ns ns hp761(lf); daf-28(lf) daf-28(gf) Figure S1
|
|
|
- Blaise Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A ns ns B % 0 0% hp761(lf); daf-28(lf) daf-28(gf) Figure S1
2 A o C 22 o C 25 o C % Dauers % 0% * 0% 0% 0% Class I alleles Class II alleles daf-2(lf;ts) B ns % Dauers % 0% Figure S2 daf-16; daf-2
3 B A GFP::DAF-16a muscle INS DAF-2 wt daf-2(e1370) X neurons DAF-16 wt daf-2(e1370) intestine NUCLEUS wt daf-2(e1370) Figure S3
4 A B kd kd * INS-4::GFP Pan Pan Pan Pan Pan ASI/ ASJ *non-specific band Figure S4
5 Supplemental Figure Legend Fig. S1. INS-5 does not regulate dauer formation (A) Wild-type animals (wt) and hpdf761; daf-28(lf) mutants exhibit 0% and 100% Dafc, respectively. Transgenic hpdf761; daf-28(lf) animals that overexpress INS-5, either from its endogenous promoter (+INS-5), or from an exogenous pan-neuronal promoter (+pan-neural INS-5), fail to alter the Daf-c penetrance. Overexpressing INS-6, under its endogenous promoter (+INS-6), in hp761; daf-28(lf), by contrast, led to a significant suppression of Daf-c penetrance. (B) An overexpression of INS-4 from either its endogenous promoter (+INS-4), or a GABAergic motor neuron promoter (+Punc-25- INS-4), in daf-28(gf) led to a full suppression of its Daf-c penetrance., p<0.001, ns, p>0.05 by the Tukey-Kramer comparison test. At least 200 animals were examined in 3 trials. Error bars, standard deviation. Figure S2. (A) hp761; daf-28(lf) mutants exhibit Daf-c penetrance that mimics daf-2(lf) A comparison of Daf-c penetrance between wild-type animals (wt), hp761; daf-28(lf) mutants, and five daf-2(lf;ts) alleles, at 15 o C (grey bars), 22 o C (yellow bars) and 25 o C (red bars). Class I and class II alleles of daf-2 were defined by their genetic interactions with another mutant daf-12 in a previous study (Gems et al., 1987). Class II daf-2 mutants were stronger loss of function alleles than Class I. At least 200 animals were examined in 3 trials., p<0.001; ns, p>0.05 by the Tukey-Kramer comparison test. Error bars, standard deviation. (B) DAF-16a and DAF-16d/f isoforms regulate dauer formation
6 Daf-c penetrance of animals of various genotypes at 25 o C. daf-16 fully suppressed the Daf-c phenotype of daf-2(lf;ts) mutants. daf-16(lf;null); daf-2(lf;ts) animals carrying an integrated transgene that expressed a single DAF-16 isoform, DAF-16a, DAF-16b, or DAF-16d/f, under the endogenous promoter, exhibited difference in Daf-c penetrance. Restoring DAF-16a and DAF-16d/f in daf-16; daf-2 both partially increased its Daf-c penetrance. Restoring DAF-16b had no effect. At least 200 animals were examined in 3 trials., p<0.001; ns, p>0.05 by the Tukey-Kramer comparison test. Error bars, standard deviation. Figure S3. Nucleus translation of tissue-specific GFP::DAF-16a transgenes in daf- 2(lf;ts) mutants (Left panel) A schematic representation of the canonical insulin signaling pathway. Activation of the insulin/igf receptor DAF-2 prevents DAF-16 from entering into nuclei. (Right panels) The subcellular localization of the GFP::DAF-16a reporter, expressed specifically in the body wall muscles (by Pmyo-3), the nervous system (by Prgef-1) and the intestine (by Pges-1) in wild-type animals and daf-2(lf;ts) mutants. In wild-type animals, all GFP::DAF-16a transgenes exhibit cytoplasmic signals. Reduced insulin signaling activity in daf-2 mutants leads to constitutive nuclear localization of GFP::DAF-16a in the respective tissues. Figure S4. DAF-28(gf) does not block INS-4 processing.
