Supplemental Figure 1 A
|
|
|
- Ruby Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Figure FLG-ZFP89 endogenous ZFP89 CTIN 1. F9 2. F9 [S/FLG-Zfp89] 3. ESC 4. ESC [2lox/FLG-Zfp89]. Zfp89 ESC Flag-ZFP89 expression/endogenous ZFP89 expression 1 1 ECCs ESCs ChIP-seq Cell type Transgene ntibody ChIP protocol Sequencing strategy FLG-ZFP89_ECC F9 ECC Multi copy S transposon FLG-ZFP89_ESC ESC 2lox single copy insertion ZFP89_ESC ESC - FLG-ZFP89_ESC #2 ESC 2lox single copy insertion ZFP89_ESC #2 ESC - No. of called MCS peaks Mean peak enrichment Mean peak p-value Mean peak FDR (%) FLG O Geen et al. 21 Illumina, single-end E-14.6 FLG arish et al. 21 Illumina, single-end E ZFP89 (763) arish et al. 21 Illumina, single-end E FLG-ZFP89 _ECC MCS peak enrichment FLG-ZFP89 F9 ECC FLG-ZFP89 ESC (+Dox) ZFP89_763 ESC FLG-ZFP89 ESC (-Dox) Input control ESC FLG-ZFP89_ECC ChIP-seq peaks (sorted by enrichment) FLG O Geen et al. 21 SOLiD, paired-end n.d. n.d. n.d. n.d. ZFP89 (763) O Geen et al. 21 SOLiD, paired-end n.d n.d. n.d n.d C FLG-ZFP89 ESC #2 (+Dox) ZFP89_763 ESC #2 Supplemental Figure 1. () (left panel) Western blot was performed with whole cell lysates from FLG ZFP89 expressing F9 ECCs and ESCs that were used for ChIP seq analysis. Endogenous ZFP89 and FLG ZFP89 were detected using a polyclonal ZFP89 antibody (kindly provided by Stephen Goff). (right panel) Quantification of FLG ZFP89 overexpression in F9 ECCs and ESCs using ImageJ. () Summary of ZFP89 ChIP seq strategies. Peaks were called by Model based nalysis of ChIP Seq (MCS). Peak calling was not performed with FLG ZFP89_ESC #2 and ZFP89_ESC #2 data due to the lack of proper input control data. n.d.: not determined. (C) Heat maps with mapped ChIP seq reads generated by different ChIP seq strategies. Peaks were called using Model based nalysis of ChIP Seq(MCS)withFLG ZFP89_ECC data and used as reference sites (extending 1 kb up and downstream of the peak summit). The dotted line indicates the fold enrichment value that was set as threshold for strong FLG ZFP89_ECC peaks. ChIP seq with FLG antibody in uninduced 2lox [FLG Zfp89] ESCs (not expressing FLG ZFP89) was performed as negative control.
2 Supplemental Figure 2 1% 1% Proportion of ERV1 elements 9% 8% 7% 6% % 4% 3% 2% 1% % Strong FLG ZFP89 peaks Genome Other ERV1 LTRIS_Mus LTRIS_Mm MMVL3 int MMERGLN int MuRRS int RLTR6_Mm RLTR6 int Proportion of peaks with target motif 9% 8% 7% 6% % 4% 3% 2% 1% % no motif PS-pro like motif PS-pro C 6 FLG-ZFP89_ECC. FLG-ZFP89_ESC.4 ZFP89_ESC mapped read mapped read mapped read PS-pro (MmERV) non-rep peaks - 3 kb + 3kb. - 3 kb + 3kb - 3 kb + 3kb. Supplemental Figure 2. nalysis of FLG ZFP89 ChIP seq peaks. () Categorization of ERV1 elements overlapping with strong (enrichment > ) FLG ZFP89 ChIP seq peaks in F9 ECCs compared to all genomic ERV1 elements in the mouse genome. ERV1 elements were categorized according to their UCSC Repeatmasker annotation. The suffix int indicates that the repeat is an internal ERV1 sequence, all other repeats are LTR sequences. () Proportion of ChIP seq peaks that contain a perfect PS pro site or a PS pro like target motif (derived from the 1 ttop scored non repetitive FLGZFP89_ECC peaks). The 2 bp core regions of all FLG ZFP89 peaks or control regions 2 kb upstream of the ChIP seq peaks were screened for target motifs under stringency settings allowing five false hits per 1 kb. Peaks were categorized according to their enrichment over the input control. (C) NGS plots showing average FLG ZFP89_ECC, FLG ZFP89_ESC and and ZFP89_ESC ChIP seq read densities at 6 kb regions around genomic MmERV PS pro (n=93) and strong non repetitive FLG ZFP89_ECC ChIP seq peaks (n=138).
