SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Nickolas Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
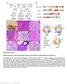
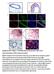
1 DOI: 1.138/ncb3623 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. a Relative cell numbers to day WB e Mel Moderate KD shctr sh shctr Days sh M r (K) 51Mel b Relative cell numbers to day WB shctr 5 1 ME142 Moderate KD shctr sh Days sh M r (K) c Cell density relative to CTR d mrna level (2- Ct) CTR KD MM57 MM165 Mel624 CTR KD N.D. MM57 MM165 Mel624 shctr sh shctr sh shctr sh - 1 kda - 7 kda α-pep1 α-ab23 α-g17 SKMel28 shctr sh shctr sh shctr sh - 1 kda - 7 kda α-pep1 α-ab23 α-g17 Supplementary Figure 1 Moderate mrna knockdown reduces melanoma cell proliferation. (a-b) Proliferation rate of shctr and sh (moderate KD) 51Mel (a) or ME142 cells (b). Cells were counted every two days during eight or ten days (n = 2 biologically independent experiments in triplicate). protein was detected by Western blot experiments; pictures are representative of three independent experiments. serves as loading control. (c-d) knockdown in two melanoma short-term cultures (MM57 & MM165) and in Mel624 melanoma cell line. Cell density (c) and mrna levels (d) have been evaluated 4 or 7 days after infection (sh) or transfection (si). N.D. for not detected. Each histogram represents the mean of 2 or 3 biologically independent experiments (n=2 for cell density experiments; n=2 for MM57 & Mel624 and n=3 for MM165 for mrna level quantification). (e) knockdown in two melanoma cell lines expressing mrna. Three different antibodies (PEP1, AB23 & G17) were used to confirm the absence of the protein in SKMel28-luc cells. Pictures are representative of three independent experiments. Source data are available in Supplementary Table 8 and unprocessed original blots are shown in Supplementary Fig
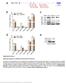
2 Supplementary Figure 2 mir-16 reduces mrna decay induced by mir-155. (a) Cartoon illustrating the 3 UTR of human with the position of the SNPs rs683 and rs91, the three MRE-155 sites (blue) and the three putative MRE-16 sites (orange). (b) MRE-155 sequences on 3 UTR. -C corresponds to the NM_55.2 and -A to NM_55.1. Alignments have been performed using RNAhybrid 34 only a few targets are known. In contrast to plant mirnas, which usually bind nearly perfectly to their targets, animal mirnas bind less tightly, with a few nucleotides being unbound, thus producing more complex secondary structures of mirna/target duplexes. Here, we present a program, RNA-hybrid, that predicts multiple potential binding sites of mirnas in large target RNAs. In general, the program finds the energetically most favorable hybridization sites of a small RNA in a large RNA. Intramolecular hybridizations, that is, base pairings between target nucleotides or between mirna nucleotides are not allowed. For large targets, the time complexity of the algorithm is linear in the target length, allowing many long targets to be searched in a short time. Statistical significance of predicted targets is assessed with an extreme value statistics of length normalized minimum free energies, a Poisson approximation of multiple binding sites, and the calculation of effective numbers of orthologous targets in comparative studies of multiple organisms. We applied our method to the prediction of Drosophila mirna targets in 3 UTRs and coding sequence. RNAhybrid, with its accompanying programs RNAcalibrate and RNAeffective, is available for download and as a Web tool on the Bielefeld Bioinformatics Server ( bibiserv.techfak.uni-bielefeld.de/rnahybrid/. Underlined sequences on MRE- 155#2C and MRE-155#3A are detailed in boxes on the right to show the position of the SNPs in the two alleles of. Arrows indicate the SNP rs683 and rs91 positions. (c) Effects of synthetic mir-155 on the identified regions of MRE-155 in 51Mel. Luciferase activity was evaluated 48h after transfection. Each histogram represents the mean ± s.d. of n=3 biologically independent experiments; two-sided unpaired t-test with Welch s correction; p < 5. (d) Northern blot quantification of mir-16 in 51Mel cells. The signal (from 51Mel cells) was fit to the standard curve from synthetic titration signals to give final copy number per cell. RNU6 served as a loading control. Pictures are representative of three experiments. (e) Northern blot quantification of mrna in 51Mel cells. The signal (from 51Mel cells) was fit to the standard curve from the 3 UTR s synthetic titration signal to give final copy number per cell. GAPDH serves as a loading control. Picture presents three biological replicates of 51Mel. Source data are available in Supplementary Table
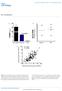