7 (A) A INS-4::GFP reporter, expressed by a panneuronal promoter, was processed in daf- 28(gf;ts) mutants. (B) A restricted expression of INS-4::GFP in ASI and ASJ (by Pdaf- 28) in daf-28(gf;ts) mutants also appeared processed.
8 List of single mutants Table S1 gene allele Comment daf-2 e1370 lf, ts e1368 lf, ts m569 lf, ts e979 lf, ts e1390 lf, ts kpc-1 gk8 lf, deletion egl-3 ok979 lf, deletion bli-4 e937 lf aex-5 sa23 lf daf-16 mu86 lf, deletion daf-28 sa191 ts,gf tm2308 lf ins-1 tm1888 lf, deletion ins-2 tm4467 lf, deletion ins-3 tm3608 lf, deletion ins-4 tm3620 lf, deletion ins-5 tm2560 lf, deletion ins-6 tm2416 lf, deletion ins-7 tm2001 lf, deletion ins-8 tm4144 lf, deletion ins-18 ok1672 lf, deletion lf= loss-of-function gf=gain-of-function ts=temperature-sensitive
9 List of Plasmids and transgenic lines Table S2 Plasmid Description background hpex pjh2292 pan-neural INS-2 daf-28(gf) 2292 pjh2293 pan-neural INS-3 daf-28(gf) 2372 pjh2265 pan-neural INS-4 daf-28(gf) 2369 pjh2356 pan-neural INS-5 daf-28(gf) 2373 pjh2266 pan-neural INS-6 daf-28(gf) 2370 pjh2947 pan-neural INS-2::GFP wt 3337 kpc egl pjh2916 pan-neural INS-3::GFP wt 3340 kpc egl pjh2255 pan-neural INS-4::GFP wt 2387 kpc egl bli-4 aex-5 pjh2256 pan-neural INS-6::GFP wt 2563 kpc egl bli-4 aex-5 pjh1922 pan-neural INS-1::GFP wt 3102 kpc egl pjh1498 pan-neural INS-18::GFP wt hpis164
10 List of Plasmids and transgenic lines pjh2741 pan-neural DAF-28::GFP wt 2876 kpc egl pjh3029 pan-neural INS-1::GFP A46A47 wt 3351 pjh3030 pan-neural INS-1::GFP A61A62 wt 3352 pjh3031 pan-neural INS-1::GFP A46A47A61A62 wt 3353 pjh2366 pan-neural INS-18::GFP A51A54 wt 2443 pjh2186 pan-neural INS-18::GFP A64A65 wt 3375 pjh2848 Pdaf-28-GFP wt 2974 pjh3374 Pdaf-28 DAF-28 hpdf761; daf-28(lf) 3505 pjh3188 Punc-25 DAF-28 hpdf761; daf-28(lf) 3355 pjh3189 Pacr-2 DAF-28 hpdf761; daf-28(lf) 3356 pjh2894 INS-4::GFP wt 2999 pjh2854 Pdaf-28 INS-4::GFP hpdf761; daf-28(lf) 3357 pjh2929 Punc-25 INS-4 hpdf761; daf-28(lf) 3316 pjh3278 Pacr-2 INS-4 hpdf761; daf-28(lf) 3315 pjh Pdaf-28 INS-4::GFP+Punc-25 INS-4 hpdf761; daf-28(lf) 3317 pjh3375 Pdaf-28 INS-6 hpdf761; daf-28(lf) 3506 pjh2974 Punc-25 INS-6 hpdf761; daf-28(lf) 3359 pjh3190 Pacr-2 INS-6 hpdf761; daf-28(lf) 3314 pjh3256 INS-1 SL2 GFP wt 3284 pjh3255 INS-18 SL2 GFP wt 3281
11 List of Plasmids and transgenic lines pjh3257 Pges-1 INS-1 ins-18; ins-1; daf-28(gf) 3285 pjh3258 Pges-1 INS-18 ins-18; ins-1; daf-28(gf) 3360 pjh1498 pan-neural INS-18::GFP ins-18; ins-1; daf-28(gf) 3361 pjh1922 pan-neural INS-1::GFP ins-18; ins-1; daf-28(gf) 3362 pjh1464 Pmyo-3 INS-18::RFP ins-18; ins-1; daf-28(gf) 3510 pjh2124 pan-neural EGL-3 egl-3 daf-28(lf) 3365 pjh3058 Pges-1 EGL-3 egl-3 daf-28(lf) 3276 pjh3376 Pmyo-3 EGL-3 egl-3 daf-28(lf) 3511 pjh3113 pan-neural KPC-1 mini-gene kpc-1; daf-28(lf) 3366 pjh3149 Pges-1 KPC-1 mini-gene kpc-1; daf-28(lf) 3362 pjh3252 KPC-1 SL-2 RFP wt 3368 pjh1630 Pdpy-30 DAF-2 daf-2(e1370) 2908 pjh616 Pmyo-3 DAF-2 daf-2(e1370) 2905 pjh664 pan-neural DAF-2 daf-2(e1370) 2906 pjh668 Pges-1 DAF-2 daf-2(e1370) 3369 pjh3043 Pdpy-30 DAF-16a daf-16(mu86); daf-2(e1370) 3370 pjh3185 pan-neural GFP::DAF-16a daf-16(mu86); daf-2(e1370) 3371 pjh2972 Pmyo-3 GFP::DAF-16a daf-16(mu86); daf-2(e1370) 3372 pjh2973 Pges-1 GFP::DAF-16a daf-16(mu86); daf-2(e1370) 3373 pjh3377 Pges-1 DAF-16d/f daf-16(mu86); daf-2(e1370) 3507 pjh2973+pjh3377 Pges-1 GFP::DAF-16a,d/f daf-16(mu86); daf-2(e1370) 3508 pjh2973+pjh3377 Pges-1 GFP::DAF-16a,d/f daf-16(mu86); hpdf761; daf-28(lf) 3509
12 List of Plasmids and transgenic lines pjh2606 MosDel targeting construct for ins-4 to ins-6 n/a hpdf761
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1: nlp-22 is expressed in the RIA interneurons and is secreted. (a) An animal expressing both the RIA specific reporter
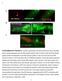 1 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1: nlp-22 is expressed in the RIA interneurons and is secreted. (a) An animal expressing both the RIA specific reporter Pglr-3:mCherry (red) and Pnlp-22:gfp (green) shows co-localization
