HA-Sin1-N (aa 1-137), HA-Sin1-CRIM (aa ) and HA-Sin1-RBD (aa ) were constructed by
|
|
|
- Ashlee Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EXTENDED METHODS Plasmids HA-Sin1-N (aa 1-137), HA-Sin1-CRIM (aa ) and HA-Sin1-RBD (aa ) were constructed by cloning the corresponding cdnas into psuper-ha-cdna3 vector via BamHI/BglII and EcoRI sites. HA-Sin1-PH (aa ) or CMV-GST-Sin1-PH was constructed by cloning the corresponding cdnas into psuper-ha-cdna3, pgex-4t-1 or pcmv-gst vector via BamHI/BglII and XhoI/SalI sites. HA-mTOR-KD and Flag-mTOR-KD (aa ) were constructed by cloning the corresponding cdnas into pcdna3-ha or pcdna3-flag vector via BamHI and EcoRI sites. pcmv-gst-mtor fragments were constructed by cloning the corresponding cdnas into pcmv-gst vector through BamHI and XhoI sites, except mtor-heat was cloned using SalI and NotI sites. The chimeric pcdna3-ha-sin1-ph-akt1-wt was constructed by ligating Sin1-PH PCR products into the pcdna3-ha-akt1-δph construct through BamHI/BglII and EcoRI sites. pgex-4t-1-sin1-n, CRIM, RBD and PH constructs are as described previously (1). pgex-4t-1-plcδ-ph was constructed by subcloning BamHI/EcoRI digested PLCδ-PH PCR products into pgex-4t-1 vector. pcmv-gst-rpl26 was constructed by cloning BamHI/SalI cut RPL26 PCR products into pcmv-gst vector. Various Sin1 mutants were generated using the QuikChange XL Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Stratagene) according to the manufacturer s instructions. shsin1-resistant mutants were generated with specific primer sequences listed below to generate the silent mutations : 5 -CGCAAATTGACATAGCCACCGTGCAAGATATGCAAGATATGCTTAGCAGCC-3 (sense) and 5 -GGCTGCTAAGCATATCTTGCACGGTGGCTATGTCAATTTGCG-3 (antisense). The CAAX versions of Sin1 constructs were generated by the following PCR primers: forward (5 -GCATAGATCTCGATCTGAGAACTTCAGG-3 ) and reverse (5 -GCATGAATTCTTACATAAT TACACACTTTGTCTTTGACTTCTTTTTCTTCTTTTTGCCGCCCTGCTGCCCGGATTTCTTC-3.
2 Details of plasmid constructions will be provided upon request. shrnas shrna vectors to deplete endogenous human PIKFYVE were purchased from GE Dharmacon (RHS4533-EG200576). shrna vectors to deplete endogenous human PIK3CA were also purchased from GE Dharmacon (RHS4533-EG5290). To generate the lenti-viral shrna construct against human Sin1, the following sequences were cloned into the plko-hygro-lenti-viral vectors (sense: 5 -GCCACAGTACAGGATATGCTT-3 ; anti-sense: 5 -AAGCATATCCTGTACTGTGGC-3 ). Cell Fractionation Cell fractionation was performed using the fractionation kit purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (9018) according to manufacture s instructions. The MST Analysis The determination of the binding affinity between GST-Akt1-PH (aa 1-107) or GST-Sin1-PH (aa 1-137) and IP4 was performed by MST according to manufacturer s instructions with 60% LED power and 40% MST power (Nano Temper, Monolith NT.115). Fluorescently labeled GST-Akt1-PH proteins or GST-Sin1-PH proteins were used as tracer. The final concentrations of peptides ranged from 122 nm to 2 mm. Colony Formation Assays Cells were seeded in 6-well plates (300 or 600 cells/well) and left for 8-12 days until formation of visible 2