3 Supplementary Figure 3 MRE-16 on human and mouse mrna and biological consequences. (a) MRE-16s sequences on mouse 3 UTR (NM_3122.3). Alignments have been performed using RNAhybrid 34 only a few targets are known. In contrast to plant mirnas, which usually bind nearly perfectly to their targets, animal mirnas bind less tightly, with a few nucleotides being unbound, thus producing more complex secondary structures of mirna/target duplexes. Here, we present a program, RNA-hybrid, that predicts multiple potential binding sites of mirnas in large target RNAs. In general, the program finds the energetically most favorable hybridization sites of a small RNA in a large RNA. Intramolecular hybridizations, that is, base pairings between target nucleotides or between mirna nucleotides are not allowed. For large targets, the time complexity of the algorithm is linear in the target length, allowing many long targets to be searched in a short time. Statistical significance of predicted targets is assessed with an extreme value statistics of length normalized minimum free energies, a Poisson approximation of multiple binding sites, and the calculation of effective numbers of orthologous targets in comparative studies of multiple organisms. We applied our method to the prediction of Drosophila mirna targets in 3 UTRs and coding sequence. RNAhybrid, with its accompanying programs RNAcalibrate and RNAeffective, is available for download and as a Web tool on the Bielefeld Bioinformatics Server ( de/rnahybrid/. (b) Schematic representation of the interaction (purple base paring) of mir-16 (orange) and mir-155 (blue) with human and mouse MRE-16#3 and MRE-155#3 respectively. (c-d) knockdown in mouse B16-F1 melanoma cells using three different sirnas. mrna levels (c) and cell density (d) have been respectively evaluated at 5 and 3 days after sirna transfection; one-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak s multiple comparisons test. (e) Effect on cell density of synthetic mir-16 transfected in mouse B16-F1 melanoma cells 3 days after mirna transfection; two-sided unpaired t-test with Welch s correction, p < 5. Each histogram represents the mean ± s.d. (n = 3 biologically independent experiments). Source data are available in Supplementary Table
4 a b sictr si #1 si #3 si #2 n=3 si n=5 n=4 #1 #2 #3 vs sictr n=3 n=3 #1 #2 Significance Analysis of Microarrays FDR=, (GEO GSE7561) Relative mrna levels to sictr MAFF NRTN RAB17 RasGRP si #2 #3 #1 MYH7B A2M MUC7 PLB1 BAIAP2L2 PPY NRTN COL7A1 GALNTL4 TNFSF9 MAFF ST3GAL4 PLA2G6 PRSS56 RAB17 SDC3 RASGRP3 PLTP HIF1A FBLN1 SEPT9 CELF2 MOXD1 HLCS ITGB8 MRPL36 C14orf169 EIF4EBP2 B3GALT6 FBXL7 FAM12C LINC34 C9orf13 ERAP1 CREM FAM198B PTP4A1 LOC IFIT1 PMP2 IFI6 FLJ4696 BFSP1 ISG15 IFI44 CHMP1B MAP2 CLDN2 proliferation of cells migration of cells quantity of cells formation of cellular protrusions generation of cells quantity of neurons invasion of cells invasion of tumor cell lines vasculogenesis proliferation of lymphocytes growth of epithelial tissue differentiation of cells Activation z-score DN UP DN UP c Relative mrna levels to shctr d Cell density relative to sictr e Relative mrna levels to mir-ctr f 2 1 MAFF NRTN RAB17 RasGRP3 CTR MAFF#1 mir-ctr mir-16 MAFF NRTN shctr RASGRP3 sh MAFF#2 NRTN#1 NRTN#2 RAB17#1 RAB17#2 RasGRP3#1 RasGRP3#2 Supplementary Figure 4 silencing decreases expression level of several mrnas. (a) Workflow to identify deregulated RNAs in KD cells. Gene expression profile of cells transfected with three different sirnas targeting or sirna CTR. Significance analysis of microarrays was done as described in methods. sirna efficacy for KD is #2>#3>#1. Heatmap focused on deregulated RNAs in function of si efficacy (top) and a z-score has been calculated using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) (bottom). (b) mrna expression levels of, MAFF, NRTN, RAB17 and RasGRP3 in response to KD using three different sirnas (#1-3) targeting the ORF of in 51Mel cells (n = 4 biologically independent experiments except for RASGRP3 expression measurement which results from n = 3 biologically independent experiments). (c) mrna expression levels of, MAFF, NRTN, RAB17 and RasGRP3 in response to KD using sh targeting the ORF of in SKMel28-luc cells (n = 3 biologically independent experiments). (d) Cell density of 51Mel cells in response to sirnas targeting MAFF, NRTN, RAB17 or RasGRP3 (n = 3 biologically independent experiments; one-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak s multiple comparisons test, p < 5). Two sirnas were used by target. (e) mrna expression levels in response to synthetic mir-16. Each histogram represents the mean ± s.d. (n = 3 biologically independent experiments). and RAB17 mrna expression in response to synthetic mir-16 are reported in Fig. 2d and 4b, respectively. (f) The MRE-16s sequence on human MAFF and NRTN mrnas have been identified using RNAhybrid 34 only a few targets are known. In contrast to plant mirnas, which usually bind nearly perfectly to their targets, animal mirnas bind less tightly, with a few nucleotides being unbound, thus producing more complex secondary structures of mirna/ target duplexes. Here, we present a program, RNA-hybrid, that predicts multiple potential binding sites of mirnas in large target RNAs. In general, the program finds the energetically most favorable hybridization sites of a small RNA in a large RNA. Intramolecular hybridizations, that is, base pairings between target nucleotides or between mirna nucleotides are not allowed. For large targets, the time complexity of the algorithm is linear in the target length, allowing many long targets to be searched in a short time. Statistical significance of predicted targets is assessed with an extreme value statistics of length normalized minimum free energies, a Poisson approximation of multiple binding sites, and the calculation of effective numbers of orthologous targets in comparative studies of multiple organisms. We applied our method to the prediction of Drosophila mirna targets in 3 UTRs and coding sequence. RNAhybrid, with its accompanying programs RNAcalibrate and RNAeffective, is available for download and as a Web tool on the Bielefeld Bioinformatics Server ( For b-c and e, two-sided unpaired t-tests with Welch s correction were done (p<5). For b-e, values correspond to the mean ± s.d. Source data are available in Supplementary Table