1 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1: nlp-22 is expressed in the RIA interneurons and is secreted. (a) An animal expressing both the RIA specific reporter Pglr-3:mCherry (red) and Pnlp-22:gfp (green) shows co-localization
Supplementary Figure 1. Gene schematics of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4, and TEM analysis of TFs in WT and hyls-1 cilia. (a) Gene structure of hyls-1,
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene schematics of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4, and TEM analysis of TFs in WT and hyls-1 cilia. (a) Gene structure of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4 based on WormBase (http://wormbase.org),
Supplementary Figure 1. Gene schematics of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4, and TEM analysis of TFs in WT and hyls-1 cilia. (a) Gene structure of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4 based on WormBase (http://wormbase.org),
Diabetic pdx1-mutant zebrafish show conserved responses to nutrient overload and anti-glycemic treatment
 Supplementary Information Diabetic pdx1-mutant zebrafish show conserved responses to nutrient overload and anti-glycemic treatment Robin A. Kimmel, Stefan Dobler, Nicole Schmitner, Tanja Walsen, Julia
Supplementary Information Diabetic pdx1-mutant zebrafish show conserved responses to nutrient overload and anti-glycemic treatment Robin A. Kimmel, Stefan Dobler, Nicole Schmitner, Tanja Walsen, Julia
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
A conserved neuronal DAF-16/FoxO plays an important role in conveying
 SREP-17-10421.R2 Supplementary Information (clean version) Scientific Reports A conserved neuronal DAF-16/FoxO plays an important role in conveying pheromone signals to elicit repulsion behavior in Caenorhabditis
SREP-17-10421.R2 Supplementary Information (clean version) Scientific Reports A conserved neuronal DAF-16/FoxO plays an important role in conveying pheromone signals to elicit repulsion behavior in Caenorhabditis
Concentration memory-dependent synaptic plasticity of a taste circuit regulates salt chemotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans
 Supplementary Information for: Concentration memory-dependent synaptic plasticity of a taste circuit regulates salt chemotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans Hirofumi Kunitomo, Hirofumi Sato, Ryo Iwata, Yohsuke
Supplementary Information for: Concentration memory-dependent synaptic plasticity of a taste circuit regulates salt chemotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans Hirofumi Kunitomo, Hirofumi Sato, Ryo Iwata, Yohsuke
A novel fragile X syndrome mutation reveals a conserved role for the carboxy-terminus in FMRP localization and function
 A novel fragile X syndrome mutation reveals a conserved role for the carboxy-terminus in FMRP localization and function Zeynep Okray, Celine E.F. de Esch, Hilde Van Esch, Koen Devriendt, Annelies Claeys,
A novel fragile X syndrome mutation reveals a conserved role for the carboxy-terminus in FMRP localization and function Zeynep Okray, Celine E.F. de Esch, Hilde Van Esch, Koen Devriendt, Annelies Claeys,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2419 Figure S1 NiGFP localization in Dl mutant dividing SOPs. a-c) time-lapse analysis of NiGFP (green) in Dl mutant SOPs (H2B-RFP, red; clones were identified by the loss of nlsgfp) showing
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2419 Figure S1 NiGFP localization in Dl mutant dividing SOPs. a-c) time-lapse analysis of NiGFP (green) in Dl mutant SOPs (H2B-RFP, red; clones were identified by the loss of nlsgfp) showing
effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of ε j2b10 show no
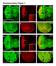 Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figures
