactgaagttcccatta 4,45,208,taattcagaaggctggagac 5,45,245,atcatctctgtctccatctc 6,45,267,agccattcccatcatctact 7,45,293,ggtgagctttggcattagaa 8,45,492,ttgctgaagatgatgctcga 9,45,538,acttcttccatgaagtcgac 10,45,574,aagtcaactgatggggtact 11,45,606,tatccataccctcctgatct 12,45,653,atactctgtgctgtctccat 13,45,684,ggtcacctattccaaactct 14,45,714,aggagaagcccttgatcttt 15,45,808,aacttgccatcaccaaacca 16,45,830,tttgtcagcagagatctcag 17,45,865,ttaaagtgctggctgaacag 18,45,887,cagcttattgaaggtagcca 19,45,911,gtacatggccttcctataag 20,45,1063,tgcttcttgttgggtttgag 21,45,1089,gcaccttcgacttattaacc 22,45,1111,aagttcctactgtctgaacg 23,45,1143,ttcgacttttgttctcgcgt 24,45,1170,aagcagcagagtcattggtt
22 25,45,1206,tatttgtcttgaggcgcttg 26,45,1273,ttggtgacttcagaagccat 27,45,1303,aaacagcggtcttccagatt 28,45,1327,acagggttcttctttccaca 29,45,1398,tgtagaagagctctaggaag 30,45,1420,tgatagccgtcctcatcata 31,45,1488,atctgcagcagcttgtgtta 32,45,1626,tgttccaatctttcctgcgt 33,45,1650,tagtgaagaagtcttgcagg 34,45,1672,aattcttccaggtcaggatc 35,45,1703,aattgctgggtacaacttgg 36,45,1732,actctaatgggcctcctttt 37,45,1761,ccgttgcaattccatcaaac 38,45,1783,aactccttgagcaccaagta 39,45,1813,gaggcaatgtacttttccac 40,45,1852,ttaacagttcccacagcgat 41,45,1889,ccggacgtcattgacatatt 42,45,1923,ggccccactcttcaatattt 43,45,1965,agagatcattgcatgggctt 44,45,1997,atataaacctttgcgggcag 45,45,2027,aaactcgaagaagagccttc 46,45,2049,gggtataattcagcaagtgg 47,45,2086,atccagaagaatggacggtt 48,45,2110,ttcatggccacaacattctc
23 List of probes used for RNA FISH analysis of Lgr5 mrna expression Probes are numbered according to their position on the LGr5 mrna starting at the 5 position. The second number indicates the CG content of the probe in %. The third number indicates the position of the probe on the target mrna. 1,45,208,ttcatactgaggtccaggta 2,45,265,aactcttctaggaagcagag 3,45,287,caaagcatttccagcaagac 4,45,338,aagcactttgaggctgtgaa 5,45,391,aaattctgtagcgcttcctc 6,45,497,attgtcatctagccacaggt 7,45,534,aacttctgaaagcctggaca 8,45,574,attttgttcagggccaaggt 9,45,599,aaaggcgtagtctgctatgt 10,45,637,ttatggagatgcagaaccac 11,45,670,aagcatttctttcccaggga 12,45,701,atctaaagtctccaggctgt 13,45,733,gtggggaattcatcaaggtt 14,45,755,gttggagagtgtcttgattg 15,45,778,ctgtggaatcctagttcctt 16,45,800,cggtattgacctgatgttgt 17,45,832,ataagagaagggttgcctac 18,45,857,ggggttgtcatagaagtgta 19,45,888,gctgaaaagcagatactcca 20,45,911,cagtgttcttagttcaggca 21,45,942,attcagtaatgtgcgaggca 22,45,987,ttaaagtcagactctccagg 23,45,1009,agagatgagatctttgctcc
24 24,45,1038,taggtaactgatcacagacg 25,45,1060,gacaaatctagcacttggag 26,45,1083,gtaagtcttcgagtaggttg 27,45,1105,ttttggcagcctgacaaact 28,45,1128,gcctcaggtcaattttctga 29,45,1166,ctgaaaagtgctgcccttaa 30,45,1188,gagatcggaggttaaacaac 31,45,1230,cattggggtgaatgatagca 32,45,1252,agagacggcaacgtagaaaa 33,45,1278,gattggatgataggtccaac 34,45,1314,aaccatgtaacccagtcaca 35,45,1345,gctcggttccctgttaattt 36,45,1367,agatggtatcaggctctgta 37,45,1389,tcttgagctctgggaagttt 38,45,1413,ggtaagcagatggcatttct 39,45,1449,tatagacattctcacacccc 40,45,1479,cgtcgtctttattccattgg 41,45,1504,ttatgaaggtcgtccacact 42,45,1527,cttgaaataacccagcgtct 43,45,1559,taggaaatcttcaaggtccc 44,45,1581,tcaggtcttcctcaaagtca 45,45,1650,taccaaataggtgctcacag 46,45,1736,agttctgaacacggtcaaag 47,45,1764,gcagctttatggaagagatg 48,45,1793,aatgtccactaccgcgatta
Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research and Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA.