3 colonies. Colonies were washed with PBS and fixed with 10% acetic acid/10% methanol for 20 min, then stained with 0.4% crystal violet/20% ethanol for 20 min. After staining, the plates were washed with distilled water and air-dried. Cell Viability Assays Cells were plated at 3,000 per well in 96-well plates, and incubated with complete DMEM medium containing different concentrations of etoposide (Sigma, E1383), cisplatin (Selleck S1166), doxorubicin (Sigma, D1515) or Taxol (Sigma T7191) for 24 or 48 hr as indicated. Assays were performed with CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay Kit according to the manufacturer s instructions (Promega). Soft Agar Assays The anchorage independence cell growth assays were performed as described previously (2). Briefly, the assays were preformed using 6-well plates and the solid medium consists of two layers. The bottom layer contains 0.8% noble agar and the top layer contains 0.4% agar. 1x10 5 cells were plated in the top layer. 500 µl complete DMEM medium was added every 3 days to keep the top layer moistured and 4 weeks later the cells were stained with iodonitrotetrazolium chloride for colony visualization and counting. Three independent experiments were performed to generate the error bar. 3
4 SUPPLEMENTAL REFERENCES 1. Liu P, Gan W, Inuzuka H, Lazorchak AS, Gao D, Arojo O, et al. Sin1 phosphorylation impairs mtorc2 complex integrity and inhibits downstream Akt signalling to suppress tumorigenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15: Liu P, Begley M, Michowski W, Inuzuka H, Ginzberg M, Gao D, et al. Cell-cycle-regulated activation of Akt kinase by phosphorylation at its carboxyl terminus. Nature. 2014;508:
5 A mtor! FRB+KD-L! FRB! N-FATC! HEAT (23)! FAT/TRD! KD! 1! ! KD-L! (kinase domain-long)! N-LBE! LBE! C! KD (kinase domain)! FRB! N! LBE! C! FATC! 2001! 2114! 2258! 2298! 2518! 2549! FRB! 2001! 2114! ΔPH! N! LBE! C! 2114! 2258! 2298! 2518! N! LBE! C! 2114! 2258! 2298! N! LBE! 2114! 2258! 2298! LBE! 2258! 2298! LBE! 2298! C! FATC! 2518! 2518! ! 2298! 2431! -total! IB: S6K-pT389! IB: S6K! 2549! B C D E H ΔPH! CMV-GST-mTOR-KD-L! Sin1! Rictor! GβL! Raptor! OVCAR5 -total! IB: S6K-pT389! IB: S6K1! HA -constructs! HA-Sin1-PH -ps473 -pt308 1 IB: PKC-pS657 GST pull down! IB: NDRG-pT346 IB: S6K-pT389 IB: S6K1 IB: Tubulin N CMV-GST-mTOR-C! I! ΔN Sin1! Rictor! 293T Raptor! HA-Sin1 GβL! -ps473 -pt308 1 IB: S6K-pT389 IB: S6K HA! HA-Sin1-PH -ps473 -pt308 1 IB: S6K-pT389 IB: S6K1 IB: Tubulin N N! CRIM! RBD! PH! 1! 137! 266! 279! 353! 376! 486! 522! MEKK2! JNK! msin1.1! Ras! F! G HA-Sin1-PH! ! PC3! HA-Sin1-N! ! N! CRIM! RBD! PH! 293T! HA-Sin1-PH! HEAT! IB: ps6! IB: S6! FAT! KDL! CMV-GST -mtor! GST-Akt1-tail ( )! GST! -! +! -! +! +! +! HA-Sin1-PH! 0 2 4! J! K L! M N O P Q ΔN HA-Sin1 -ps473 -pt308 1 IB: S6K-pT389 IB: S6K OVCAR5! HA-Sin1-N! ! U2OS! ΔPH! FRB! N-FATC! +! +! +! GST-Sin1-N! mtor! GST-Sin1-N! GST-Akt1-tail! GST! γ 32 P-Akt! -total! IB: S6K-pT389! IB: S6K1! CMV-GST -mtor! HA-Sin1-PH! R SK-MEL-28! N-FATC! KD-L! N-LBE! +! +! +! +! CMV-GST -mtor! HA-Sin1-PH! S N-FATC! KD-L! PC3! KD-L! C! LBE! +! +! +! +! +! +! J! CMV-GST -mtor! HA-Sin1-PH! KD-L! KD! 293 CMV-GST-mTOR! +! +! +! HA-Sin1-PH! IB: Tubulin T! U IP: Flag! ΔPH! 231 +! +! +! Flag-mTOR-KD! IB: Flag! IB: Flag! IB: Tubulin V ΔPH! +! +! +! Flag-mTOR! IB: Flag! IB: Flag! W IP: Flag! IB: Flag! IB: Flag! HA-Sin1-PH! +! +! +! +! HA-Rictor! +! +! +! +! Flag-mTOR! IB: HA-Sin1-PH! IB: HA-Rictor! IB: HA-Sin1-PH! IB: HA-RIctor! X EV N CRIM RBD PH WT ΔPH ΔN HA-Sin1 +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! Flag-mTOR IB: Flag Y Rictor! Sin1! IB: Flag KD! PH! PH! mtor! GßL! 5