 J. Cell Sci. 128: doi:10.1242/jcs.173807: Supplementary Material Supplementary Figures Fig. S1 Fig. S1. Description and/or validation of reagents used. All panels show Drosophila tissues oriented with
J. Cell Sci. 128: doi:10.1242/jcs.173807: Supplementary Material Supplementary Figures Fig. S1 Fig. S1. Description and/or validation of reagents used. All panels show Drosophila tissues oriented with
Supplemental Information. Figures. Figure S1
 Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0450 TITLE: The role of NF1 in memory retrieval PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yi Zhong, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0450 TITLE: The role of NF1 in memory retrieval PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yi Zhong, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724
Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
marker. DAPI labels nuclei. Flies were 20 days old. Scale bar is 5 µm. Ctrl is
 Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Aurora-A is essential for SAC establishment in early mitosis. (a-c) RPE cells were treated with DMSO (a), MLN8237 (b) or BI2536 (c) for Two hours.
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Aurora-A is essential for SAC establishment in early mitosis. (a-c) RPE cells were treated with DMSO (a), MLN8237 (b) or BI2536 (c) for Two hours.
Supplementary Figure 1. Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states.
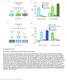 Supplementary Figure 1 Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states. (a) Protocol to produce exclusively hungry or thirsty flies for 6 h water memory retrieval. (b) Consumption assays
Supplementary Figure 1 Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states. (a) Protocol to produce exclusively hungry or thirsty flies for 6 h water memory retrieval. (b) Consumption assays
The Anticonvulsant Ethosuximide Disrupts Sensory Function to Extend C. elegans Lifespan
 The Anticonvulsant Ethosuximide Disrupts Sensory Function to Extend C. elegans Lifespan James J. Collins, Kimberley Evason, Christopher L. Pickett, Daniel L. Schneider, Kerry Kornfeld* Department of Developmental
The Anticonvulsant Ethosuximide Disrupts Sensory Function to Extend C. elegans Lifespan James J. Collins, Kimberley Evason, Christopher L. Pickett, Daniel L. Schneider, Kerry Kornfeld* Department of Developmental
WDR62 is associated with the spindle pole and mutated in human microcephaly
 WDR62 is associated with the spindle pole and mutated in human microcephaly Adeline K. Nicholas, Maryam Khurshid, Julie Désir, Ofélia P. Carvalho, James J. Cox, Gemma Thornton, Rizwana Kausar, Muhammad
WDR62 is associated with the spindle pole and mutated in human microcephaly Adeline K. Nicholas, Maryam Khurshid, Julie Désir, Ofélia P. Carvalho, James J. Cox, Gemma Thornton, Rizwana Kausar, Muhammad
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
Infect MCF-7 cells carrying dcas9-vp64 + psm2-p65-hsf1 with SAM library or vector. Introduce AKT reporter
 Infect MCF-7 cells carrying dcas9-vp64 + psm2-p65-hsf1 with SM library or vector Introduce reporter Grow cells in presence of puromycin for 5 days Vector control SM library fewer surviving cells More surviving
Infect MCF-7 cells carrying dcas9-vp64 + psm2-p65-hsf1 with SM library or vector Introduce reporter Grow cells in presence of puromycin for 5 days Vector control SM library fewer surviving cells More surviving
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figures
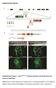 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplemental Data. Deinlein et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 µm Zn 2+ 15 µm Zn 2+ Growth (% of control) empty vector NS1 NS2 NS3 NS4 S. pombe zhfδ Supplemental Figure 1. Functional characterization of. halleri NS genes in Zn 2+ hypersensitive S. pombe Δzhf mutant
µm Zn 2+ 15 µm Zn 2+ Growth (% of control) empty vector NS1 NS2 NS3 NS4 S. pombe zhfδ Supplemental Figure 1. Functional characterization of. halleri NS genes in Zn 2+ hypersensitive S. pombe Δzhf mutant