3 Supplemental Figure 3 FLG-ZFP89_ECC FLG-ZFP89_ECC Input Input Cacna1g Zfp36 chr11:94,264,99-94,339,883 chr7:29,19,398-29,167,883 FLG-ZFP89_ECC FLG-ZFP89_ECC Input Input Sos1 Serping1 chr17:8,788,6-8,891,87 chr2:84,6,23-84,617,184 Zfp36 target Sos1 target Cacna1g target PS-pro target LJ-QdMLPEnh- MoLTR PS-gln PS-pro dmlp neo MoLTR % of normalized plj-q titer Supplemental Figure 3. Non repetitive ZFP89 target sites do not induce efficient silencing of retroviral vectors. () Integrative Genome rowser(igv) view of a selection of strong FLG ZFP89_ECC peaks near gene promoters containing PS pro like target motifs with mapped FLG ZFP89_ECC ChIPseq and Input control read densities. ()(left panel) 29 bp oligos, containing PS pro like ZFP89 target motifs identified in ChIP seq peaks close to gene promoters including 11 bp downstream flanking regions, or the PS pro sequence including the 11 bp downstream region of the Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus (MLV) PS pro were inserted upstream of the dmlp promoter of the retroviral LJQdMLPEnh vector (Modin C, Pedersen FS, Duch M. 2. Lack of shielding of primer binding site silencer mediated repression of an internal promoter in a retrovirus vector by the putative insulators scs, ED 1, and HS4. J Virol 74: ). (right panel) F9 ECCs and NIH/3T3 fibroblasts were transduced in parallel with serial dilutions of retroviral particles containing the indicated ZFP89 target sequences. Viral titers (CFU/ml) for each vector were determined by counting resistant colonies after G418 selection. Viral titers in F9 cells were normalized to titers in NIH/3T3 cells and are shown relative to the normalized titer of a vector containingthe empty LJQdMLPEnh vector. Graphs show mean normalized titers as percent relative to the empty control vector (n=2, technical replicates). Error bars represent s.d.
4 Supplemental Figure 4 % of input KP1 % of input (normalized) H3K9me3 % of input (normalized) H4K2me3 F9 F9 [ps/flg- Zfp89] ±3.1 Fold change in expression F9 [ps/empty] F9 [ps/flg-zfp89] Supplemental Figure 4. Heterochromatin formation and transcriptional silencing of FLG ZFP89 target genes upon FLG ZFP89 overexpression. () ChIP qpcr analysis of FLG ZFP89 binding sites in FLG ZFP89 overexpressing F9 cells. Cross linked chromatin of F9 cells and F9 cells stably expressing FLG ZFP89 was immunoprecipitated with antibodies against KP1, H3K9me3 (bcam, ab8898) or H4K2me3 (bcam, ab93). Enrichment at target regions was determined by qpcr. Graphs show mean enrichment over input (n=3, technical replicates). Error bars represent s.d. H3K9me3 and H4K2me3 ChIP qpcr data were normalized to equal enrichment atthemest promoter, a known KP1 binding sitethatis notenriched in FLG ZFP89. () RT qpcr expression analysis of FLG ZFP89 target genes in FLG ZFP89 overexpressing F9 cells. Graphs show mean fold enrichment (n=3, technical replicates) over expression in F9cells (normalized toctin) stably transfected with an empty control vector. Error bars represent s.d.