6 Figure S1. The Sin1-PH domain binds the mtor kinase domain to inhibit mtor kinase activity, Related to Figure 1. A, A schematic illustration of the mtor truncations used in this study. B, The kinase domain (KD-L, aa ) of the mtor kinase mainly interacts with Sin1 and GβL. Immunoblot (IB) analysis of whole cell lysates (WCLs) and HA-immunoprecipitates (IP) derived from HEK293T cells transfected with CMV-GST-mTOR-KD-L and indicated HA tagged mtorc2 subunits. C, The C-loop (aa ) of the mtor kinase domain (KD) mainly interacts with Sin1, but not other mtorc2 components. IB analysis of whole cell lysates (WCLs) and GST pull downs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with CMV-GST-mTOR-C and indicated HA tagged mtorc2 subunits. D, A schematic illustration of Sin1 interaction domains with indicated enzymes. E, In vitro kinase assays to demonstrate that addition of increasing doses of bacterially purified GST-Sin1-N proteins did not significantly interfere with active mtor to phosphorylation Akt in vitro. F-G, Sin1-PH motif, but not Sin1-N terminus, suppresses mtorc2 to phosphorylate Akt-S473 in cells. IB analysis of WCLs derived from PC3 (F) or OVCAR5 (G) cells transfected with increasing doses of HA-Sin1-PH. H-I, Expression of Sin1-PH leads to reduced mtorc2, but not mtorc1 activity in cells. IB analysis of WCLs derived from OVCAR5 (H) or 293T (I) cells transfected with increasing doses of HA-Sin1-PH construct. J, Expression of Sin1-PH, but not other domains of Sin1 leads to reduced Akt-pS473 in cells. IB analysis of WCLs derived from 293T cells transfected with increasing doses of HA-Sin1 constructs. K-M, Expression of full-length Sin1, but not PH domain truncated Sin1 leads to reduced mtorc2, but not mtorc1 activity in cells. IB analysis of WCLs derived from U2OS (K), SK-MEL-28 (L) or PC3 (M) cells transfected with increasing doses of HA-Sin1 constructs. N-O, Expression of N-terminus truncated Sin1, but not N-terminus itself leads to reduced Akt-pS473, but not mtorc1 activity in cells. IB analysis of WCLs derived from HEK293 (N) or MDA-MB-231 (O) cells transfected with increasing doses of HA-Sin1 constructs. P, Sin1-PH interacts with mtor kinase domain (mtor-kdl), but not the mtor-heat or FAT domain in cells. IB analysis of WCLs and HA-IPs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with indicated constructs. Q, Sin1-PH interacts with mtor-n-fatc, but not mtor-frb domain in cells. IB analysis of WCLs and HA-IPs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with indicated constructs. R, The C-loop of the mtor catalytic region is critical for mtor interaction with Sin1-PH. IB analysis of WCLs and HA-IPs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with indicated constructs. S, mtor-c-loop but not mtor-lbe domain binds Sin1-PH in cells. IB analysis of WCLs and HA-IPs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with indicated constructs. T, mtor-kd-l and mtor-kd have similar affinity towards binding Sin1-PH in cells. IB analysis of WCLs and HA-IPs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with indicated constructs. U, The mtor kinase domain mainly interacts with Sin1-PH motif. IB analysis of WCLs and Flag-IPs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with GST-mTOR-KD-L and indicated HA-Sin1 constructs. V, Full-length mtor interacts with Sin1 through motifs including, but not restricted to, the Sin1-PH motif. IB analysis of WCLs and HA-IPs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with Flag-mTOR and indicated HA-Sin1 constructs. 6
7 W, Sin1-PH motif does not interfere with Rictor and mtor interaction. IB analysis of WCLs and Flag-IPs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with indicated constructs. X, Various Sin1 truncation mutants remain contacts with full-length mtor. IB analysis of WCLs and HA-IPs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with indicated Sin1 constructs with Flag-mTOR. Y, A schematic illustration of how Sin1-PH motif blocks Sin1 interaction with mtor-kd. 7