5 a RAB17 (IJB cohort) b + RAB17 (IJB cohort) c + RAB17 (TCGA cohort) High (n=92) p=52 HR=1.4 95% CI=-1.97 Low (n=92) Time (years) p<1.8 HR= % CI= High (n=13) Low (n=54) Time (years) High (n=157) p < 1 HR=2. 95 % Cl= Low (n=157) Time (years) d f NRTN (TCGA cohort) low NRTN (n = 46) high NRTN (n = 46) p =.1172 HR = % Cl = Time (Days) mir-16 (IJB cohort) e g + NRTN (TCGA cohort) mir-16 (TCGA cohort) low NRTN+ (n = 46) high NRTN + (n=46) p = 19 HR = % Cl = Time (Days) p=.7142 HR=96 95 % Cl= low mir-16 (n=43) high mir-16 (n=42) Time (years) p=.8336 HR=3 95 % Cl= low mir-16 (n=175) high mir-16 (n=174) Time (years) Supplementary Figure 5 of patients with metastatic melanoma according to, RAB17, NRTN mrnas or mir-16 expression levels. (a-b) Determination of overall survival (OS) curves by Kaplan-Meier analysis, according to the expression levels of RAB17 (a) or and RAB17 (b). Based on 184 skin and lymph node metastases from melanoma patients (IJB cohort). High and low expression of and RAB17 (a) alone were defined based on their median values and scored as 1 and, respectively. For combination (b), scores of (1 or ) and RAB17 (1 or ) are added and the resulting scores 1 and 2 are combined as the high score (n = 13 patients), which was significantly different from the low score (n = 54 patients) regarding to OS values (two-sided Mann-Whitney test, p = 4). Cox regression was used to calculate P values, hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). (c) Association of and RAB17 expression with patient survival. and RAB17 expression levels were assessed in the TCGA SKCM melanoma cohort. Patients were ranked decreasingly according to and RAB17 expression, resulting in almost three equal groups. The Kaplan-Meier curve representing the highest third of and RAB17 expressers shows a significantly lower OS as compared to the lowest third (log-rank test). (d-e) Determination of OS curves by Kaplan-Meier analysis, according to the expression levels of NRTN (d) or and NRTN (e). Patients were ranked decreasingly according to NRTN (d) or and NRTN expression (e), resulting in almost four equal groups. The Kaplan-Meier curve represents the highest and the lower quarters of expressers (log-rank test). (f-g) Determination of OS curves by Kaplan-Meier analysis, according to the expression levels of mir-16 from n = 85 patients of the IJB cohort (f) or from n=349 patients from the TCGA cohort (g). High and low expression groups of mir-16 were defined based on its median value (log-rank test). 5
6 a b 2,5 TSB-C1 TSB-T3 TSB: C1 T3 mouse 1 - liver mouse 3 - liver 2, mouse 2 - liver mouse 4 - liver Tumor volume (mm 3 ) 1,5 1, 5 TSB-C1 mouse 1 - kidney TSB-T3 mouse 3 - kidney c Days after treatment 2 mouse 2 - kidney mouse 4 - kidney LAMP2 mrna level (2- Ct) 1 n.s. TSB-C1 TSB-T3 Supplementary Figure 6 Histological analyses of liver and kidney from PDX mice and long-term tumor growth. (a) Representative micrographs of liver and kidney slices stained with hematoxylin from PDX-mice exposed to TSB- C1 or TSB-T3. Toxicity evaluation was blindly examined by two independent pathologists. Two mice have been showed per group among five mice analysed given similar results. Scale bar : 1µm. (b) Tumor volume for individual PDX mice treated with TSB-C1 or TSB-T3 as described in Fig. 6b. (c) Quantification of LAMP2 mrna in melanoma tumors treated with TSB-C1 or TSB-T3 (n = 5 mice per group). LAMP2 is not a mir-16 target. For c, lines represent the mean ± s.d.; values represent fold change relative to the mean of TSB-C1 condition; two-sided unpaired t-tests with Welch s correction; n.s., non-significant. Source data are available in Supplementary Table
7 Figure 1b Figure 1e sh shctr Figure 3b GAPDH GAPDH 15 kda - Figure 4a aspecific signal RAB17 Figure 4b RAB17 15 kda - RAB17 Figure 4f RAB17 4 kda - 15 kda - 15 kda - 15 kda - aspecific signal Sup. Figure 1a Sup. Figure 1b Sup. Figure 1e : PEP1 51Mel AB93 G17 Sup. Figure 1e SKMel28 : PEP1 AB93 G17 Supplementary Figure 7 Unprocessed original scans of blots. 7
8 Supplementary Table Legends Supplementary Table 1 Metastatic melanoma cell lines and short-term cultures. Supplementary Table 2 mirna quantification in 51Mel cells. Supplementary Table 3 Clinical characteristics of the patients and tissues from the Institute Jules Bordet cohort. Supplementary Table 4 Correlation between and RAB17, NRTN or MAFF in the TCGA cutaneous skin cancer cohort. Supplementary Table 5 TSB-T3 efficacy, mutation state and mrnas expression in 51Mel and short-term cultures. Supplementary Table 6 sirna, mirna, TSB, inserts and probes sequences. Supplementary Table 7 Antibodies. Supplementary Table 8 Statistics Source Data. 8