5 Supplemental Figure mapped reads MmERV-pro MmERV-gly FLG-ZFP89_ECC mapped read VL3-pro VL3-gly FLG-ZFP89_ECC mapped reads KP1 (ESC) mapped read KP1 (ESC) mapped reads SETD1 (ESC) mapped read SETD1 (ESC).3.4 mapped reads.2.1. H3K9me3 (ESC) mapped read H3K9me3 (ESC) 1 kb 6 kb Supplemental Figure. Differential repressor binding patterns at MmERV and VL3 subgroups using different PS sequences. NGS plots show average ChIP seq read densities at 1 kb or 6 kb regions around genomic MmERV pro (n=93) and MmERV gly (n=69) (left panel), and VL3 pro (n=1) and VL3 gly (n=6) elements (right panel). Yellow rectangles indicate coding regions for retroviral proteins, red rectangles indicate LTRs. In addition to FLG ZFP89 ChIP seq data from F9 ECCs, previously published KP1 (SR accession: SRR61129), SETD1 (SR accession: SRR31683) and H3K9me3 (SR accession: SRR61121) ChIP seq data (all generated in ESCs) were re aligned to the mouse genome as described in the methods section.
6 Supplemental Figure 6 Zfp89 GT Zfp89 KO-first FLP recombination Zfp89 FL Cre recombination Zfp89 KO (-) Supplemental Figure 6. Schematic representation of Zfp89 gene trap (GT) and knock out first (KO first) alleles used to generate mutant mice. Grey rectangles represent Zfp89 exons. The two recombination steps in which the KO first allele turns into a KO ( ) allele are shown.
7 Supplemental Figure 7 1. ChIP 2. ChIP H3K9me3 H3K4me3 2. % of input % of input Enrichment at VL3-pro % of input (1. ChIP) H3K9me3 H3K4me3 IgG H3K9me3 H3K4me3 IgG 1. ChIP: H3K9me3 1. ChIP: H3K4me3 pcpgl-vl3-3 [EcoRI, sshii] CpG methylation: - + DN ladder (bp) Supplemental Figure 7. () (left panel) H3K9me3 and H3K4me3 enrichment at ERVs and the Gapdh promoter in Zfp89 MEFs after one round of ChIP. (right panel)re ChIPanalysis of H3K9me3 and H3K4me3 atvl3 pro. Chromatin immunoprecipitated with H3K9me3 or H3K4me3 specific antibodies was immunoprecipitated a second time with the indicated antibodies. Enrichment is shown as mean percentage of the corresponding input samples (n=3, technical replicates). Error bars represent s.d. () In vitro methylation of CpG free luciferase vectors. (left) Vector map of the pcggl plasmid with an inserted VL3 pro LTR element (including PS). CpG sites and restriction sites for EcoRI and sshii are indicated. The sshii site overlaps with two CpG sites and is inhibited by CpG methylation. (right) Unmethylated and CpG methylated plasmids were digested with EcoRI and sshii and run on an agarose gel to visualize fragment lengths. The two larger fragments of the digested unmethylated plasmid are both about 2 kb long and therefore appear as a single bond.