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical
 Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical representation using all SNPs (n= 13,515,798) including the region on chromosome 1 including SORT1 which was previously
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical representation using all SNPs (n= 13,515,798) including the region on chromosome 1 including SORT1 which was previously
A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis. Midbrain Forebrain/ Forebrain/ Hindbrain Spinal cord Hindbrain Hindbrain
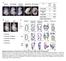 A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis NTD Number of embryos % among NTD Embryos Exencephaly 52 74.3% Craniorachischisis 6 8.6% Spina bifida 5 7.1% Microcephaly 7 1% B Normal
A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis NTD Number of embryos % among NTD Embryos Exencephaly 52 74.3% Craniorachischisis 6 8.6% Spina bifida 5 7.1% Microcephaly 7 1% B Normal
Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation.
 ` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
Supplemental Information. Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like. Behaviors in Mice by Modulating. Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation
 Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN
 UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
Supplementary Information
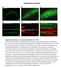 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Luminal localization of CCM-3. (a) The CCM-3::GFP fusion protein localizes along the apical (luminal) surface of the pharynx (b) as well as the lumen of
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Luminal localization of CCM-3. (a) The CCM-3::GFP fusion protein localizes along the apical (luminal) surface of the pharynx (b) as well as the lumen of
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1701143/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Impaired DNA replication derepresses chromatin and generates a transgenerationally inherited epigenetic memory Adam
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1701143/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Impaired DNA replication derepresses chromatin and generates a transgenerationally inherited epigenetic memory Adam
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SYPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Figure S1. Phylogenic studies of the mir-183/96/182 cluster and 3 -UTR of Casp2. (A) Genomic arrangement of the mir-183/96/182 cluster in vertebrates.
SYPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Figure S1. Phylogenic studies of the mir-183/96/182 cluster and 3 -UTR of Casp2. (A) Genomic arrangement of the mir-183/96/182 cluster in vertebrates.
Supplemental Figures
 Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1. Fasting-dependent regulation of the SREBP ortholog SBP-1 and lipid homeostasis mediated by the SIRT1 ortholog SIR-2.1 in C. elegans. (A) Wild-type or sir-2.1(lof)
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1. Fasting-dependent regulation of the SREBP ortholog SBP-1 and lipid homeostasis mediated by the SIRT1 ortholog SIR-2.1 in C. elegans. (A) Wild-type or sir-2.1(lof)
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of Per2 deletion in neuronal cells in N Per2 -/- mice. (a) Western blot from liver extracts of mice held under ad
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of Per2 deletion in neuronal cells in N Per2 -/- mice. (a) Western blot from liver extracts of mice held under ad libitum conditions detecting PER2 protein in brain and
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of Per2 deletion in neuronal cells in N Per2 -/- mice. (a) Western blot from liver extracts of mice held under ad libitum conditions detecting PER2 protein in brain and
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
GFP/Iba1/GFAP. Brain. Liver. Kidney. Lung. Hoechst/Iba1/TLR9!
 Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Ras V12 expression in the entire eye-antennal disc does not cause invasive tumours. a, Eye-antennal discs expressing Ras V12 in all cells (marked with GFP, green) overgrow moderately
Supplementary Figure 1. Ras V12 expression in the entire eye-antennal disc does not cause invasive tumours. a, Eye-antennal discs expressing Ras V12 in all cells (marked with GFP, green) overgrow moderately
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS... 2 11 MOVIE S1... 2 FIGURE S1 LEGEND... 3 FIGURE S2 LEGEND... 4 FIGURE S3 LEGEND... 5 FIGURE S4 LEGEND... 6 FIGURE S5 LEGEND... 7 FIGURE S6 LEGEND... 8 FIGURE
TABLE OF CONTENTS SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS... 2 11 MOVIE S1... 2 FIGURE S1 LEGEND... 3 FIGURE S2 LEGEND... 4 FIGURE S3 LEGEND... 5 FIGURE S4 LEGEND... 6 FIGURE S5 LEGEND... 7 FIGURE S6 LEGEND... 8 FIGURE
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 how HFD how HFD Epi WT p p Hypothalamus p p Inguinal WT T Liver Lean mouse adipocytes p p p p p p Obese mouse adipocytes Kidney Muscle Spleen Heart p p p p p p p p Extracellular
Supplementary Figure 1 how HFD how HFD Epi WT p p Hypothalamus p p Inguinal WT T Liver Lean mouse adipocytes p p p p p p Obese mouse adipocytes Kidney Muscle Spleen Heart p p p p p p p p Extracellular
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary s Supplementary 1 All three types of foods suppress subsequent feeding in both sexes when the same food is used in the pre-feeding test feeding. (a) Adjusted pre-feeding
Supplementary Information Supplementary s Supplementary 1 All three types of foods suppress subsequent feeding in both sexes when the same food is used in the pre-feeding test feeding. (a) Adjusted pre-feeding
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Mutations in the Caenorhabditis elegans U2AF Large Subunit UAF-1 Al= of a 3' Splice Site In Vivo
 Mutations in the Caenorhabditis elegans U2AF Large Subunit UAF-1 Al= of a 3' Splice Site In Vivo The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Mutations in the Caenorhabditis elegans U2AF Large Subunit UAF-1 Al= of a 3' Splice Site In Vivo The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
CD3 coated cover slips indicating stimulatory contact site, F-actin polymerization and
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES FIGURE S1. Detection of MCs. A, Schematic representation of T cells stimulated on anti- CD3 coated cover slips indicating stimulatory contact site, F-actin polymerization and microclusters.
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES FIGURE S1. Detection of MCs. A, Schematic representation of T cells stimulated on anti- CD3 coated cover slips indicating stimulatory contact site, F-actin polymerization and microclusters.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
 Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Normal sleep bouts are not essential for C. elegans survival and FoxO is important for compensatory changes in sleep
 Bennett et al. BMC Neurosci (218) 19:1 https://doi.org/1.1186/s12868-18-48-1 BMC Neuroscience RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Normal sleep bouts are not essential for C. elegans survival and FoxO is important
Bennett et al. BMC Neurosci (218) 19:1 https://doi.org/1.1186/s12868-18-48-1 BMC Neuroscience RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Normal sleep bouts are not essential for C. elegans survival and FoxO is important
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Overall, this is an interesting study. The authors used a custom microfluidic device to deliver precise concentrations of bacterial food to worms
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Overall, this is an interesting study. The authors used a custom microfluidic device to deliver precise concentrations of bacterial food to worms
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
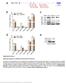 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Information. Cofilin Regulates Nuclear Architecture through a Myosin-II Dependent Mechanotransduction Module
 Supplementary Information Cofilin Regulates Nuclear Architecture through a Myosin-II Dependent Mechanotransduction Module O Neil Wiggan, Bryce Schroder, Diego Krapf, James R. Bamurg and Jennifer G. DeLuca
Supplementary Information Cofilin Regulates Nuclear Architecture through a Myosin-II Dependent Mechanotransduction Module O Neil Wiggan, Bryce Schroder, Diego Krapf, James R. Bamurg and Jennifer G. DeLuca
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed
 Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Kidney. Heart. Lung. Sirt1. Gapdh. Mouse IgG DAPI. Rabbit IgG DAPI
 a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 sirna pool: Control Tetherin -HA-GFP HA-Tetherin -Tubulin Supplementary Figure S1. Knockdown of HA-tagged tetherin expression by tetherin specific sirnas. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing
sirna pool: Control Tetherin -HA-GFP HA-Tetherin -Tubulin Supplementary Figure S1. Knockdown of HA-tagged tetherin expression by tetherin specific sirnas. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing
33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58
 Pro-rich region Trans-membrane region 214 246 359 381 UL50 1 397 211SSRTAS216PPPPPR222 NLS CR1 CR2 CR3 CR4 UL53 1 376 11RERRS15ALRS19LLRKRRR25 33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58 FIG S1. UL97 phosphorylation
Pro-rich region Trans-membrane region 214 246 359 381 UL50 1 397 211SSRTAS216PPPPPR222 NLS CR1 CR2 CR3 CR4 UL53 1 376 11RERRS15ALRS19LLRKRRR25 33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58 FIG S1. UL97 phosphorylation
Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state Thirsty but not sated wild-type flies form robust 3 min memory. For the thirsty group, the flies were water-deprived
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state Thirsty but not sated wild-type flies form robust 3 min memory. For the thirsty group, the flies were water-deprived
Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc.
 Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc. a,b, Test of put RNAi. a, In wildtype discs the Dpp target gene Sal (red) is expressed in a broad stripe in the centre of the ventral
Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc. a,b, Test of put RNAi. a, In wildtype discs the Dpp target gene Sal (red) is expressed in a broad stripe in the centre of the ventral
supplementary information
 DOI: 1.138/ncb1 Control Atg7 / NAC 1 1 1 1 (mm) Control Atg7 / NAC 1 1 1 1 (mm) Lamin B Gstm1 Figure S1 Neither the translocation of into the nucleus nor the induction of antioxidant proteins in autophagydeficient
DOI: 1.138/ncb1 Control Atg7 / NAC 1 1 1 1 (mm) Control Atg7 / NAC 1 1 1 1 (mm) Lamin B Gstm1 Figure S1 Neither the translocation of into the nucleus nor the induction of antioxidant proteins in autophagydeficient
Pervasive positive and negative feedback regulation of insulin-like signaling in Caenorhabditis. elegans
 Genetics: Early Online, published on November 13, 2018 as 10.1534/genetics.118.301702 1 2 Pervasive positive and negative feedback regulation of insulin-like signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans 3 4 Rebecca
Genetics: Early Online, published on November 13, 2018 as 10.1534/genetics.118.301702 1 2 Pervasive positive and negative feedback regulation of insulin-like signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans 3 4 Rebecca
Supplemental Data. Di Giorgio et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Synteny analysis of NIP4;1 and NIP4;2. Examination of the NIP4;1-NIP4;2 region in rabidopsis thaliana and equivalent evolutionary regions in other dicot genomes are shown on the
Supplemental Figure 1. Synteny analysis of NIP4;1 and NIP4;2. Examination of the NIP4;1-NIP4;2 region in rabidopsis thaliana and equivalent evolutionary regions in other dicot genomes are shown on the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10643 Supplementary Table 1. Identification of hecw-1 coding polymorphisms at amino acid positions 322 and 325 in 162 strains of C. elegans. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 Supplementary Figure
doi:10.1038/nature10643 Supplementary Table 1. Identification of hecw-1 coding polymorphisms at amino acid positions 322 and 325 in 162 strains of C. elegans. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells. a. Schematic of the V-ATPase proton pump macro-complex structure. The V1 complex is composed of
Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells. a. Schematic of the V-ATPase proton pump macro-complex structure. The V1 complex is composed of
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.2860
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1: Hypomorphic expression of IFT88 results in olfactory signaling proteins no longer localizing to the ciliary layer. (a) ACIII localizes to the cilia and
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1: Hypomorphic expression of IFT88 results in olfactory signaling proteins no longer localizing to the ciliary layer. (a) ACIII localizes to the cilia and
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
p.r623c p.p976l p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r2922w p.r2370h p.c1201y p.a868v p.s952* RING_C BP PHD Cbp HAT_KAT11
 ARID2 p.r623c KMT2D p.v650fs p.p976l p.r2922w p.l1212r p.d1400h DNA binding RFX DNA binding Zinc finger KMT2C p.a51s p.d372v p.c1103* p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r4586h PHD/ RING DHHC/ PHD PHD FYR N
ARID2 p.r623c KMT2D p.v650fs p.p976l p.r2922w p.l1212r p.d1400h DNA binding RFX DNA binding Zinc finger KMT2C p.a51s p.d372v p.c1103* p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r4586h PHD/ RING DHHC/ PHD PHD FYR N
50mM D-Glucose. Percentage PI. L-Glucose
 Monica Dus, Minrong Ai, Greg S.B Suh. Taste-independent nutrient selection is mediated by a brain-specific Na+/solute cotransporter in Drosophila. Control + Phlorizin mm D-Glucose 1 2mM 1 L-Glucose Gr5a;Gr64a
Monica Dus, Minrong Ai, Greg S.B Suh. Taste-independent nutrient selection is mediated by a brain-specific Na+/solute cotransporter in Drosophila. Control + Phlorizin mm D-Glucose 1 2mM 1 L-Glucose Gr5a;Gr64a