8 A B C HA-Akt1-PH GST-PDK1-PH CMV-GST -Sin1-PH! CMV-GST -PDK1-PH! 5! 1 15! 3 6 ΔPH! 5! 1 15! 3 6 HA-Akt1! Insulin (min)! -ps473 -pt308 1 IB: HA-Akt1-PH IB: HA-Akt1! IB: GST-PDK1-PH IB: Tubulin IB: HA-Akt1! IB: Vinculin! Figure S2. The PH domain is a unique and physiological functional PH domain, Related to Figure 2. A-B, Only Sin1-PH, but not Akt1-PH, nor PDK1-PH, suppresses mtorc2 to phosphorylate Akt-S473 in cells. IB analysis of WCLs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with indicated HA-Sin1-PH/HA-Akt1-PH (A) or GST-Sin1-PH/GST-PDK1-PH (B) constructs. C, Deletion of the PH domain of Akt1 leads to attenuated Akt phosphorylation in cells. IB analysis of WCLs or HA-IPs derived from 293 cells transfected with indicated HA-Akt1 constructs. 8
9 A B C DMSO! LY! YM! 15! 3 45! 15! 3 45! 15! 3 45! insulin (min)! IB: p-foxo! IB: FOXO! Medium! Starved! DMSO! LY! pp242! AKTVIII! S6K1-I! IB: HA-Akt1! IB: HA-Akt1! IB: S6K-pT389! GFP! PIK3CA! #2! #4! shrna! IB: p-foxo! IB: FOXO! D -pt45 GFP! PIKFYVE! H2! H4! H5! shrna! -ps473! -pt308! IB: p-foxo! IB: FOXO! IB: PIKFYVE! IB: PIK3CA! E Fnorm [1/1000]! Data Analysis Thermophoresis + T-Jump! LED: 60% MST Power: 40%! Fit Kd! 742! Kd= ! ! 736! 734! 732! ! 10-1! ! 10 2! Concentration! 10 3! F! Fnorm [1/1000]! Data Analysis Thermophoresis + T-Jump! LED: 60% MST Power: 40%! Fit Kd! Kd= ! Kd= ! ! 10-1! ! 10 2! 10 3! Concentration! G! pull down! Ctrl! PIP 3! +/+ -/- +/+ -/- +/+ -/-! beads! Sin1 MEFs! IB: Sin1! IB: Rictor! H ctrl! PI(3,5)P 2! PI(3,4,5)P 3! ctrl! GST-Akt1-PH and IP 4! PI(3,5)P 2! PI(3,4,5)P 3! PIP beads pull down! IB: GST-Akt1 -tail! I! GST-Akt1-tail only! Crtl! Sin1 +/+! PIP 3 beads pull down! DMSO! Torin1! pp242! rapamycin! Sin1 -/-! Crtl! PIP 3! GST-Sin1-PH and IP 4! -ps473! IB: GST -Akt1-tail! K Sin1 +/+! Sin1 -/-! Rictor! DAPI! Merged! J! GFP-SIn1-PH! DAPI! Merged! shgfp+ insulin! Sin1 +/+ +BKM! shpik3ca2 + insulin! L! Rictor +/+! Rictor -/-! shpikfyve + insulin! Rictor (CST)! 9
10 Figure S3. PI(3,4,5)P 3 binds the Sin1-PH motif to activate mtorc2, Related to Figure 3. A, Inhibition of PI3K, but not PIKFYVE, leads to reduced Akt-pS473 in cells. Immunoblot (IB) analysis of whole cell lysates (WCLs) derived from HeLa cells with indicated treatments. Where indicated, HeLa cells were serum starved for 24 h, treated with indicated inhibitors for 1 h (LY : 1 µm and YM201636: 500 nm) and stimulated with 100 nm insulin at the indicated time periods before harvest for IB analysis. B, IB analysis and HA-IPs of WCLs derived from Sin1 -/- MEFs transfected with HA-Akt1 and indicated treatments. Where indicated, cells were serum starved for 24 h, treated with indicated inhibitors for 1 h (LY : 10 µm, pp242: 1 µm, AktVIII: 10 µm and S6K1-I: 10 µm) and stimulated with 100 nm insulin at the indicated time periods before harvest for IB analysis. C-D, Depletion of endogenous PIK3CA (C), but not endogenous PIKFYVE (D), leads to reduced Akt-pS473 in cells. IB of WCLs derived from HeLa cells infected with shpik3ca (C) or shpikfyve (D) lenti-viruses. 