8 Supplemental Figure 8 ERV expression (U) VL3-pro MmERV-pro +/+ +/+ +/+ +/+ +/+ +/+ ESC MEF Relative ERV expression E9. embryos +/+ +/+ -/+ -/+ -/- -/- VL3-pro MmERV-pro C D E Relative ERV expression Luciferase activity (U) E3. embryos +/+ -/- VL3-Pro Zfp89 KP1 CTIN MEF ESC ESC MEF ipsc ZFP89 CTIN WT ESC WT MEF WT ipsc ipsc Supplemental Figure 8. () RT qpcr analysis of MmERV pro and VL3 pro expression in Zfp89 GT ESCs and MEFs. ERV expression was normalized to Hprt and is shown in arbitrary units (U). Graphs show mean expression (n=3, technical replicates). Error bars represent s.d. () VL3 pro expression in Zfp89 knock out embryos. Two E9. littermate embryos of each genotype were analyzed. Values represent mean expression (normalized to Hprt) relative to one WT embryo (n=3, technical replicates). Error bars represent s.d. (C) Five to six preimplantation embryos per genotype were harvested at E3. and pooled for RN purification and RT qpcr analysis. Values represent mean expression (normalized to Gapdh) relative to Zfp89 +/+ embryos (n=3, technical replicates). Error bars represent s.d. (D) (left panel) Western blot with whole cell lysates of Zfp89 and ESCs, MEFs and ipscs using antibodies against KP1 or CTIN. (right panel) Western blot with whole cell lysates of WT ESCs, MEFs and ipscs using antibodies against ZFP89 (763) or CTIN. Cell lysates of Zfp89 ipscs were blotted to confirm the identity of the ZFP89 band. (E) Promoter activity of subcloned VL3 pro and MmERV pro LTR elements (including PS pro) in indicated cell types using dual luciferase assay in transiently transfected cells. Luciferase activity was normalized to Renilla Luciferase activity of a cotransfected plasmid. ssay was performed in triplicates. Error bars represent s.d. LTR sequences are shown in Supplemental Fig. 9.
9 Supplemental Figure 9 Supplemental Figure 9. lignment of VL3 pro and MmERV pro LTR sequences that have been tested for transcriptional activity (Supplemental Fig. 8E).
10 Supplemental Figure 1 C FLG F9 F9 [S/FLG-Zfp89] ESC ESC [2lox/FLG-Zfp89] MEF [Ctrl] MEF[S/FLG-Zfp89] MEF [Ctrl] MEF [S/FLG-Zfp89] Flag-ZFP89 Endog. ZFP89 ESC [2lox/FLG-Zfp89] ESC MEF [Ctrl] MEF [FLG-Zfp89] MEF [Ctrl] MEF [FLG-Zfp89] Input IP FLG FLG-ZFP89: KP1 FLG CTIN CTIN D E % of input VL3-pro FLG [Ctrl] [S/FLG-Zfp89] Gapdh PS-gly / PS-pro titer [Ctrl] [S/FLG- Zfp89] F G 8 ESC H3K9me3 3. MEF H3K9me3 % of input /+ [Ctrl] [Ctrl] [S/FLG-Zfp89] % of input [Ctrl] [Ctrl] [S/FLG-Zfp89] VL3-pro Gapdh. VL3-pro Gapdh Supplemental Figure 1. () Western blot with whole cell lysates of FLG ZFP89 overexpressing F9 and ESCs and FLG ZFP89 complemented MEFs using antibodies against the FLG epitope or CTIN. () Western blot with whole cell lysates of FLG ZFP89 overexpressing ESCs and FLG ZFP89 complemented MEFs using antibodies against endogenous ZFP89 (kindly provided by Stephen Goff) or CTIN. (C) Wholecell lysates from Zfp89 MEFs stably transfected with S/FLG Zfp89 (+) or an empty control vector ( ) were immunoprecipitated with FLG antibody. 1% input controls and FLG immunoprecipitates were analyzed by western blot using anti FLG and anti KP1 antibodies. (D) ChIPqPCR analysis of FLG ZFP89 recruitment to VL3 pro ERVs in FLG ZFP89 complemented Zfp89 MEFs. Enrichment is shown as mean percentage of input DN (n=3, technical replicates). Error bars represent s.d. (E) Control and FLG ZFP89 complemented Zfp89 MEFs were transduced with retroviral vectors containing PS pro or the repression escape mutant PS gly upstream of a hygromycin resistance gene and treated with 2 µg/ml hygromycin for ten days to determine viral titers (CFU/ml). Graphs show the mean ratios of PS gly/ps pro viral titers as determined in three replicates. Error bars represent s.d. (F) ChIP qpcr analysis of H3K9me3 at VL3 pro elements in FLG ZFP89 complemented Zfp89 MEFs. Enrichment is shown as mean percentage of input DN (n=3, technical replicates). Error bars represent s.d. (G) NChIP qpcr analysis of H3K9me3 at VL3 pro elements in FLG ZFP89 complemented Zfp89 ESCs. Enrichment is shown as mean percentage of input DN (n=3,technical replicates). Error bars represent s.d.