 Eveline J. Steine, 1 Mathias Ehrich, 2 George W. Bell, 1 Arjun Raj, 3 Seshamma Reddy, 1 Alexander van Oudenaarden, 3 Rudolf Jaenisch, 1 and Heinz G. Linhart 1,4,5 1 Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research
Eveline J. Steine, 1 Mathias Ehrich, 2 George W. Bell, 1 Arjun Raj, 3 Seshamma Reddy, 1 Alexander van Oudenaarden, 3 Rudolf Jaenisch, 1 and Heinz G. Linhart 1,4,5 1 Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research
Genes methylated by DNA methyltransferase 3b are similar in mouse intestine and human colon cancer
 Genes methylated by DNA methyltransferase 3b are similar in mouse intestine and human colon cancer The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Genes methylated by DNA methyltransferase 3b are similar in mouse intestine and human colon cancer The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Detection and differential diagnosis of colon cancer by a cumulative analysis of promoter methylation Qiong Yang 1,3*, Ying Dong 2,3, Wei Wu 1, Chunlei Zhu 1, Hui Chong 1, Jiangyang
Supplementary Information Detection and differential diagnosis of colon cancer by a cumulative analysis of promoter methylation Qiong Yang 1,3*, Ying Dong 2,3, Wei Wu 1, Chunlei Zhu 1, Hui Chong 1, Jiangyang
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Figure 1. Growth characteristics of GLI2 expressing cells in monolayer culture (A) Expression of GLI2 and downstream targets GLI1 and PTCH in control
 Figure 1. Growth characteristics of GLI2 expressing cells in monolayer culture (A) Expression of GLI2 and downstream targets GLI1 and PTCH in control HaCaT Tet, uninduced HaCaT GLI2 and induced HaCaT GLI2
Figure 1. Growth characteristics of GLI2 expressing cells in monolayer culture (A) Expression of GLI2 and downstream targets GLI1 and PTCH in control HaCaT Tet, uninduced HaCaT GLI2 and induced HaCaT GLI2
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Plasma-Seq conducted with blood from male individuals without cancer.
