Supplementary Figure 1. Gene schematics of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4, and TEM analysis of TFs in WT and hyls-1 cilia. (a) Gene structure of hyls-1,
|
|
|
- Arabella Daniels
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene schematics of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4, and TEM analysis of TFs in WT and hyls-1 cilia. (a) Gene structure of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4 based on WormBase ( indicating available mutants. The tm3067 allele has a 493bp DNA fragment deletion, encompassing the 1 st, 2 nd and part of the 3 rd exon of the hyls-1 gene, removing the first 361bp of the 825bp CDS including the ATG. The gk567 allele has a 1561bp DNA fragment deletion, encompassing exons 1 to 6 of k10g6.4 and removing the the first 871bp of the 1380bp CDS including the ATG. The gk1232 allele has an 884bp DNA fragment deletion, which removes exon 2 of gasr-8 and is predicted to result in an in-frame deletion of 261aa (S28-Q288) of the 410aa wild-type protein. All three alleles are putative null due to the large deletion. (b) TEM analysis of TFs in WT and hyls-1 cilia. TEM images of four consecutive serial sections (~80 nm thickness each) of the basal body region from WT or hyls-1 mutants. Fiber-like structures in similar size can be observed in serial sections of WT cilia. In contrast, only a few areas of electrondense material but no organized fibers remain in the basal body region of hyls-1 mutants. Scale bar, 200 nm.
2 Supplementary Figure 2. Quantitation of the expression level of IFT components, and visualization of IFT-A, IFT-B and motor association in cilia of WT and hyls-1 mutants. (a) Upper panel, OSM-6::GFP was immunoprecipitated from whole worm lysates with anti-gfp monoclonal antibody and then probed with anti-gfp antibody. Lower panel: whole worm lysate was probed with anti-β-actin (loading control). After normalization against actin levels, OSM-6::GFP shows no difference in expression level in WT and hyls-1 mutants. (b-d) Quantitation of IFT fluorescence intensities in the cell body shows no difference in levels between WT and hyls-1 mutants. Error bars indicate S.D. n represents the number of cilia analyzed. (e) Schematic of amphid sensory organ. Each amphid contains ten cilia whose distal segments bundle together. Green dots indicate ciliary base. (f-h) All BiFC pairs, CHE-11::VN + IFT-20::VC (f), XBX-1::VN + IFT-20::VC (g), and KAP-1::VN + IFT-20::VC IFT-A (h), show fluorescence complementation in both WT and hyls-1 amphid cilia, indicating formation of functional IFT complexes. However, fluorescence complementation signal is largely restricted to the cilia base in hyls-1 mutants. Asterisks indicate the cilia bases. Note that not all ten cilia can be visualized in one focal plane in confocal imaging. VN, N-terminus of Venus. VC, C-terminus of Venus. Scale bar, 5 m.
3 Supplementary Figure 3. Genetic interactions between hyls-1 and TF mutants. (a) TEM analysis of amphid sensory cilia of hyls-1 and hyls-1;dyf-19 double mutants. Red box indicates a cilium cut at the level of the TZ. Black box indicates axoneme immediately adjacent to the TZ. Compared to hyls-1 single mutants, most axonemes terminate immediately distal to the TZ in hyls-1; dyf-19 double mutants (Black arrows). Bar, 200 nm. (b) hyls-1 shows no genetic interactions with gasr-8 or k10g6.4 in ciliogenesis. Asterisks indicate cilia base of phasmid cilia expressing the IFT marker OSM-6::GFP. Scale bar, 5 m. (c) Quantification of ciliation in phasmid neurons based on TBB-4::mCherry in different genetic backgrounds, >100 phasmid neurons analyzed for each genetic background.