9 Life Sciences Reporting Summary Corresponding author(s): Galibert M.-D. & Gilot D. Initial submission Revised version Final submission Nature Research wishes to improve the reproducibility of the work that we publish. This form is intended for publication with all accepted life science papers and provides structure for consistency and transparency in reporting. Every life science submission will use this form; some list items might not apply to an individual manuscript, but all fields must be completed for clarity. For further information on the points included in this form, see Reporting Life Sciences Research. For further information on Nature Research policies, including our data availability policy, see Authors & Referees and the Editorial Policy Checklist. Experimental design 1. Sample size Describe how sample size was determined. 2. Data exclusions Describe any data exclusions. 3. Replication Describe whether the experimental findings were reliably reproduced. 4. Randomization Describe how samples/organisms/participants were allocated into experimental groups. 5. Blinding Describe whether the investigators were blinded to group allocation during data collection and/or analysis. No sample size calculation was performed. Three to more independent results were used to perform statistical analyses. If less, no statistics were performed from these samples. All raw data required for statistical tests are in indicated in supplementary Table 1 (Statistics data source) Data were excluded only for PDX mice treatments. PDX mice were chosen by the range of their initial tumor volume: 18 mm3 (median, mm3). All attempts at replication were successful. Samples were allocated to groups randomly but no specific methods were used. Investigators were blinded to group allocation during data collection only for the PDX mice treatments. For other experiments, investigators who performed experiments were the same who took care of cell lines, did extractions, etc., so blinding was not possible. Note: all studies involving animals and/or human research participants must disclose whether blinding and randomization were used. 6. Statistical parameters n/a For all figures and tables that use statistical methods, confirm that the following items are present in relevant figure legends (or in the Methods section if additional space is needed). Confirmed The exact sample size (n) for each experimental group/condition, given as a discrete number and unit of measurement (animals, litters, cultures, etc.) A description of how samples were collected, noting whether measurements were taken from distinct samples or whether the same sample was measured repeatedly A statement indicating how many times each experiment was replicated The statistical test(s) used and whether they are one- or two-sided (note: only common tests should be described solely by name; more complex techniques should be described in the Methods section) A description of any assumptions or corrections, such as an adjustment for multiple comparisons The test results (e.g. P values) given as exact values whenever possible and with confidence intervals noted A clear description of statistics including central tendency (e.g. median, mean) and variation (e.g. standard deviation, interquartile range) Clearly defined error bars nature research life sciences reporting summary June 217 See the web collection on statistics for biologists for further resources and guidance. 1
10 Software Policy information about availability of computer code 7. Software Describe the software used to analyze the data in this study. 4peaks, NDP.view (Nanozoomer digital pathology), serial cloner 3., IGV (Integrative Genomics Viewer), R, microsoft excel, Image J, SDS v2. (Applied Biosystems), Bowtie, bioconductor LIMMA, SVA, MultiExperiment Viewer (MeV v4.8), IPA (Ingenuity Pathway Analysis), Prism 6 (GraphPad), SPSS Statistics 15., nsolver Analysis Software (Nanostring) and ArrayScan VTI High-Content Systems (ThermoFisher Scientific) For manuscripts utilizing custom algorithms or software that are central to the paper but not yet described in the published literature, software must be made available to editors and reviewers upon request. We strongly encourage code deposition in a community repository (e.g. GitHub). Nature Methods guidance for providing algorithms and software for publication provides further information on this topic. Materials and reagents Policy information about availability of materials 8. Materials availability Indicate whether there are restrictions on availability of unique materials or if these materials are only available for distribution by a for-profit company. 9. Antibodies Describe the antibodies used and how they were validated for use in the system under study (i.e. assay and species). Target site blockers are only available for distribution by a for-profit company (Exiqon). Anti- (PEP1) antibody was kindly provided by Prof. V.J. Hearing (National Institute of Health, Bethesda, Maryland). Full information about the anitbodies used in this study is provided in Supplementary Table 9. All primary antibodies anti- and anti-rab17 were also tested and validated in our lab using human shrna cell lines against and RAB17 gene by Western- Blot. Anti- detects a weaker band in sh cell extracts compared to shcontrol cell extracts, validating the antibody. Anti-RAB17 detects a weaker band in shrab17 cell extracts compared to shcontrol cell extracts, validating the antibody. 1. Eukaryotic cell lines a. State the source of each eukaryotic cell line used. Metastatic melanoma (MM) cell lines were derived from tumors by the Laboratory of Oncology and Experimental Surgery (Prof. G Ghanem) at the Institute Jules Bordet, Brussels. 