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2153 Figure S1 Ectopic expression of HAUSP up-regulates REST protein. (a) Immunoblotting showed that ectopic expression of HAUSP increased REST protein levels in ENStemA NPCs. (b) Immunofluorescent
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2153 Figure S1 Ectopic expression of HAUSP up-regulates REST protein. (a) Immunoblotting showed that ectopic expression of HAUSP increased REST protein levels in ENStemA NPCs. (b) Immunofluorescent
a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1. Induction of p53 LOH by MADM. a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53 mouse revealed increased p53 KO/KO (green,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1. Induction of p53 LOH by MADM. a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53 mouse revealed increased p53 KO/KO (green,
Supplementary material Legends to Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3.
 Supplementary material Legends to Supplementary Figures. Figure S1. Expression of BICD-N-MTS fusion does not affect the distribution of the Golgi and endosomes. HeLa cells were transfected with GFP-BICD-N-MTS
Supplementary material Legends to Supplementary Figures. Figure S1. Expression of BICD-N-MTS fusion does not affect the distribution of the Golgi and endosomes. HeLa cells were transfected with GFP-BICD-N-MTS
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh
 Developmental Cell 13 Supplemental Data Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh that Maintains Microtubule Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Katja Dahlgaard, Alexandre A.S.F. Raposo, Teresa
Developmental Cell 13 Supplemental Data Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh that Maintains Microtubule Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Katja Dahlgaard, Alexandre A.S.F. Raposo, Teresa
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
Supplementary Figure 1. MAT IIα is Acetylated at Lysine 81.
 IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
Phenomena first observed in petunia
 Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Fig. S1. Weights of full-dose treatment groups comparing 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd generation gene replacement therapy. Mice were treated at p1 with 4x10 11 GC of the three different
Supplementary Materials Fig. S1. Weights of full-dose treatment groups comparing 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd generation gene replacement therapy. Mice were treated at p1 with 4x10 11 GC of the three different
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Information A Hydrophobic Barrier Deep Within the Inner Pore of the TWIK-1 K2P Potassium Channel Aryal et al.
 Supplementary Information A Hydrophobic Barrier Deep Within the Inner Pore of the TWIK-1 K2P Potassium Channel Aryal et al. Supplementary Figure 1 TWIK-1 stability during MD simulations in a phospholipid
Supplementary Information A Hydrophobic Barrier Deep Within the Inner Pore of the TWIK-1 K2P Potassium Channel Aryal et al. Supplementary Figure 1 TWIK-1 stability during MD simulations in a phospholipid
Genetic suppressors and enhancers provide clues to gene regulation and genetic pathways
 Genetic suppressors and enhancers provide clues to gene regulation and genetic pathways Suppressor mutation: a second mutation results in a less severe phenotype than the original mutation Suppressor mutations
Genetic suppressors and enhancers provide clues to gene regulation and genetic pathways Suppressor mutation: a second mutation results in a less severe phenotype than the original mutation Suppressor mutations
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 NLRP12 is downregulated in biopsy samples from patients with active ulcerative colitis (UC). (a-g) NLRP12 expression in 7 UC mrna profiling studies deposited in NCBI GEO database.
Supplementary Figure 1 NLRP12 is downregulated in biopsy samples from patients with active ulcerative colitis (UC). (a-g) NLRP12 expression in 7 UC mrna profiling studies deposited in NCBI GEO database.