4 Supplementary Figure 4. Genetic interactions between HYLS-1 and TZ proteins and compromised gating in HYLS-1-deficient cilia. (a) Localization of TZ components in hyls-1 mutants. HYLS-1 is not required for proper TZ localization of MKS-3, MKS-6, MKSR-2, NPHP-4, and CCEP-290. Scale bar, 1 m. (b) Quantification of dendrite collapse in double mutants of hyls-1 and various TZ genes. Severe shortened dendrites were observed in hyls-1; nphp-1 and hyls-1; mks-5 double mutants. No genetic interaction was observed between hyls-1 and MKS module mutants (mks-1, mks-3 or mks-6). > 100 phasmid neurons analyzed for each genetic background. Error bars indicate S.D. Student s t-test for significant differences, * P< (c) tdtomato-tagged non-ciliary membrane protein TRAM-1 leaks into phasmid cilia in hyls-1 mutants. GFP-tagged MKS-3 was used as a marker to label the TZ. Scale bar, 5 m. (d) Non-ciliary cytoplasmic protein DAF-21 leaks into phasmid cilia in hyls-1 mutants. Scale bar, 5 m.
5 Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative Analysis of Transition Fibers (TFs) and Transition Zone (TZ) in serial section TEM study. WT hyls-1 dyf-19 hyls-1; dyf-19 Number of cilia examined TF Number of TFs with fiber-like structures 19 2 (*) 8 0 Percentage of TFs with fiber-like 100% 12.5% (*) 100% 0 structures TZ Number of TZ with Y-links Percentage of TZ with Y-links 100% 100% 100% 100% *: the fiber-like structure observed in hyls-1 mutants is not intact.
6 Supplementary Table 2. C. elegans strains used in this study Strain name OD192 ZP541 VC2343 VC1268 FX2705 FX2547 FX3100 RB743 VC1466 ZP2174 ZP2175 ZP2176 ZP2177 ZP2203 ZP2204 ZP2205 ZP2179 ZP1389 ZP1993 ZP1997 ZP2001 ZP1880 SP2101 ZP1986 ZP2035 PT50 ZP1205 ZP1397 Genotype hyls-1(tm3067)v dyf-19(jhu455)v gasr-8 (gk1232)v k10g6.4 (gk567)ii mks-1 (tm2705)iii mks-3 (tm2547)ii mks-5 (tm3100)ii nphp-1(ok500)ii mks-6(gk674)i mks-1 (tm2705)iii; hyls-1(tm3067)v; IsOSM6 mks-6(gk674)i; hyls-1(tm3067)v;isosm6 nphp-1(ok500)ii; hyls-1(tm3067)v;isosm6 gasr-8 (gk1232)v; hyls-1(tm3067)v; IsOSM6 dyf-19(jhu455)v; hyls-1(tm3067)v;isosm-6 k10g6.4 (gk567)ii; hyls-1(tm3067)v;isosm-6 mks-5 (tm3100)ii; hyls-1(tm3067)v;isosm-6 mks-3 (tm2547)ii ; hyls-1(tm3067)v;isosm6 jhuex [HYLS1:GFP+DYF-9:mCherry+pRF4] jhuex [FBF1::mCherry+GASR-8::GFP+pRF4] jhuex [NPHP1::GFP+GASR-8::mCherry+pRF4] jhuex [NPHP1::GFP+FBF1::mCherry+pRF4] jhuex [K10G6.4::GFP+DYF-9::mCherry+pRF4] mnis17 [OSM6::GFP] hyls-1(tm3067)v; IsOSM-6 hyls-1(tm3067)v; Ex [CHE-11::GFP+pRF4] che-11(e1810)v; Ex [CHE-11::GFP+pRF4] jhuex [BBS-7::GFP +prf4] jhuex [BBS-7::GFP+MKS-5::mCherry+pRF4]
7 ZP2156 ZP2180 YH490 YH751 YH652 ZP2024 ZP2025 ZP2026 ZP2027 ZP2032 ZP2033 ZP1855 ZP1170 ZP1346 ZP2291 ZP2299 ZP2290 ZP2292 ZP2293 ZP2294 ZP2285 ZP2287 YH670 ZP2297 ZP2056 ZP2296 ZP2289 ZP2298 DAM278 DAM323 DAM324 hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex [BBS-7::GFP +prf4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex [BBS-7::GFP+MKS-5::mCherry+pRF4] yhex [MKS-1::YFP+CHE-13::CFP+pRF4] yhex [MKS-6::GFP+XBX-1::tdTomao+pRF4] yhex [GFP::MKS-3+XBX-1::tdTomato+pRF4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex [TBB-4::mCherry+DYF-19::GFP+pRF4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; yhex [GFP::MKS-3+XBX-1::tdTomato+pRF4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; yhex [MKS-1::YFP+CHE-13::CFP+pRF4] jhuex [TBB-4::mCherry+DYF-19::GFP+pRF4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex [NPHP1::GFP+FBF1::mCherry+pRF4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex [NPHP1::GFP+Gasr-8::mCherry+pRF4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex [RPI-2::GFP+MKS-5::mCherry+pRF4] jhuex [CHE-11::Venus1-173+IFT-20::Venus pRF4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex [CHE-11::Venus1-173+IFT-20::Venus pRF4] jhuex [XBX-1::Venus1-173+IFT-20::Venus pRF4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex [XBX-1::Venus1-173+IFT-20::Venus pRF4] jhuex [KAP-1::Venus1-173+IFT-20::Venus pRF4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex [KAP-1::Venus1-173+IFT-20::Venus pRF4] jhuex [OSM-3::Venus1-173+IFT-20::Venus pRF4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex [OSM-3::Venus1-173+IFT-20::Venus pRF4] jhuex[f29g9.2::gfp+mks-5::mcherry+prf4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex[f29g9.2::gfp+mks-5::mcherry+prf4] yhex[tram-1::tdtomato+mks-3::gfp+prf4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; yhex[tram-1::tdtomato+mks-3::gfp+prf4] jhuex[posm-9::osm-9::gfp+prf4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex[posm-9::osm-9::gfp+prf4] jhuex[parl-13::daf-21::gfp+prf4] hyls-1(tm3067)v; jhuex[parl-13::daf-21::gfp+prf4] viesi12[gfp::ccep-290; cb unc-119(+)] viesi22[gfp::mksr-2; cb unc-119(+)] viesi23[gfp::nphp-4; cb unc-119(+)]
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Functional Redundancy of the B9 Proteins and Nephrocystins in C. elegans Ciliogenesis. Bradley K. Yoder*
 Functional Redundancy of the B9 Proteins and Nephrocystins in C. elegans Ciliogenesis Corey L. Williams,* Marlene E. Winkelbauer, Jenny C. Schafer, Edward J. Michaud, and Bradley K. Yoder* *Department
Functional Redundancy of the B9 Proteins and Nephrocystins in C. elegans Ciliogenesis Corey L. Williams,* Marlene E. Winkelbauer, Jenny C. Schafer, Edward J. Michaud, and Bradley K. Yoder* *Department
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1: nlp-22 is expressed in the RIA interneurons and is secreted. (a) An animal expressing both the RIA specific reporter
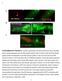 1 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1: nlp-22 is expressed in the RIA interneurons and is secreted. (a) An animal expressing both the RIA specific reporter Pglr-3:mCherry (red) and Pnlp-22:gfp (green) shows co-localization
1 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1: nlp-22 is expressed in the RIA interneurons and is secreted. (a) An animal expressing both the RIA specific reporter Pglr-3:mCherry (red) and Pnlp-22:gfp (green) shows co-localization
XBX-1 Encodes a Dynein Light Intermediate Chain Required for Retrograde Intraflagellar Transport and Cilia Assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans V
 Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 14, 2057 2070, May 2003 XBX-1 Encodes a Dynein Light Intermediate Chain Required for Retrograde Intraflagellar Transport and Cilia Assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans
Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 14, 2057 2070, May 2003 XBX-1 Encodes a Dynein Light Intermediate Chain Required for Retrograde Intraflagellar Transport and Cilia Assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans
Concentration memory-dependent synaptic plasticity of a taste circuit regulates salt chemotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans
 Supplementary Information for: Concentration memory-dependent synaptic plasticity of a taste circuit regulates salt chemotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans Hirofumi Kunitomo, Hirofumi Sato, Ryo Iwata, Yohsuke
Supplementary Information for: Concentration memory-dependent synaptic plasticity of a taste circuit regulates salt chemotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans Hirofumi Kunitomo, Hirofumi Sato, Ryo Iwata, Yohsuke
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.2860
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1: Hypomorphic expression of IFT88 results in olfactory signaling proteins no longer localizing to the ciliary layer. (a) ACIII localizes to the cilia and
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1: Hypomorphic expression of IFT88 results in olfactory signaling proteins no longer localizing to the ciliary layer. (a) ACIII localizes to the cilia and
Loss of C. elegans BBS-7 and BBS-8 protein function results in cilia defects and compromised intraflagellar transport
 Loss of C. elegans BBS-7 and BBS-8 protein function results in cilia defects and compromised intraflagellar transport Oliver E. Blacque, 1 Michael J. Reardon, 2 Chunmei Li, 1 Jonathan McCarthy, 1 Moe R.