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Plasma-Seq conducted with blood from male individuals without cancer. Copy number patterns established from plasma samples of male individuals without cancer
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Plasma-Seq conducted with blood from male individuals without cancer. Copy number patterns established from plasma samples of male individuals without cancer
For the 5 GATC-overhang two-oligo adaptors set up the following reactions in 96-well plate format:
 Supplementary Protocol 1. Adaptor preparation: For the 5 GATC-overhang two-oligo adaptors set up the following reactions in 96-well plate format: Per reaction X96 10X NEBuffer 2 10 µl 10 µl x 96 5 -GATC
Supplementary Protocol 1. Adaptor preparation: For the 5 GATC-overhang two-oligo adaptors set up the following reactions in 96-well plate format: Per reaction X96 10X NEBuffer 2 10 µl 10 µl x 96 5 -GATC
MSI positive MSI negative
 Pritchard et al. 2014 Supplementary Figure 1 MSI positive MSI negative Hypermutated Median: 673 Average: 659.2 Non-Hypermutated Median: 37.5 Average: 43.6 Supplementary Figure 1: Somatic Mutation Burden
Pritchard et al. 2014 Supplementary Figure 1 MSI positive MSI negative Hypermutated Median: 673 Average: 659.2 Non-Hypermutated Median: 37.5 Average: 43.6 Supplementary Figure 1: Somatic Mutation Burden
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Results. Abstract. Introduc4on. Conclusions. Methods. Funding
 . expression that plays a role in many cellular processes affecting a variety of traits. In this study DNA methylation was assessed in neuronal tissue from three pigs (frontal lobe) and one great tit (whole
. expression that plays a role in many cellular processes affecting a variety of traits. In this study DNA methylation was assessed in neuronal tissue from three pigs (frontal lobe) and one great tit (whole
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
SALSA MS-MLPA KIT ME011-A1 Mismatch Repair genes (MMR) Lot 0609, 0408, 0807, 0407
 SALSA MS-MLPA KIT ME011-A1 Mismatch Repair genes (MMR) Lot 0609, 0408, 0807, 0407 The Mismatch Repair (MMR) system is critical for the maintenance of genomic stability. MMR increases the fidelity of DNA
SALSA MS-MLPA KIT ME011-A1 Mismatch Repair genes (MMR) Lot 0609, 0408, 0807, 0407 The Mismatch Repair (MMR) system is critical for the maintenance of genomic stability. MMR increases the fidelity of DNA
Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin
 Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Analysis of shotgun bisulfite sequencing of cancer samples
 Analysis of shotgun bisulfite sequencing of cancer samples Kasper Daniel Hansen Postdoc with Rafael Irizarry Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Brixen, July 1st, 2011 The
Analysis of shotgun bisulfite sequencing of cancer samples Kasper Daniel Hansen Postdoc with Rafael Irizarry Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Brixen, July 1st, 2011 The
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Aberrant CpG Island Hypermethylation in Pediatric Gastric Mucosa in Association With Helicobacter pylori Infection
 Aberrant CpG Island Hypermethylation in Pediatric Gastric Mucosa in Association With Helicobacter pylori Infection So-Hyun Shin, MSc; Seog-Yun Park, MD; Jae-Sung Ko, MD; Nayoung Kim, MD; Gyeong Hoon Kang,
Aberrant CpG Island Hypermethylation in Pediatric Gastric Mucosa in Association With Helicobacter pylori Infection So-Hyun Shin, MSc; Seog-Yun Park, MD; Jae-Sung Ko, MD; Nayoung Kim, MD; Gyeong Hoon Kang,
gliomas. Fetal brain expected who each low-
 Supplementary Figure S1. Grade-specificity aberrant expression of HOXA genes in gliomas. (A) Representative RT-PCR analyses of HOXA gene expression in human astrocytomas. Exemplified glioma samples include
Supplementary Figure S1. Grade-specificity aberrant expression of HOXA genes in gliomas. (A) Representative RT-PCR analyses of HOXA gene expression in human astrocytomas. Exemplified glioma samples include
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
The silence of the genes: clinical applications of (colorectal) cancer epigenetics
 The silence of the genes: clinical applications of (colorectal) cancer epigenetics Manon van Engeland, PhD Dept. of Pathology GROW - School for Oncology & Developmental Biology Maastricht University Medical
The silence of the genes: clinical applications of (colorectal) cancer epigenetics Manon van Engeland, PhD Dept. of Pathology GROW - School for Oncology & Developmental Biology Maastricht University Medical
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION GO term analysis of differentially methylated SUMIs. GO term analysis of the 458 SUMIs with the largest differential methylation between human and chimp shows that they are more
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION GO term analysis of differentially methylated SUMIs. GO term analysis of the 458 SUMIs with the largest differential methylation between human and chimp shows that they are more
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region
 Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
For Research Use Only Ver
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Miniprep Kit Catalog Nos. R1054 & R1055 Highlights High-quality total RNA (including small RNAs) from a wide range of samples. You can opt to isolate small and large RNAs in
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Miniprep Kit Catalog Nos. R1054 & R1055 Highlights High-quality total RNA (including small RNAs) from a wide range of samples. You can opt to isolate small and large RNAs in
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
 Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
iplex genotyping IDH1 and IDH2 assays utilized the following primer sets (forward and reverse primers along with extension primers).