11 Supplemental Figure 11 Zfp89 homology (%) DN Protein ds/dn ds/dn (specificity aa) M. spicilegus M. spretus M. caroli M. dunni M. pahari C. griseus N. galili Supplemental Figure 11. Conservation of the DN binding domain of putative ZFP89 orthologues. (top) Homology and synonymous to nonsynonymous mutation ratios (ds/dn) of the 79 bp DN binding region of Zfp89 in wild Mus species relative to M. musculus. (bottom) lignment of translated ZFP89 DN binding domains identified in Muroidea species. The positions of the seven C2H2 zinc finger domains are marked by black rectangles. The amino acids known to be directly responsible for binding specificity (specificity aa) are marked by asterisks on top of the alignment. ZFP89 DN binding domains of Mus species were sequenced from genomic DN samples. The putative ZFP89 DN binding sequences of C. griseus (NCI accession: XP_3164) and N. galili (Genank: JO2639) were identified by LST searches. The JO2639 sequence contains a single nucleotide deletion in the fourth zinc finger domain, causing a frame shift mutation. The deletion, located after six consecutive adenine bases and possibly theresult of a sequencing error was manually corrected to reconstruct the ORF.
12 Supplemental Figure 12 Gene base Mean base log2fold change Spleen lfcse pvalue padj base mean base log2fold change MEF lfcse pvalue padj Zfp E E E-26 7.E-23 Tdrd E-7 9.8E E-8 2.6E- Gm E E E-1 1.E+ Dnahc7a E E E-7 3.E-4 spleen RN-seq WT spleen MEF MEF H3K9me3 ESC ChIP-seq H3K9me3 WT ESC ZFP89 ESC #2 FLG-ZFP89 ESC #2 FLG-ZFP89 F9 ECC Refseq genes LTR repeats Dnah7a spleen RN-seq WT spleen MEF MEF H3K9me3 ESC ChIP-seq H3K9me3 WT ESC ZFP89 ESC #2 FLG-ZFP89 ESC #2 FLG-ZFP89 F9 ECC Refseq genes LTR repeats Cyp4f37 Supplemental Figure 12. () Statistical analysis of differential gene expression in Zfp89 GT mice. RN seq data from Zfp89 and MEFs or +/+ and spleen samples (two independent MEF lines/mice per genotype) were analysed using DESeq (nders S, Huber W. 21. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome iol 11: R16.). () RN seq and ChIP seqreaddensityatdnah7a (top) andcyp4f37 (bottom).
13 Supplementary methods: Re ChIP Chromatin was harvested from cross linked Zfp89 MEFs as described previously (arish et al. 21). riefly, chromatin from cells was immunoprecipitated with 1 µg H3K9me3 (abcam ab8898), 1 µg H3K4me3 (abcam ab88). fter washing, immunoprecipitated chromatin was eluted with Re ChIP IT elution buffer (Re ChIP IT kit, ctive Motif), desalted, and immunoprecipitated for the second time with 1 µg H3K9me3 (abcam ab8898), 1 µg H3K4me3 (abcam ab88) or 1 µg unspecific IgG according to the manufacturers protocol. Target enrichment was determined by qpcr. Immunoprecipitation (IP) CellswerelysedinRIPbufferandwholecellextractswerediluted1:1inIPbuffer(1mM Tris HCl [ph 7.]; 1% NP4; 1 mm NaCl) and incubated with Flag garose beads (Sigma) over night at 4 C. eads were washed times with IP buffer before western blot analysis.