51Mel, ME142 and SKMel28 cell lines were obtained from ATCC. SKMel28-luc was obtained from Prof. T. Montier (INSERM U178) and Mel624 from Dr. G. Lizée (Department of Melanoma Medical Oncology and Department of Immunology, Houston, TX, USA). Mouse melanoma B16-F1-luc-G5 cells were obtained from PerkinElmer (Waltham, MA). Huh7.5 Drosha knockout cells were obtained from Prof. R.B. Darnell (Rockefeller University, New York, USA). b. Describe the method of cell line authentication used. Sources cited above authenticated their cell lines. c. Report whether the cell lines were tested for mycoplasma contamination. d. If any of the cell lines used are listed in the database of commonly misidentified cell lines maintained by ICLAC, provide a scientific rationale for their use. Animals and human research participants All cell lines were tested negative for mycoplasma contamination. No commonly misidentified cell lines were used. Policy information about studies involving animals; when reporting animal research, follow the ARRIVE guidelines 11. Description of research animals Provide details on animals and/or animal-derived materials used in the study. ~ 6-week-old females NMRI nude mice were used. nature research life sciences reporting summary June 217 2
11 Policy information about studies involving human research participants 12. Description of human research participants Describe the covariate-relevant population characteristics of the human research participants. Cutaneous and lymph node metastases (n = 191) were collected from patients with stages III and IV melanoma undergoing surgery as a part of the diagnostic work-up or therapeutic strategy at the Institut Jules Bordet (Brussels, Belgium) between 1998 to 29. But no information about treatment categories were given. This cohort were composed of 8 males and 111 females from 2 to 87 years old (median: 55 years old). The majority of the melanomas were of superficial spreading or nodular histological subtypes with Breslow s thicknesses > 1 mm. nature research life sciences reporting summary June 217 3
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Roger Thompson NNA52598C Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 7 # Supplementary Figures: 9 # Supplementary Tables:
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Roger Thompson NNA52598C Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 7 # Supplementary Figures: 9 # Supplementary Tables:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Daniel O'Connor NNA53650A Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 7 # Supplementary Figures: 10 # Supplementary Tables:
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Daniel O'Connor NNA53650A Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 7 # Supplementary Figures: 10 # Supplementary Tables:
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Alex Pouget NN-A46249B Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 7 # Supplementary Figures: 3 # Supplementary Tables:
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Alex Pouget NN-A46249B Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 7 # Supplementary Figures: 3 # Supplementary Tables:
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting
 mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Rutishauser NNA57105 Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 8 # Supplementary Figures: 6 # Supplementary Tables: 1
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Rutishauser NNA57105 Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 8 # Supplementary Figures: 6 # Supplementary Tables: 1
Figure S1: Effects on haptotaxis are independent of effects on cell velocity A)
 Supplemental Figures Figure S1: Effects on haptotaxis are independent of effects on cell velocity A) Velocity of MV D7 fibroblasts expressing different GFP-tagged Ena/VASP family proteins in the haptotaxis
Supplemental Figures Figure S1: Effects on haptotaxis are independent of effects on cell velocity A) Velocity of MV D7 fibroblasts expressing different GFP-tagged Ena/VASP family proteins in the haptotaxis
Supplementary methods:
 Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Subhojit Roy NNA51787 Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: Eight # lementary Figures: Seven # lementary Tables:
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Subhojit Roy NNA51787 Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: Eight # lementary Figures: Seven # lementary Tables:
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: N. P. Franks NNA49691 Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 7 # Supplementary Figures: 9 # Supplementary Tables:
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: N. P. Franks NNA49691 Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 7 # Supplementary Figures: 9 # Supplementary Tables:
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2
 Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
PID1 increases chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cells in a manner that involves NFκB
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: PID1 increases chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cells in a manner that involves NFκB Jingying Xu, Xiuhai Ren, Anup Singh Pathania, G. Esteban Fernandez,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: PID1 increases chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cells in a manner that involves NFκB Jingying Xu, Xiuhai Ren, Anup Singh Pathania, G. Esteban Fernandez,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2211 a! mir-143! b! mir-103/107! let-7a! mir-144! mir-122a! mir-126-3p! mir-194! mir-27a! mir-30c! Figure S1 Northern blot analysis of mir-143 expression dependent on feeding conditions.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2211 a! mir-143! b! mir-103/107! let-7a! mir-144! mir-122a! mir-126-3p! mir-194! mir-27a! mir-30c! Figure S1 Northern blot analysis of mir-143 expression dependent on feeding conditions.