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Methods iplex genotyping IDH1 and IDH2 assays utilized the following primer sets (forward and reverse primers along with extension primers). IDH1 R132H and R132L Forward:
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Methods iplex genotyping IDH1 and IDH2 assays utilized the following primer sets (forward and reverse primers along with extension primers). IDH1 R132H and R132L Forward:
For Research Use Only Ver
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Miniprep Kit Catalog Nos. R1054 & R1055 Highlights High-quality total RNA (including small RNAs) from a wide range of samples. You can opt to isolate small and large RNAs in
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Miniprep Kit Catalog Nos. R1054 & R1055 Highlights High-quality total RNA (including small RNAs) from a wide range of samples. You can opt to isolate small and large RNAs in
R. Piazza (MD, PhD), Dept. of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca EPIGENETICS
 R. Piazza (MD, PhD), Dept. of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca EPIGENETICS EPIGENETICS THE STUDY OF CHANGES IN GENE EXPRESSION THAT ARE POTENTIALLY HERITABLE AND THAT DO NOT ENTAIL A
R. Piazza (MD, PhD), Dept. of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca EPIGENETICS EPIGENETICS THE STUDY OF CHANGES IN GENE EXPRESSION THAT ARE POTENTIALLY HERITABLE AND THAT DO NOT ENTAIL A
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Chromatin-Based Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chromatin-Based Regulation of Gene Expression.George J. Quellhorst, Jr., PhD.Associate Director, R&D.Biological Content Development Topics to be Discussed Importance of Chromatin-Based Regulation Mechanism
Chromatin-Based Regulation of Gene Expression.George J. Quellhorst, Jr., PhD.Associate Director, R&D.Biological Content Development Topics to be Discussed Importance of Chromatin-Based Regulation Mechanism
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread
 Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in
 Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated
 Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Measuring DNA Methylation with the MinION. Winston Timp Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 12/1/16
 Measuring DNA Methylation with the MinION Winston Timp Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 12/1/16 Epigenetics: Modern Modern Definition of epigenetics involves heritable changes
Measuring DNA Methylation with the MinION Winston Timp Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 12/1/16 Epigenetics: Modern Modern Definition of epigenetics involves heritable changes
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1: Quality assessment of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-derived DNA and nuclei. (a) Multiplex PCR analysis of unrepaired and repaired bulk FFPE gdna from
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1: Quality assessment of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-derived DNA and nuclei. (a) Multiplex PCR analysis of unrepaired and repaired bulk FFPE gdna from
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
Evaluation of Markers for CpG Island Methylator Phenotype (CIMP) in Colorectal Cancer by a Large Population-Based Sample
 JMD CME Program Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, Vol. 9, No. 3, July 2007 Copyright American Society for Investigative Pathology and the Association for Molecular Pathology DOI: 10.2353/jmoldx.2007.060170
JMD CME Program Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, Vol. 9, No. 3, July 2007 Copyright American Society for Investigative Pathology and the Association for Molecular Pathology DOI: 10.2353/jmoldx.2007.060170
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
SOPten flox/flox (KO) Pten flox/flox (WT) flox allele 6.0 kb. Pten. Actin. ! allele 2.3 kb. Supplementary Figure S1. Yanagi, et al.