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3731
 Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
S1a S1b S1c. S1d. S1f S1g S1h SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. - si sc Il17rd Il17ra bp. rig/s IL-17RD (ng) -100 IL-17RD
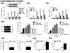 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Sirt1 Hmg20b Gm (0.17) 24 (17.3) 877 (857)
 3 (0.17) 24 (17.3) Sirt1 Hmg20 Gm4763 877 (857) c d Suppl. Figure 1. Screen validation for top candidate antagonists of Dot1L (a) Numer of genes with one (gray), two (cyan) or three (red) shrna scored
3 (0.17) 24 (17.3) Sirt1 Hmg20 Gm4763 877 (857) c d Suppl. Figure 1. Screen validation for top candidate antagonists of Dot1L (a) Numer of genes with one (gray), two (cyan) or three (red) shrna scored
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S2
 Supplementary Figure S A) The blots shown in Figure B were qualified by using Gel-Pro analyzer software (Rockville, MD, USA). The ratio of LC3II/LC3I to actin was then calculated. The data are represented
Supplementary Figure S A) The blots shown in Figure B were qualified by using Gel-Pro analyzer software (Rockville, MD, USA). The ratio of LC3II/LC3I to actin was then calculated. The data are represented
FIG S1 Examination of eif4b expression after virus infection. (A) A549 cells
 Supplementary Figure Legends FIG S1 Examination of expression after virus infection. () 549 cells were infected with herpes simplex virus (HSV) (MOI = 1), and harvested at the indicated times, followed
Supplementary Figure Legends FIG S1 Examination of expression after virus infection. () 549 cells were infected with herpes simplex virus (HSV) (MOI = 1), and harvested at the indicated times, followed
Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent Protein.
 prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
p.r623c p.p976l p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r2922w p.r2370h p.c1201y p.a868v p.s952* RING_C BP PHD Cbp HAT_KAT11
 ARID2 p.r623c KMT2D p.v650fs p.p976l p.r2922w p.l1212r p.d1400h DNA binding RFX DNA binding Zinc finger KMT2C p.a51s p.d372v p.c1103* p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r4586h PHD/ RING DHHC/ PHD PHD FYR N
ARID2 p.r623c KMT2D p.v650fs p.p976l p.r2922w p.l1212r p.d1400h DNA binding RFX DNA binding Zinc finger KMT2C p.a51s p.d372v p.c1103* p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r4586h PHD/ RING DHHC/ PHD PHD FYR N
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice
 An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice Mei-Yi Wu 1 *, Ming Jiang 1, Xiaodong Zhai 2, Arthur L. Beaudet 2, Ray-Chang Wu 1 * 1 Department of
An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice Mei-Yi Wu 1 *, Ming Jiang 1, Xiaodong Zhai 2, Arthur L. Beaudet 2, Ray-Chang Wu 1 * 1 Department of
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Chairoungdua et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201002049/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Expression of CD9 and CD82 inhibits Wnt/ -catenin
Supplemental material Chairoungdua et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201002049/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Expression of CD9 and CD82 inhibits Wnt/ -catenin
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT ACTB AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT LCOR
 Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Soluble ADAM33 initiates airway remodeling to promote susceptibility for. Elizabeth R. Davies, Joanne F.C. Kelly, Peter H. Howarth, David I Wilson,
 Revised Suppl. Data: Soluble ADAM33 1 Soluble ADAM33 initiates airway remodeling to promote susceptibility for allergic asthma in early life Elizabeth R. Davies, Joanne F.C. Kelly, Peter H. Howarth, David