72 hrs post-puromycin selection (1 µg/ml), cells were harvested for IB analysis. E-F, MicroScale Thermophoresis (MST) analysis determined the K d of GST-Akt1-PH (aa 1-107) (E) interaction with IP 4 in vitro to be 20.6 µm. The K d value of the interaction between GST-Sin1-PH (aa 1-137) (F) was determined to be 48.2 µm in vitro. G, PIP 3 beads pull down Rictor mainly through Sin1. IB analysis of WCLs and Ctrl or PIP 3 beads pull downs in RIPA buffer with 1% TritonX-100 in Sin1 +/+ or Sin1 -/- MEFs. H-I, PIP 3 beads pull down active mtorc2 complex in CHAPS buffer conditions. In vitro kinase assays indicating that PIP 3 beads pull-down mtorc2 complexes are active in phosphorylating Akt-S473. Where indicated, Torin (1 µm), pp242 (1 µm) and rapamycin (20 nm) were added to cell culture medium for 4 hrs before harvesting cells for PIP 3 pull-down. J, Representative confocal images illustrating that depletion of PI3KCA, but not PIKFYVE, leads to attenuated Sin1-PH plasma membrane proximity localization. K, Representative immuno-florescent images to illustrate endogenous Rictor could be in part enriched on the plasma membrane upon insulin stimulation in Sin1 +/+, but not Sin1 -/- MEFs, nor Sin1 +/+ MEFs treated with PIK3CA inhibitor BKM120. Cells were serum starved for 24 hr before adding insulin (100 nm) for 15 min. Where indicated, BKM120 (100 nm) were added in cells for 2 hr before insulin stimulation. L, Representative immuno-florescent images to illustrate that the Rictor antibody used in (K) mainly detects specific Rictor-derived signals in Rictor +/+, but not Rictor -/- MEFs. 10
11 A IP: Flag! ! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! EGF (min)! Flag-mTOR-KD! HA-Sin1-PH! IB: Flag! IB: Flag! B GST-pulldown! HCT116! +! +! +! +! CMV-GST-mTOR-KD-C! -! +! -! +! HA-Sin1-PH! IB:PTEN! Figure S4. The presence of PIP3 species leads to attenuated Sin1-PH domain interaction with mtor-kd, Related to Figure 4. A, EGF stimulation attenuates the Sin1-PH interaction with mtor-kd. Immunoblot (IB) analysis of whole cell lysates (WCLs) and HA-immunoprecipitates (IP)s derived from 293 cells transfected with indicated constructs. Where indicated, cells were serum starved for 24 hrs and stimulated by 100 ng/ml EGF for the indicated time periods before harvesting. B, PTEN loss leads to a reduced Sin1-PH domain interaction with mtor-kd. IB analysis of GST-pulldowns and WCLs derived from HCT116 cells with indicated PTEN status transfected with indicated constructs. 11
12 A +! +! +! +! Sin1 -/-! +! +! +! +! insulin! Sin1 +/+! Sin1 -/-! MSCV-Sin1-HA! IB: Rictor! B insulin (nm)! C R393C! K464A! R395C! K428A! IB: mtor! IB: GβL! total! IB: Rictor! IB: p-foxo! IB: FOXO3a! IB: Sin1! IB: p-ndrg1! IB: GβL! IB: mtor! D PIP 3 some WT CAA Flag-Sin1 _! Flag-mTOR _! +! +! +! +! +! _! +! +! +! +! +! _! +! +! +! +! +! _! CMV-GST-GβL +! +! +! +! +! _! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! HA-Rictor +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! GST-Akt1-tail G Akt/Sin1 -PH- Akt/Sin1 -PH- -ps473 IB: GST-Akt1-tail IB: Flag-Sin1 IB: HA-Rictor IB: GST-GβL GFP! DAPI! Merged! J! K! L! HA! ! IGF-1 (min)! -ps473! -pt308! GFP-PLCδ-PH! GFP-Sin1-PH - GFP-Sin1-PH - GFP-Sin1-PH -CAAX- GFP-Sin1-PH -CAAX- E H! GST pulldown! F! Fnorm [1/1000]! -ps473! Data Analysis Thermophoresis + T-Jump! LED: 60% MST Power: 40%! Fit Kd! Akt/Sin1 Akt/Sin1 -PH- -PH- HA! ! EGF (min)! WT CAA HA-Sin insulin (min) ps473 OVCAR5-shSin1 CMV-GST-RPL26 EV WT pt308 CAA WT-CAAX 1 IB: Sin1 IB: Tubulin CAA-CAAX M Relative viability (%)! Relative viability (%)! HA-Sin1 IB: GST IB: GST IB: GST pt308! 52 Kd= ! ! ! 10 2! 10 3! Concentration! I! 1! 2! 5! 1 Doxorubicin (µm)! GST-Sin1-CAA-PH and IP 4! Mem! Cyto! Fractionation! EGF (min)! 5! Cisplatin (µm)! N Sin1 -/-! DMSO! Dox! Cisplatin! OVCAR5-shSin1! IB: EGFR! MSCV -Sin1-HA! -ps473! -pt308! IB: Vinculin! 12