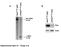 s1 A Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () flox allele 6. kb B Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () Pten Actin! allele 2.3 kb Supplementary Figure S1. Yanagi, et al. A B BrdU BrdU positive cells ( ) 3
s1 A Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () flox allele 6. kb B Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () Pten Actin! allele 2.3 kb Supplementary Figure S1. Yanagi, et al. A B BrdU BrdU positive cells ( ) 3
Methylation patterns in ejaculated sperm from Nellore-Angus crossbred bulls
 Methylation patterns in ejaculated sperm from Nellore-Angus crossbred bulls M. R. Prause 1, G. Wang 1, & C. A. Gill 1 1 Texas A&M University, Department of Animal Science, College Station, TX 77843, USA
Methylation patterns in ejaculated sperm from Nellore-Angus crossbred bulls M. R. Prause 1, G. Wang 1, & C. A. Gill 1 1 Texas A&M University, Department of Animal Science, College Station, TX 77843, USA
Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum...1. Trademarks: HiLyte Fluor (AnaSpec, Inc.)
 Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
Iso-Seq Method Updates and Target Enrichment Without Amplification for SMRT Sequencing
 Iso-Seq Method Updates and Target Enrichment Without Amplification for SMRT Sequencing PacBio Americas User Group Meeting Sample Prep Workshop June.27.2017 Tyson Clark, Ph.D. For Research Use Only. Not
Iso-Seq Method Updates and Target Enrichment Without Amplification for SMRT Sequencing PacBio Americas User Group Meeting Sample Prep Workshop June.27.2017 Tyson Clark, Ph.D. For Research Use Only. Not
Supplementary Figure 1. Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints
 Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
Dnmt3b promotes tumorigenesis in vivo by gene-specific de novo methylation and transcriptional silencing
 Dnmt3b promotes tumorigenesis in vivo by gene-specific de novo methylation and transcriptional silencing Heinz G. Linhart, 1 Haijiang Lin, 1,6 Yasuhiro Yamada, 2 Eva Moran, 1 Eveline J. Steine, 1 Sumita
Dnmt3b promotes tumorigenesis in vivo by gene-specific de novo methylation and transcriptional silencing Heinz G. Linhart, 1 Haijiang Lin, 1,6 Yasuhiro Yamada, 2 Eva Moran, 1 Eveline J. Steine, 1 Sumita
Supplementary material. Supplementary Figure legends
 Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice
 Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols
 Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative
Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative
PRADER WILLI/ANGELMAN
 SALSA MS-MLPA probemix ME028-B2 PRADER WILLI/ANGELMAN Lot B2-0811: As compared to version B1 (lot B1-0609, B1-1108), the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME
SALSA MS-MLPA probemix ME028-B2 PRADER WILLI/ANGELMAN Lot B2-0811: As compared to version B1 (lot B1-0609, B1-1108), the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME
Supplementary methods:
 Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 A S100A4: SFLGKRTDEAAFQKLMSNLDSNRDNEVDFQEYCVFLSCIAMMCNEFFEGFPDK Overlap: SF G DE KLM LD N D VDFQEY VFL I M N FF G PD S100A2: SFVGEKVDEEGLKKLMGSLDENSDQQVDFQEYAVFLALITVMCNDFFQGCPDR
Supplemental Figure 1 A S100A4: SFLGKRTDEAAFQKLMSNLDSNRDNEVDFQEYCVFLSCIAMMCNEFFEGFPDK Overlap: SF G DE KLM LD N D VDFQEY VFL I M N FF G PD S100A2: SFVGEKVDEEGLKKLMGSLDENSDQQVDFQEYAVFLALITVMCNDFFQGCPDR
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4 Related Products..