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Prof. Giulio Tononi N56649CZ Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main s: 5 # lementary s: 8 # lementary s: 4 # lementary Videos:
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Prof. Giulio Tononi N56649CZ Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main s: 5 # lementary s: 8 # lementary s: 4 # lementary Videos:
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Yves De Koninck NNBC47734A Brief Communication Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 3 # Supplementary Figures: 1 # Supplementary
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Yves De Koninck NNBC47734A Brief Communication Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 3 # Supplementary Figures: 1 # Supplementary
ANGPTL2 increases bone metastasis of breast cancer cells through. Tetsuro Masuda, Motoyoshi Endo, Yutaka Yamamoto, Haruki Odagiri, Tsuyoshi
 Masuda et al. Supplementary information for ANGPTL2 increases bone metastasis of breast cancer cells through enhancing CXCR4 signaling Tetsuro Masuda, Motoyoshi Endo, Yutaka Yamamoto, Haruki Odagiri, Tsuyoshi
Masuda et al. Supplementary information for ANGPTL2 increases bone metastasis of breast cancer cells through enhancing CXCR4 signaling Tetsuro Masuda, Motoyoshi Endo, Yutaka Yamamoto, Haruki Odagiri, Tsuyoshi
Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma. (a) Breeding scheme. R26-LSL-SB11 homozygous mice were bred to Trp53 LSL-R270H/+
Supplementary Figure 1 Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma. (a) Breeding scheme. R26-LSL-SB11 homozygous mice were bred to Trp53 LSL-R270H/+
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Malenka, RC N5579A Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main s: 6 # lementary s: 0 # lementary Tables: 0 # lementary Videos: 0
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Malenka, RC N5579A Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main s: 6 # lementary s: 0 # lementary Tables: 0 # lementary Videos: 0
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Leonard Petrucelli RS51511B Resource Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main s: 6 1 table # s: 13 # Tables: 11 # Videos: 0 This checklist
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Leonard Petrucelli RS51511B Resource Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main s: 6 1 table # s: 13 # Tables: 11 # Videos: 0 This checklist
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Tali Sharot NNA549D Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main ures: 4 # lementary ures: 5 # lementary Tables: 4 # lementary Videos:
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Tali Sharot NNA549D Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main ures: 4 # lementary ures: 5 # lementary Tables: 4 # lementary Videos:
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Simon Musall NNA47695 Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 6 # Supplementary Figures: 14 # Supplementary Tables:
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Simon Musall NNA47695 Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 6 # Supplementary Figures: 14 # Supplementary Tables:
(A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC,
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier
 Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplemental Table S1
 Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
TEB. Id4 p63 DAPI Merge. Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge
 a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Figure 1 Cell line TRIB2 status. Supplementary Figure 2 TRIB2 status has no impact on the cell cycle after PI3K inhibition. a. b.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cell line TRIB2 status. TRIB2 protein expression to determine endogenous expression and to determine the effectiveness of each of our TRIB2 knockdown constructs. Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure 1 Cell line TRIB2 status. TRIB2 protein expression to determine endogenous expression and to determine the effectiveness of each of our TRIB2 knockdown constructs. Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions. In brief, 10ng of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: NNA49200 Manuscript Type: Matthew Walker & Bryce Mander Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 4 # Supplementary Figures: 3 # Supplementary
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: NNA49200 Manuscript Type: Matthew Walker & Bryce Mander Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 4 # Supplementary Figures: 3 # Supplementary
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1. Galectin-3 is present within tumors. (A) mrna expression levels of Lgals3 (galectin-3) and Lgals8 (galectin-8) in the four classes of cell lines as determined
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1. Galectin-3 is present within tumors. (A) mrna expression levels of Lgals3 (galectin-3) and Lgals8 (galectin-8) in the four classes of cell lines as determined
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation
 Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells.
 Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX
 SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
omiras: MicroRNA regulation of gene expression
 omiras: MicroRNA regulation of gene expression Sören Müller, Goethe University of Frankfurt am Main Molecular Bioinformatics Group, Institute of Computer Science Plant Molecular Biology Group, Institute
omiras: MicroRNA regulation of gene expression Sören Müller, Goethe University of Frankfurt am Main Molecular Bioinformatics Group, Institute of Computer Science Plant Molecular Biology Group, Institute
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Normal Skin. Tissue Samples and Melanoma Cell Lines. BRAF Mut. RAS Mut RAS WT /BRAF WT
 Supplemental Figure 1. MERTK gene expression in melanoma cell line panel from Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. A. Microarray analysis of melanoma cell lines from UNC collection grouped by oncogenic mutation.
Supplemental Figure 1. MERTK gene expression in melanoma cell line panel from Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. A. Microarray analysis of melanoma cell lines from UNC collection grouped by oncogenic mutation.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of mir mimics and anti-mirs on DTPs a, Representative fluorescence microscopy images of GFP vector control or mir mimicexpressing parental and DTP
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of mir mimics and anti-mirs on DTPs a, Representative fluorescence microscopy images of GFP vector control or mir mimicexpressing parental and DTP
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the
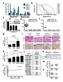 Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Bernhard Staresina A51406B Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 5 # Supplementary Figures: 10 # Supplementary Tables:
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Bernhard Staresina A51406B Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 5 # Supplementary Figures: 10 # Supplementary Tables:
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Timothy Gardner NNA55425A Article Reporting Checklist Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 6 # Supplementary Figures: 9 # Supplementary Tables:
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Timothy Gardner NNA55425A Article Reporting Checklist Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 6 # Supplementary Figures: 9 # Supplementary Tables:
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Patient cohorts and study design. To define and interrogate the genetic alterations underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Patient cohorts and study design. To define and interrogate the genetic alterations underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
injected subcutaneously into flanks of 6-8 week old athymic male nude mice (LNCaP SQ) and body
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1: Generation of ENZR Xenografts and Cell Lines: (A) 1x10 6 LNCaP cells in matrigel were injected subcutaneously into flanks of 6-8 week old athymic male nude mice (LNCaP
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1: Generation of ENZR Xenografts and Cell Lines: (A) 1x10 6 LNCaP cells in matrigel were injected subcutaneously into flanks of 6-8 week old athymic male nude mice (LNCaP
Supplemental Figures:
 Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical
 Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical representation using all SNPs (n= 13,515,798) including the region on chromosome 1 including SORT1 which was previously
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical representation using all SNPs (n= 13,515,798) including the region on chromosome 1 including SORT1 which was previously
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
Figure S1A. Blood glucose levels in mice after glucose injection
 ## Figure S1A. Blood glucose levels in mice after glucose injection Blood glucose (mm/l) 25 2 15 1 5 # 15 3 6 3+3 Time after glucose injection (min) # Figure S1B. α-kg levels in mouse livers after glucose
## Figure S1A. Blood glucose levels in mice after glucose injection Blood glucose (mm/l) 25 2 15 1 5 # 15 3 6 3+3 Time after glucose injection (min) # Figure S1B. α-kg levels in mouse livers after glucose
A263 A352 A204. Pan CK. pstat STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3. Columns Columns 1-6 Positive control. Omentum. Rectosigmoid A195.
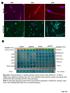 pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of acgh-based and expression-based CNA analysis of tumors from breast cancer GEMMs.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of acgh-based and expression-based CNA analysis of tumors from breast cancer GEMMs. (a) CNA analysis of expression microarray data obtained from 15 tumors in the SV40Tag
Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of acgh-based and expression-based CNA analysis of tumors from breast cancer GEMMs. (a) CNA analysis of expression microarray data obtained from 15 tumors in the SV40Tag
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the. mutated sequence.
 Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors
 Wang et al LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors A. Induced expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in AME vs PDA
Wang et al LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors A. Induced expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in AME vs PDA
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Micro-RNA web tools. Introduction. UBio Training Courses. mirnas, target prediction, biology. Gonzalo
 Micro-RNA web tools UBio Training Courses Gonzalo Gómez//ggomez@cnio.es Introduction mirnas, target prediction, biology Experimental data Network Filtering Pathway interpretation mirs-pathways network
Micro-RNA web tools UBio Training Courses Gonzalo Gómez//ggomez@cnio.es Introduction mirnas, target prediction, biology Experimental data Network Filtering Pathway interpretation mirs-pathways network
Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granule, DDX3X and IKK-α Mediates Multiple Functions in
 Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granule, and Mediates Multiple Functions in Hepatitis C Virus Infection Véronique Pène, Qisheng Li#, Catherine Sodroski, Ching-Sheng Hsu, T. Jake Liang# Liver Diseases Branch,
Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granule, and Mediates Multiple Functions in Hepatitis C Virus Infection Véronique Pène, Qisheng Li#, Catherine Sodroski, Ching-Sheng Hsu, T. Jake Liang# Liver Diseases Branch,
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Table S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort. Chr. # of Gene 2. Chr. # of Gene 1
 Supplementary Tale S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort TCGA Case ID Gene-1 Gene-2 Chr. # of Gene 1 Chr. # of Gene 2 Genomic coordiante of Gene 1 at fusion junction Genomic
Supplementary Tale S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort TCGA Case ID Gene-1 Gene-2 Chr. # of Gene 1 Chr. # of Gene 2 Genomic coordiante of Gene 1 at fusion junction Genomic
Supplementary Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs
 Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
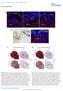 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2535 Figure S1 SOX10 is expressed in human giant congenital nevi and its expression in human melanoma samples suggests that SOX10 functions in a MITF-independent manner. a, b, Representative
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2535 Figure S1 SOX10 is expressed in human giant congenital nevi and its expression in human melanoma samples suggests that SOX10 functions in a MITF-independent manner. a, b, Representative
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 -. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
-. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/393/rs9/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Identification of potential drug targets for tuberous sclerosis complex by synthetic screens combining CRISPR-based knockouts
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/393/rs9/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Identification of potential drug targets for tuberous sclerosis complex by synthetic screens combining CRISPR-based knockouts
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS
 Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Jeffrey C. Magee NNA726 Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 7 # em Figures: 14 # em s: # em Videos: This checklist
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Jeffrey C. Magee NNA726 Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 7 # em Figures: 14 # em s: # em Videos: This checklist
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 14 12 SEM4C PLXN2 8 SEM4C C 3 Cancer Cell Non Cancer Cell Expression 1 8 6 6 4 log2 ratio Expression 2 1 4 2 2 p value.1 D Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Sema4C and Plexin2
Supplementary Figure 1 14 12 SEM4C PLXN2 8 SEM4C C 3 Cancer Cell Non Cancer Cell Expression 1 8 6 6 4 log2 ratio Expression 2 1 4 2 2 p value.1 D Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Sema4C and Plexin2
Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded
 Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded from TCGA and differentially expressed metabolic genes
Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded from TCGA and differentially expressed metabolic genes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Amelio et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203134/dc1 Figure S1. mir-24 regulates proliferation and by itself induces
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Amelio et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203134/dc1 Figure S1. mir-24 regulates proliferation and by itself induces
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from
 Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Title page. Title: MicroRNA-155 Controls Exosome Synthesis and Promotes Gemcitabine Resistance in
 Title page Title: MicroRNA- Controls Synthesis and Promotes Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Authors Manabu Mikamori, Daisaku Yamada, Hidetoshi Eguchi, Shinichiro Hasegawa, Tomoya
Title page Title: MicroRNA- Controls Synthesis and Promotes Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Authors Manabu Mikamori, Daisaku Yamada, Hidetoshi Eguchi, Shinichiro Hasegawa, Tomoya
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY
 Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY Methodology The test is based on the reported 50-gene classifier algorithm originally named PAM50 and is performed on the ncounter Dx Analysis System
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY Methodology The test is based on the reported 50-gene classifier algorithm originally named PAM50 and is performed on the ncounter Dx Analysis System
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY
 Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING WITH PROSIGNA What is Prosigna? Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay is an FDA-approved assay which provides
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING WITH PROSIGNA What is Prosigna? Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay is an FDA-approved assay which provides
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis
 The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