13 Figure S5. The Sin1-PH motif mainly interacts with PI(3,4,5)P 3 through three critical residues including R393, K428 and K464, Related to Figure 5. A, The Sin1-R393A/K428A/K464A mutant is deficient in promoting Akt-S473 phosphorylation in cells. Immunoblot (IB) analysis of whole cell lysates (WCLs) derived from Sin1 -/- MEFs transfected with indicated HA-Sin1 constructs. Where indicated, 24 hr post-transfection, cells were serum starved for 24 hr before adding insulin (100 nm) for 30 min. B, Sin1-CAA is deficient in activating Akt-S473 phosphorylation in an insulin dose-dependent manner. HAP1-Sin1 -/- cells (#002) were infected with MSCV-Sin1-HA-WT or CAA retroviruses and recovered for 24 hr before splited for serum starvation for an additional 24 hr. Subsequently, resulting cells were treated with indicated doses of insulin for 40 min before harvested for IB analysis. C, All Sin1 mutants examined maintain binding ability to other mtorc2 components. IB analysis of WCLs and HA-IPs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with indicated HA-Sin1 constructs. D, PIP 3 polysomes promote Sin1-WT, but not Sin1-CAA containing mtorc2 complex activation in vitro. Indicated mtorc2 component constructs were transfected into Sin1 -/- MEFs and inactive mtorc2 complexes were immune-precipitated against HA-Rictor after 48 hr serum starvation. Increasing amounts of PIP 3- polysomes were added to the inactive precipitates and incubated for 30 min before other kinase reaction components were added. The kinase reactions were carried out at 30 o C for 1 hr and terminated by addition of SDS sample buffers. E, RPL26 retains its interaction with Sin1-CAA to a comparable level to Sin1-WT in cells. IB analysis of WCLs and HA-IPs or GST pulldowns derived from HEK293T cells transfected with indicated HA-Sin1 constructs together with GST-PRL26. F, MicroScale Thermophoresis (MST) analysis determined the K d of the interaction between GST-Sin1-PH-CAA (aa 1-137) and IP 4 was determined to be 365 µm in vitro. G-H, The Sin1-PH-CAA mutant is deficient in Akt phosphorylation in cells in response to EGF (G) or IGF-1 (H). IB analysis of HA-IPs derived from HeLa cells transfected with indicated chimeric constructs. Where indicated, cells were serum starved for 24 hr before addition of EGF (100 ng/ml) for 10 min or IGF-1 (100 ng/ml) for 30 min. I, Sin1-WT, but not Sin1-CAA, could be in part enriched on the plasma membrane upon stimulation by EGF (100 ng/ml) for 5 min. Please refer to the method section for detailed cell fractionation protocol. J, Representative immuno-florescent images to illustrate that GFP-Sin1-PH-WT, but not GFP-Sin1-PH-CAA, is in part enriched on plasma membrane upon stimulation by insulin (100 nm) for 15 min. K, Sin1-CAA is deficient in activating Akt in cells. IB analysis of WCLs derived from Sin1 depleted OVCAR5 cells stably expressing either MSCV-Sin1-WT-HA or MSCV-Sin1-CAA-HA via retro-viral infections. Where indicated, cells were serum starved for 36 hr before insulin (100 nm) was added for the indicated time periods before cell collection. L-M, The endogenous Sin1-depleted OVCAR5 cell lines stably expressing either MSCV-Sin1-HA-WT or MSCV-Sin1-HA-CAA were cultured in 10% FBS-containing medium with the indicated concentrations of doxorubicin (L) or cisplatin (M) for 24 hrs before performing the cell viability assays. Data was shown as mean + SD for three independent experiments. No statistical significance was observed between WT and CAA at each drug concentration (Student s t-test). N, Doxorubicin or cisplatin treatment leads to elevated Akt phosphorylation in cells. Indicated cells were treated with 5 µm doxorubicin or 20 µm cisplatin for 24 hr and harvested for IB analysis. 13