Revised Suppl. Data: Soluble ADAM33 1 Soluble ADAM33 initiates airway remodeling to promote susceptibility for allergic asthma in early life Elizabeth R. Davies, Joanne F.C. Kelly, Peter H. Howarth, David
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq
 Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated
 Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
 open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supp. Fig. 1. Autoimmunity. Tolerance APC APC. T cell. T cell. doi: /nature06253 ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 TCR CD28
 Supp. Fig. 1 a APC b APC ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 mir P TCR CD28 P T cell Tolerance Roquin WT SG Icos mrna T cell Autoimmunity Roquin M199R SG Icos mrna www.nature.com/nature 1 Supp. Fig. 2 CD4 + CD44 low CD4
Supp. Fig. 1 a APC b APC ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 mir P TCR CD28 P T cell Tolerance Roquin WT SG Icos mrna T cell Autoimmunity Roquin M199R SG Icos mrna www.nature.com/nature 1 Supp. Fig. 2 CD4 + CD44 low CD4
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables. File Name: Peer Review File Description:
 File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables File Name: Peer Review File Description: Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') AT ( C) RT-PCR USP21 F 5'-TTCCCATGGCTCCTTCCACATGAT-3'
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables File Name: Peer Review File Description: Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') AT ( C) RT-PCR USP21 F 5'-TTCCCATGGCTCCTTCCACATGAT-3'
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Whole Mount X-Gal Staining Whole tissues were collected, rinsed with PBS and fixed with 4% PFA. Tissues were then rinsed in rinse buffer (100 mm Sodium Phosphate ph
Supplementary Materials and Methods Whole Mount X-Gal Staining Whole tissues were collected, rinsed with PBS and fixed with 4% PFA. Tissues were then rinsed in rinse buffer (100 mm Sodium Phosphate ph
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2419
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
ddm1a (PFG_3A-51065) ATG ddm1b (PFG_2B-60109) ATG osdrm2 (PFG_3A-04110) osdrm2 osdrm2 osdrm2
 Relative expression.6.5.4.3.2.1 OsDDM1a OsDDM1b OsDRM2 TG TG TG ddm1a (PFG_3-5165) P1 P3 ddm1b (PFG_2-619) P2 531bp 5233bp P1 P4 P3 P2 F1 R1 F1 TG TG TG F1 R1 C ddm1a -/- -/- ddm1b -/- +/- +/- -/- D (PFG_3-411)
Relative expression.6.5.4.3.2.1 OsDDM1a OsDDM1b OsDRM2 TG TG TG ddm1a (PFG_3-5165) P1 P3 ddm1b (PFG_2-619) P2 531bp 5233bp P1 P4 P3 P2 F1 R1 F1 TG TG TG F1 R1 C ddm1a -/- -/- ddm1b -/- +/- +/- -/- D (PFG_3-411)
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/430/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The 4E-BP eif4e axis promotes rapamycinsensitive growth and proliferation in lymphocytes Lomon So, Jongdae Lee, Miguel
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/430/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The 4E-BP eif4e axis promotes rapamycinsensitive growth and proliferation in lymphocytes Lomon So, Jongdae Lee, Miguel
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS
 Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance.! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014
 Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
In vitro DNase I foot printing. In vitro DNase I footprinting was performed as described
 Supplemental Methods In vitro DNase I foot printing. In vitro DNase I footprinting was performed as described previously 1 2 using 32P-labeled 211 bp fragment from 3 HS1. Footprinting reaction mixes contained
Supplemental Methods In vitro DNase I foot printing. In vitro DNase I footprinting was performed as described previously 1 2 using 32P-labeled 211 bp fragment from 3 HS1. Footprinting reaction mixes contained
Supplemental Figure 1. Genes showing ectopic H3K9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study.
 mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
VIROLOGY. Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors
 VIROLOGY Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors Viral vectors Retrovirus replicative cycle Most mammalian retroviruses use trna PRO, trna Lys3, trna Lys1,2 The partially unfolded trna is annealed
VIROLOGY Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors Viral vectors Retrovirus replicative cycle Most mammalian retroviruses use trna PRO, trna Lys3, trna Lys1,2 The partially unfolded trna is annealed
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supp. Fig. NL43R Metabolic labelling Cytoplasmic grn (% of control) 4 2 8 6 4 2 grn translation (% of control) 4 2 8 6 4 2 Methionine incorporation (% of control) 2 8 6 4 2 C pcirenilla D Renilla luciferase
Supp. Fig. NL43R Metabolic labelling Cytoplasmic grn (% of control) 4 2 8 6 4 2 grn translation (% of control) 4 2 8 6 4 2 Methionine incorporation (% of control) 2 8 6 4 2 C pcirenilla D Renilla luciferase
A complete next-generation sequencing workfl ow for circulating cell-free DNA isolation and analysis
 APPLICATION NOTE Cell-Free DNA Isolation Kit A complete next-generation sequencing workfl ow for circulating cell-free DNA isolation and analysis Abstract Circulating cell-free DNA (cfdna) has been shown
APPLICATION NOTE Cell-Free DNA Isolation Kit A complete next-generation sequencing workfl ow for circulating cell-free DNA isolation and analysis Abstract Circulating cell-free DNA (cfdna) has been shown
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Scaffold function of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in protein ubiquitination
 Yoon et al, page Scaffold function of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in protein ubiquitination Je-Hyun Yoon,, Kotb Abdelmohsen, Jiyoung Kim, Xiaoling Yang, Jennifer L. Martindale, Kumiko Tominaga-Yamanaka,
Yoon et al, page Scaffold function of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in protein ubiquitination Je-Hyun Yoon,, Kotb Abdelmohsen, Jiyoung Kim, Xiaoling Yang, Jennifer L. Martindale, Kumiko Tominaga-Yamanaka,
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers
 Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures. for. pirna-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional
 Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures for pirn-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional silencing via specifying the nuclear pirn repertoire Kirsten-ndré
Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures for pirn-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional silencing via specifying the nuclear pirn repertoire Kirsten-ndré
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Supplementary. presence of the. (c) mrna expression. Error. in naive or
 Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna
 Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna targeted for hamster PAQR3. At 24 h after the transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna targeted for hamster PAQR3. At 24 h after the transfection,
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table.
 Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tale. Type of file: VI Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description:
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tale. Type of file: VI Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description:
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood
 Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood tree illustrating CRF01_AE gp120 protein sequence relationships between 107 Envs sampled in the RV144 trial
Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood tree illustrating CRF01_AE gp120 protein sequence relationships between 107 Envs sampled in the RV144 trial
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Supplemental Fig. 1. Relative mrna Expression. Relative mrna Expression WT KO WT KO RT 4 0 C
 Supplemental Fig. 1 A 1.5 1..5 Hdac11 (ibat) n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 WT KO WT KO WT KO WT KO RT 4 C RT 4 C Supplemental Figure 1. Hdac11 mrna is undetectable in KO adipose tissue. Quantitative
Supplemental Fig. 1 A 1.5 1..5 Hdac11 (ibat) n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 WT KO WT KO WT KO WT KO RT 4 C RT 4 C Supplemental Figure 1. Hdac11 mrna is undetectable in KO adipose tissue. Quantitative
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
Recruitment of HBO1 Histone Acetylase and Blocks
 Molecular Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information JNK1 Phosphorylation of Cdt1 Inhibits Recruitment of HO1 Histone cetylase and locks Replication Licensing in Response to Stress enoit Miotto and Kevin
Molecular Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information JNK1 Phosphorylation of Cdt1 Inhibits Recruitment of HO1 Histone cetylase and locks Replication Licensing in Response to Stress enoit Miotto and Kevin
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Assessment of sample purity and quality.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplemental Information. NRF2 Is a Major Target of ARF. in p53-independent Tumor Suppression
 Molecular Cell, Volume 68 Supplemental Information NRF2 Is a Major Target of ARF in p53-independent Tumor Suppression Delin Chen, Omid Tavana, Bo Chu, Luke Erber, Yue Chen, Richard Baer, and Wei Gu Figure
Molecular Cell, Volume 68 Supplemental Information NRF2 Is a Major Target of ARF in p53-independent Tumor Suppression Delin Chen, Omid Tavana, Bo Chu, Luke Erber, Yue Chen, Richard Baer, and Wei Gu Figure
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from murine
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
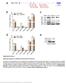 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