Loss of C. elegans BBS-7 and BBS-8 protein function results in cilia defects and compromised intraflagellar transport Oliver E. Blacque, 1 Michael J. Reardon, 2 Chunmei Li, 1 Jonathan McCarthy, 1 Moe R.
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) .
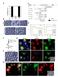 Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
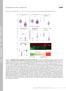 Supplemental material Brooks and Wallingford, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201204072/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Quantification of ciliary compartments in control
Supplemental material Brooks and Wallingford, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201204072/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Quantification of ciliary compartments in control
The Anticonvulsant Ethosuximide Disrupts Sensory Function to Extend C. elegans Lifespan
 The Anticonvulsant Ethosuximide Disrupts Sensory Function to Extend C. elegans Lifespan James J. Collins, Kimberley Evason, Christopher L. Pickett, Daniel L. Schneider, Kerry Kornfeld* Department of Developmental
The Anticonvulsant Ethosuximide Disrupts Sensory Function to Extend C. elegans Lifespan James J. Collins, Kimberley Evason, Christopher L. Pickett, Daniel L. Schneider, Kerry Kornfeld* Department of Developmental
Nephronophthisis (NPHP) is the most common genetic
 JCB: ARTICLE The Caenorhabditis elegans nephrocystins act as global modifiers of cilium structure Andrew R. Jauregui, 1,2 Ken C.Q. Nguyen, 4 David H. Hall, 4 and Maureen M. Barr 1,3 1 Department of Genetics,
JCB: ARTICLE The Caenorhabditis elegans nephrocystins act as global modifiers of cilium structure Andrew R. Jauregui, 1,2 Ken C.Q. Nguyen, 4 David H. Hall, 4 and Maureen M. Barr 1,3 1 Department of Genetics,
Cilia are present on almost every vertebrate cell and have
 Mutation of the MAP kinase DYF-5 affects docking and undocking of kinesin-2 motors and reduces their speed in the cilia of Caenorhabditis elegans Jan Burghoorn*, Martijn P. J. Dekkers*, Suzanne Rademakers*,
Mutation of the MAP kinase DYF-5 affects docking and undocking of kinesin-2 motors and reduces their speed in the cilia of Caenorhabditis elegans Jan Burghoorn*, Martijn P. J. Dekkers*, Suzanne Rademakers*,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
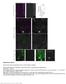 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Report. Kinesin-3 KLP-6 Regulates Intraflagellar Transport in Male-Specific Cilia of Caenorhabditis elegans
 Current Biology 21, 1 6, July 26, 211 ª211 Elsevier Ltd ll rights reserved DOI 1.116/j.cub.211.6.27 Kinesin-3 KLP-6 Regulates Intraflagellar Transport in Male-Specific Cilia of Caenorhabditis elegans Report
Current Biology 21, 1 6, July 26, 211 ª211 Elsevier Ltd ll rights reserved DOI 1.116/j.cub.211.6.27 Kinesin-3 KLP-6 Regulates Intraflagellar Transport in Male-Specific Cilia of Caenorhabditis elegans Report
General and cell-type specific mechanisms target TRPP2/PKD-2 to cilia
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 3859 Development 133, 3859-3870 (2006) doi:10.1242/dev.02555 General and cell-type specific mechanisms target TRPP2/PKD-2 to cilia Young-Kyung Bae 1,2, Hongmin Qin 3, *, Karla M. Knobel