14 A PIP 3 pulldown! D H Relative viability (%)! L! ! +! +! CMV-GST-mTOR-KD-L! HA-Sin1-PH! B R15Q! V30I! L31V! D37G! Q55H! G59C! R81T! S84L! R94Q! I101M! R145C! P156S! S161C! Y180C! A201T! G208W! T215C! S216I! 219L! CRIM! RBD! PH! 1! 137! 266! 279! 353!376! 486! 522! *! *! 5! 1 15! 2 Etoposide (µm) 48hr! E F! I! Relative viability (%)! * * H233Y! R282Q! F289L! L291I! R311Q! Human Sin1.1! ΔPH! _! +! _! +! _! +! _! +! _! +! _! +! _! +! _! +! _! +! insulin! 1! 2! 5! 1 * Doxoubicin (µm) 24hr! R T! 12 U 12 S V EV WT D412G S449I A451E T456M L402P A472T HA-Sin1 +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! IGF-1 GFP! Akt1! GFP! Akt2! Sin1 -/- shrna! shrna! 2! Relative viability (%)! -ps473 -pt308 1 IB: Tubulin WT S449I MSCV-Sin1-HA WT A451E T456M MSCV-Sin1-HA insulin (min) insulin (min) -ps473 -ps473 OVCAR5-shSin pt308 1 IB: Tubulin M *! *! OVCAR5-shSin1 1! 2! 5! 1 Cisplatin (µm)! shgfp! shakt1! shakt2! W *! -pt308 total IB: HA-Sin1 IB: Tubulin shakt1! shakt2! Relative viability (%)! N O * *! Relative viability (%)! J! D360G! shgfp! shakt1! shakt2! 140! 120! 100! 80! 60! 40! 20! 0! L402P! OVCAR5-shSin1 MSCV-Sin1-HA *! *! 1! 2! 5! 1 Dox (µm)! S449I! A451E! T456M! WT S449I T456M WT S449I T456M Medium! A472T! R494L! K501E! K517N! G520R! Starved! *! *! 5! 1 15! 2 *! Taxol (µm)! % colony # % colony # 250! 200! 150! 100! 50! 0! 250! 200! 150! 100! 50! 0! shakt1! shakt2! X Z! *! *! C insulin! GST-pulldown! P Q *! *! L402P! S449I! IB: GST-Akt1-tail! A451E! A472T! T456M! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! +! K G0G1: %! G2M: %! S-Phase: %! G Y MSCV-Sin1-HA! OVCAR5-shSin1! WT A451E T456M WT A451E T456M CMV-GST-Sin1-PH! HA-mTOR-KD! IB: HA-mTOR-KD! IB: GST-Sin1-PH! IB: HA-mTOR-KD! IB: GST-Sin1-PH! IB: p-foxo! IB: FOXO3a! % colony # % colony # ! 200! 150! 100! 50! 0! G0G1: %! G2M: 25.84! S-Phase: %! *! *! *! *! Colony number! *! *! shgfp! shakt1! shakt2! Colony number! *! *! shgfp! shakt1! shakt2! G0G1: %! G2M: %! S-Phase: %! 14
15 Figure S6. The cancerous Sin1-PH mutant lose binding with the mtor-kinase domain, leading to elevated Akt-S473 phosphorylation and enhanced oncogenic activities, Related to Figure 6. A, PIP 3 competes with mtor-kd-l to bind Sin1-PH. Immunoblot (IB) analysis of whole cell lysates (WCLs), PIP 3 pulldowns, and HA-IPs derived from 293T cells transfected with indicated constructs. B, A schematic illustration of currently identified cancer patient-derived Sin1 mutations from cbio and Cosmic databases. C, Most of the Sin1-PH cancer derived mutations lead to reduced Sin1-PH interactions with mtor-kd in cells. IB analysis of WCLs and GST-pull downs derived from 293T cells transfected with indicated constructs. D-E, Sin1-D412G leads to increased Akt-S473 phosphorylation in cells. IB analysis of WCLs derived from Sin1 -/- MEFs transfected with indicated HA-Sin1 constructs. Where indicated, 24 hr post-transfection, cells were serum starved for 24 hr before adding IGF-1 (100 ng/ml) for 30 min (D) or insulin (100 nm) for 30 min (E). F, Sin1-D412G-containing mtorc2 complexes displays elevated kinase activity to phosphorylation Akt in vitro. HEK293 cells expressing various HA-Sin1 constructs were maintained in normal medium or serum starved or adding 100 nm insulin as indicated were harvested in CHAPs buffer following HA-Sin1 