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA MidiPrep Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA MidiPrep Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Supplementary webappendix
 Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Kratz JR, He J, Van Den Eeden SK, et
Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Kratz JR, He J, Van Den Eeden SK, et
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
EGFR shrna A: CCGGCGCAAGTGTAAGAAGTGCGAACTCGAGTTCGCACTTCTTACACTTGCG TTTTTG. EGFR shrna B: CCGGAGAATGTGGAATACCTAAGGCTCGAGCCTTAGGTATTCCACATTCTCTT TTTG
 Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Modern Epigenomics. DNA Methylomics
 Modern Epigenomics DNA Methylomics Ting Wang Department of Genetics Center for Genome Sciences and Systems Biology Washington University Dragon Star 2012 Changchun, China July 2, 2012 Informa(on Email:
Modern Epigenomics DNA Methylomics Ting Wang Department of Genetics Center for Genome Sciences and Systems Biology Washington University Dragon Star 2012 Changchun, China July 2, 2012 Informa(on Email:
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Figures. T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ
 Supplementary Figures T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ Qing Yu, Archna Sharma, Sun Young Oh, Hyung-Geun Moon, M. Zulfiquer Hossain, Theresa M. Salay,
Supplementary Figures T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ Qing Yu, Archna Sharma, Sun Young Oh, Hyung-Geun Moon, M. Zulfiquer Hossain, Theresa M. Salay,
Instructions for Use. RealStar Influenza S&T RT-PCR Kit /2017 EN
 Instructions for Use RealStar Influenza S&T RT-PCR Kit 3.0 01/2017 EN RealStar Influenza S&T RT-PCR Kit 3.0 For research use only! (RUO) 163003 INS-163000-EN-S02 96 01 2017 altona Diagnostics GmbH Mörkenstr.
Instructions for Use RealStar Influenza S&T RT-PCR Kit 3.0 01/2017 EN RealStar Influenza S&T RT-PCR Kit 3.0 For research use only! (RUO) 163003 INS-163000-EN-S02 96 01 2017 altona Diagnostics GmbH Mörkenstr.
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by
 The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance.! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014
 Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
(Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) (Supplemental Fig. 1A). A 5.4-kb EcoRI fragment
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Supplemental Methods Generation of RyR2-S2808D Mice Murine genomic RyR2 clones were isolated from a 129/SvEvTacfBR λ-phage library (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) (Supplemental Fig.
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Supplemental Methods Generation of RyR2-S2808D Mice Murine genomic RyR2 clones were isolated from a 129/SvEvTacfBR λ-phage library (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) (Supplemental Fig.
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3
 Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
Pharmacologic inhibition of histone demethylation as a therapy for pediatric brainstem glioma
 Supplementary information for: Pharmacologic inhibition of histone demethylation as a therapy for pediatric brainstem glioma Rintaro Hashizume 1, Noemi Andor 2, Yuichiro Ihara 2, Robin Lerner 2, Haiyun
Supplementary information for: Pharmacologic inhibition of histone demethylation as a therapy for pediatric brainstem glioma Rintaro Hashizume 1, Noemi Andor 2, Yuichiro Ihara 2, Robin Lerner 2, Haiyun
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS
 Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Targeted Agent and Profiling Utilization Registry (TAPUR ) Study. February 2018
 Targeted Agent and Profiling Utilization Registry (TAPUR ) Study February 2018 Precision Medicine Therapies designed to target the molecular alteration that aids cancer development 30 TARGET gene alterations
Targeted Agent and Profiling Utilization Registry (TAPUR ) Study February 2018 Precision Medicine Therapies designed to target the molecular alteration that aids cancer development 30 TARGET gene alterations
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4059 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4059 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric)
EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4059 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric)
Supplementary Data. (continued)
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Gating strategy for Figure 1. Splenocytes were gated for dimension and for positivity to the different markers representing different cell populations. (A) B cells,
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Gating strategy for Figure 1. Splenocytes were gated for dimension and for positivity to the different markers representing different cell populations. (A) B cells,
EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
 EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center Seattle, WA 98109
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-10-1-0711 TITLE: Transgenerational Radiation Epigenetics PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Christopher J. Kemp, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center Seattle,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-10-1-0711 TITLE: Transgenerational Radiation Epigenetics PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Christopher J. Kemp, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center Seattle,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: Chemokine receptor expression profiles of CCR6 + and CCR6 - CD4 + IL-17A +/ex and Treg cells. Quantitative PCR analysis of chemokine receptor transcript abundance
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: Chemokine receptor expression profiles of CCR6 + and CCR6 - CD4 + IL-17A +/ex and Treg cells. Quantitative PCR analysis of chemokine receptor transcript abundance