RESEARCH ARTICLE 3859 Development 133, 3859-3870 (2006) doi:10.1242/dev.02555 General and cell-type specific mechanisms target TRPP2/PKD-2 to cilia Young-Kyung Bae 1,2, Hongmin Qin 3, *, Karla M. Knobel
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell extracts were subjected
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
Normal Ciliogenesis Requires Synergy between the Cystic Kidney Disease Genes MKS-3 and NPHP-4
 BASIC RESEARCH www.jasn.org Normal Ciliogenesis Requires Synergy between the Cystic Kidney Disease Genes MKS-3 and NPHP-4 Corey L. Williams, Svetlana V. Masyukova, and Bradley K. Yoder Department of Cell
BASIC RESEARCH www.jasn.org Normal Ciliogenesis Requires Synergy between the Cystic Kidney Disease Genes MKS-3 and NPHP-4 Corey L. Williams, Svetlana V. Masyukova, and Bradley K. Yoder Department of Cell
ns ns hp761(lf); daf-28(lf) daf-28(gf) Figure S1
 A ns ns B 100 100 80 80 60 60 40 40 20 20 0 0% 0 0% hp761(lf); daf-28(lf) daf-28(gf) Figure S1 A 100 80 15 o C 22 o C 25 o C % Dauers 60 40 20 0 0% 0% * 0% 0% 0% Class I alleles Class II alleles daf-2(lf;ts)
A ns ns B 100 100 80 80 60 60 40 40 20 20 0 0% 0 0% hp761(lf); daf-28(lf) daf-28(gf) Figure S1 A 100 80 15 o C 22 o C 25 o C % Dauers 60 40 20 0 0% 0% * 0% 0% 0% Class I alleles Class II alleles daf-2(lf;ts)
Supplementary Information
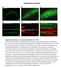 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Luminal localization of CCM-3. (a) The CCM-3::GFP fusion protein localizes along the apical (luminal) surface of the pharynx (b) as well as the lumen of
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Luminal localization of CCM-3. (a) The CCM-3::GFP fusion protein localizes along the apical (luminal) surface of the pharynx (b) as well as the lumen of
Active Transport and Diffusion Barriers Restrict Joubert Syndrome-Associated ARL13B/ARL-13 to an Inv-like Ciliary Membrane Subdomain
 Active Transport and Diffusion Barriers Restrict Joubert Syndrome-Associated ARL13B/ARL-13 to an Inv-like Ciliary Membrane Subdomain Sebiha Cevik 1, Anna A. W. M. Sanders 1., Erwin Van Wijk 2,3,4., Karsten
Active Transport and Diffusion Barriers Restrict Joubert Syndrome-Associated ARL13B/ARL-13 to an Inv-like Ciliary Membrane Subdomain Sebiha Cevik 1, Anna A. W. M. Sanders 1., Erwin Van Wijk 2,3,4., Karsten
Supplementary Figures
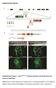 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
McWilliams et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB McWilliams et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201603039 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. In vitro characterization of mito-qc. (A and B) Analysis
Supplemental material JCB McWilliams et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201603039 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. In vitro characterization of mito-qc. (A and B) Analysis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by
 The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
 open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
Primary Cilia Can Both Mediate and Suppress Hedgehog Pathway- Dependent Tumorigenesis (Supplementary Figures and Materials)
 Primary Cilia Can Both Mediate and Suppress Hedgehog Pathway- Dependent Tumorigenesis (Supplementary Figures and Materials) Sunny Y. Wong, Allen D. Seol, Po-Lin So, Alexandre N. Ermilov, Christopher K.
Primary Cilia Can Both Mediate and Suppress Hedgehog Pathway- Dependent Tumorigenesis (Supplementary Figures and Materials) Sunny Y. Wong, Allen D. Seol, Po-Lin So, Alexandre N. Ermilov, Christopher K.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information CEP41 is mutated in Joubert syndrome and is required for tubulin glutamylation at the cilium Ji Eun Lee, Jennifer L. Silhavy, Maha S. Zaki, Jana Schroth, Stephanie L. Bielas,
Supplementary Information CEP41 is mutated in Joubert syndrome and is required for tubulin glutamylation at the cilium Ji Eun Lee, Jennifer L. Silhavy, Maha S. Zaki, Jana Schroth, Stephanie L. Bielas,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10643 Supplementary Table 1. Identification of hecw-1 coding polymorphisms at amino acid positions 322 and 325 in 162 strains of C. elegans. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 Supplementary Figure
doi:10.1038/nature10643 Supplementary Table 1. Identification of hecw-1 coding polymorphisms at amino acid positions 322 and 325 in 162 strains of C. elegans. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 Supplementary Figure
Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al
 Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Intraflagellar Transport Is Required for the Vectorial Movement of TRPV Channels in the Ciliary Membrane
 Current Biology, Vol. 15, 1695 1699, September 20, 2005, 2005 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved. DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2005.08.047 Intraflagellar Transport Is Required for the Vectorial Movement of TRPV Channels
Current Biology, Vol. 15, 1695 1699, September 20, 2005, 2005 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved. DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2005.08.047 Intraflagellar Transport Is Required for the Vectorial Movement of TRPV Channels
Supplementary Figure S1: Defective heterochromatin repair in HGPS progeroid cells
 Supplementary Figure S1: Defective heterochromatin repair in HGPS progeroid cells Immunofluorescence staining of H3K9me3 and 53BP1 in PH and HGADFN003 (HG003) cells at 24 h after γ-irradiation. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure S1: Defective heterochromatin repair in HGPS progeroid cells Immunofluorescence staining of H3K9me3 and 53BP1 in PH and HGADFN003 (HG003) cells at 24 h after γ-irradiation. Scale bar,
Supplementary Information
 1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
Base of Primary Cilia Using Superresolution STED Microscopy
 Revealing the Molecular Structure and the Transport Mechanism at the Base of Primary Cilia Using Superresolution STED Microscopy Tung-Lin Yang A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Revealing the Molecular Structure and the Transport Mechanism at the Base of Primary Cilia Using Superresolution STED Microscopy Tung-Lin Yang A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN
 UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
Expanded View Figures
 PEX13 functions in selective autophagy Ming Y Lee et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. PEX13 is required for Sindbis virophagy. A, B Quantification of mcherry-capsid puncta per cell (A) and GFP-LC3
PEX13 functions in selective autophagy Ming Y Lee et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. PEX13 is required for Sindbis virophagy. A, B Quantification of mcherry-capsid puncta per cell (A) and GFP-LC3
Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells. a. Schematic of the V-ATPase proton pump macro-complex structure. The V1 complex is composed of
Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells. a. Schematic of the V-ATPase proton pump macro-complex structure. The V1 complex is composed of
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass
 Supplementary material Figure S1. Interaction between UBL5 and FANCI A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis of UBL5-interacting proteins,
Supplementary material Figure S1. Interaction between UBL5 and FANCI A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis of UBL5-interacting proteins,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal
 Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal hydrocephalus Fadel TISSIR, Yibo QU, Mireille MONTCOUQUIOL, Libing ZHOU, Kouji KOMATSU, Dongbo SHI, Toshihiko FUJIMORI,
Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal hydrocephalus Fadel TISSIR, Yibo QU, Mireille MONTCOUQUIOL, Libing ZHOU, Kouji KOMATSU, Dongbo SHI, Toshihiko FUJIMORI,
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Chen et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201210119/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Lack of fast reversibility of UVR8 dissociation. (A) HEK293T
Supplemental material Chen et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201210119/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Lack of fast reversibility of UVR8 dissociation. (A) HEK293T
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1701143/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Impaired DNA replication derepresses chromatin and generates a transgenerationally inherited epigenetic memory Adam
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1701143/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Impaired DNA replication derepresses chromatin and generates a transgenerationally inherited epigenetic memory Adam
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
Supplementary table 1
 Supplementary table 1 S. pombe strain list Fig. 1A JX38 h + ade6-m216 nda3-km311 PX476 PW775 PX545 PX546 h- ade6-m216 sgo2::ura4 + nda3-km311 h 9 mad2::ura4 + nda3-km311 h + ade6-m21 nda3-km311 rad21 +
Supplementary table 1 S. pombe strain list Fig. 1A JX38 h + ade6-m216 nda3-km311 PX476 PW775 PX545 PX546 h- ade6-m216 sgo2::ura4 + nda3-km311 h 9 mad2::ura4 + nda3-km311 h + ade6-m21 nda3-km311 rad21 +
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
EGFR shrna A: CCGGCGCAAGTGTAAGAAGTGCGAACTCGAGTTCGCACTTCTTACACTTGCG TTTTTG. EGFR shrna B: CCGGAGAATGTGGAATACCTAAGGCTCGAGCCTTAGGTATTCCACATTCTCTT TTTG
 Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation.
 ` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
Supplementary Figure 1. MAT IIα is Acetylated at Lysine 81.
 IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
Supplemental Information. Proprioceptive Opsin Functions. in Drosophila Larval Locomotion
 Neuron, Volume 98 Supplemental Information Proprioceptive Opsin Functions in Drosophila Larval Locomotion Damiano Zanini, Diego Giraldo, Ben Warren, Radoslaw Katana, Marta Andrés, Suneel Reddy, Stephanie
Neuron, Volume 98 Supplemental Information Proprioceptive Opsin Functions in Drosophila Larval Locomotion Damiano Zanini, Diego Giraldo, Ben Warren, Radoslaw Katana, Marta Andrés, Suneel Reddy, Stephanie
Supporting Information
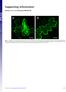 Supporting Information Harries et al. 1.173/pnas.9923916 A Fig. S1. Disruption of microfilaments within epidermal cells after treatment with 5 M Lat. Images of N. benthamiana cells are from plants expressing
Supporting Information Harries et al. 1.173/pnas.9923916 A Fig. S1. Disruption of microfilaments within epidermal cells after treatment with 5 M Lat. Images of N. benthamiana cells are from plants expressing
Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions
 nature methods Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions Mandy Glaß, Andreas Busche, Karen Wagner, Martin Messerle & Eva Maria Borst Supplementary figures and text:
nature methods Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions Mandy Glaß, Andreas Busche, Karen Wagner, Martin Messerle & Eva Maria Borst Supplementary figures and text:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
Jona Mijalkovic, Bram Prevo, Felix Oswald, Pierre Mangeol and Erwin J.G. Peterman. Nat Commun. 8, (2017)
 Jona Mijalkovic, Bram Prevo, Felix Oswald, Pierre Mangeol and Erwin J.G. Peterman Nat Commun. 8, 14591 (2017) Cytoplasmic dyneins drive microtubule-based, minus-end directed transport in eukaryotic cells.
Jona Mijalkovic, Bram Prevo, Felix Oswald, Pierre Mangeol and Erwin J.G. Peterman Nat Commun. 8, 14591 (2017) Cytoplasmic dyneins drive microtubule-based, minus-end directed transport in eukaryotic cells.
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
 Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1: Imaging T-ALL progression and growth in transplanted
 Supplementary Figure 1: Imaging T-ALL progression and growth in transplanted rag2e450fs fish. Monoclonal T-ALLs were serially passaged in strain fish and then used as donors (left panel). Cells were transplanted
Supplementary Figure 1: Imaging T-ALL progression and growth in transplanted rag2e450fs fish. Monoclonal T-ALLs were serially passaged in strain fish and then used as donors (left panel). Cells were transplanted
* * A3027. A4623 e A3507 A3507 A3507
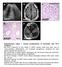 a c L A327 d e A37 A37 A37 Supplementary Figure 1. Clinical manifestations of individuals with mutations. (a) Renal ultrasound of right kidney in A327 reveals small renal cysts, loss of corticomedullary
a c L A327 d e A37 A37 A37 Supplementary Figure 1. Clinical manifestations of individuals with mutations. (a) Renal ultrasound of right kidney in A327 reveals small renal cysts, loss of corticomedullary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from WT and Adcy1 KO mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody.
 ADCY1 13 kda β-actin 45 kda Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from and mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody. a DHPG perk1/2 ERK1/2 Relative level min 1.6 *
ADCY1 13 kda β-actin 45 kda Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from and mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody. a DHPG perk1/2 ERK1/2 Relative level min 1.6 *
A. One to three months of age. Anterior Lens (Mean ± SEM) Posterior Lens (Mean ± SEM) Mid Lens (Mean ± SEM) Cornea (Mean ± SEM) Genotype
 Supplementary Table 1. Location of lens opacification in Aldh1a1(-/-), Aldh3a1(-/-) single and Aldh1a1(-/-)/Aldh3a1(-/-) double knockout mice (DKO) at different ages. A. One to three months of age Genotype
Supplementary Table 1. Location of lens opacification in Aldh1a1(-/-), Aldh3a1(-/-) single and Aldh1a1(-/-)/Aldh3a1(-/-) double knockout mice (DKO) at different ages. A. One to three months of age Genotype
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation
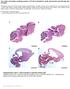 The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation Anita Becker-Heck#, Irene Zohn#, Noriko Okabe#, Andrew Pollock#, Kari Baker Lenhart,
The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation Anita Becker-Heck#, Irene Zohn#, Noriko Okabe#, Andrew Pollock#, Kari Baker Lenhart,
Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ).
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of the AA5x. a, Camera lucida drawing of embryo at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf, modified from Kimmel et al. Dev Dyn. 1995 203:253-310). b, Confocal microangiogram
Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of the AA5x. a, Camera lucida drawing of embryo at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf, modified from Kimmel et al. Dev Dyn. 1995 203:253-310). b, Confocal microangiogram
S1a S1b S1c. S1d. S1f S1g S1h SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. - si sc Il17rd Il17ra bp. rig/s IL-17RD (ng) -100 IL-17RD
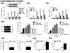 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Appendix. Table of Contents
 Appendix Table of Contents Appendix Figures Figure S1: Gp78 is not required for the degradation of mcherry-cl1 in Hela Cells. Figure S2: Indel formation in the MARCH6 sgrna targeted HeLa clones. Figure
Appendix Table of Contents Appendix Figures Figure S1: Gp78 is not required for the degradation of mcherry-cl1 in Hela Cells. Figure S2: Indel formation in the MARCH6 sgrna targeted HeLa clones. Figure
Kidney. Heart. Lung. Sirt1. Gapdh. Mouse IgG DAPI. Rabbit IgG DAPI
 a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Advances in pancreatic islet monolayer culture on glass surfaces enable superresolution microscopy and insights into beta cell ciliogenesis and proliferation Edward A. Phelps,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Advances in pancreatic islet monolayer culture on glass surfaces enable superresolution microscopy and insights into beta cell ciliogenesis and proliferation Edward A. Phelps,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR
 Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature07173 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure Legends: Supplementary Figure 1: Model of SSC and CPC divisions a, Somatic stem cells (SSC) reside adjacent to the hub (red), self-renew
doi: 10.1038/nature07173 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure Legends: Supplementary Figure 1: Model of SSC and CPC divisions a, Somatic stem cells (SSC) reside adjacent to the hub (red), self-renew
s -1 (A) and (B) 2 s 1 in WT, riq1, and the riq1 mutant complemented by
 A 250-2 s -1 B 250-2 s -1 Supplemental Figure 1. The NPQ Phenotype in riq Mutants Was Complemented by Introduction of RIQ Genes. (A) and (B) 2 s 1 in, riq1, and the riq1 mutant complemented by the RIQ1
A 250-2 s -1 B 250-2 s -1 Supplemental Figure 1. The NPQ Phenotype in riq Mutants Was Complemented by Introduction of RIQ Genes. (A) and (B) 2 s 1 in, riq1, and the riq1 mutant complemented by the RIQ1
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Supplementary Figure 1: Components of Arabidopsis tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Schematic summary of the TCA cycle and the enzymes related to the reactions. The large text and
Supplementary information Supplementary Figure 1: Components of Arabidopsis tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Schematic summary of the TCA cycle and the enzymes related to the reactions. The large text and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2294 Figure S1 Localization and function of cell wall polysaccharides in root hair cells. (a) Spinning-disk confocal sections of seven day-old A. thaliana seedlings stained with 0.1% S4B
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2294 Figure S1 Localization and function of cell wall polysaccharides in root hair cells. (a) Spinning-disk confocal sections of seven day-old A. thaliana seedlings stained with 0.1% S4B
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Supplemental Table S1. The list of peptides identified in TAP-WPP1 LC/MS/MS analysis, corresponding to HSC70.
 Supplemental Table S1. The list of peptides identified in TAP-WPP1 LC/MS/MS analysis, corresponding to HSC70. peptide MH+ charge XCorr score Delta Cn score Protein ID KNAVVTVPAYFNDSQRQ 1680.83 2 2.22 0.37
Supplemental Table S1. The list of peptides identified in TAP-WPP1 LC/MS/MS analysis, corresponding to HSC70. peptide MH+ charge XCorr score Delta Cn score Protein ID KNAVVTVPAYFNDSQRQ 1680.83 2 2.22 0.37