immunoprecipitations, which were used as the kinase source to phosphorylate GST-Akt1-tail (aa ) in vitro. G, IB analysis of endogenous Sin1-depleted OVCAR5 cells stably expressing either MSCV-Sin1-HA-WT or MSCV-Sin1-HA-D412G. H-J, The OVCAR5 cell lines generated in (G) were cultured in 10% FBS-containing medium with the indicated concentrations of etoposide (H), doxorubicin (I), or taxol (J) for 24 hrs before performing the cell viability assays. Data was shown as mean + SD for three independent experiments. * indicates p<0.05 (Student s t-test). K, 3x10 6 of the generated cells in (F) were injected into nude mice (n=10 for each group) and monitored for tumor formation. L-M, Compared to WT-Sin1, stable expression of the Sin1-S449I, A451E or T456M mutant leads to an elevated Akt activation upon insulin stimulation. IB of WCLs derived from endogenous Sin1-depleted OVCAR5 cells stably expressing indicated Sin1 constructs. Where indicated, cells were serum starved for 36 hr before insulin (100 nm) was added for the indicated time periods. N-Q, Compared to WT-Sin1, indicated Sin1-PH mutant expressing cells display enhanced colony formation (N, P) and soft-agar growth abilities (O, Q). Data was shown as mean + SD for three independent experiments. * indicates p<0.05 (student s t-test). R-S, Immuno-blot (IB) analysis of OVCAR5 cells generated in (Figure S6F) depleted of endogenous Akt1 (R) or Akt2 (S) via lenti-viral infections. T-U, Depletion of either Akt1 or Akt2 sensitizes OVCAR5-D412G cells to chemotherapeutic agents. The OVCAR5 cell lines generated in (R-S) were cultured in 10% FBS-containing medium with the indicated concentrations of cisplatin (T) or doxorubicin (U) for 24 hrs before performing the cell viability assays. Data was shown as mean + SD for three independent experiments. * indicates p<0.05 (Student s t-test). V, Depletion of Akt1 or Akt2 leads to attenuated colony formation abilities. 400 cells generated in (R and S) were plated on 6 well plates. 14 days later formed colonies were visualized and counted. W, Depletion of Akt1 or Akt2 leads to attenuated anchorage-independent growth ability in soft agar. 1x
16 cells generated in (R and S) were plated on top layer of agar in 6 well plates. 22 days later formed colonies were visualized and counted. X-Z, FACS analyses of cell cycle distribution profiles by Modfit indicated that expression of indicated Sin1 mutant dose not significantly alter cell cycle profiles, compared with Sin1-WT expressing cells. 16
17 A Sin1 +/+! Sin1 -/-! WT -CAAX! CAA -CAAX! _! +! _! +! _! +! _! +! _! +! _! +! insulin! C WT-CAAX starved! DAPI! Merged! IB: WT-CAAX +insulin! D DAPI! Merged! B GST-Akt1-tail! Myr- CAAX- CAAX- CAA-CAAX starved! CAA-CAAX +insulin! E WT-CAAX! HA-Akt1! EGF (min)! -ps473! IB: Vinculin! F! Sin1 +/+! Sin1 -/-! WT-CAAX! CAA-CAAX! ! HA-Akt1 -E17K! -ps473! -pt308! G DMSO! LY! WORT! Medium! WT-CAAX! WT-CAAX! YM! DMSO! HA-Akt1-E17K! LY! WORT! YM! DMSO! LY! WORT! insulin! YM! DMSO! LY! WORT! YM! -ps473! -pt308! H Ovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma (TCGA, Provisional)/Tumors with sequencing and CNA data: (311)/User-defined List/2genes.! Case Set: Tumors with sequencing and CNA data: All tumor samples that have CNA and sequencing data (311 samples)! Altered in 22 (7%) of cases! R81T! MAPKAP1 2% AKT1 5% Odds Ratio: < [strong tendency toward mutual exclusivity]! 95% Confidence Interval: < NaN! p-value: [Fisher's Exact Test]! I! Ovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma (TCGA, Provisional)/Tumors with sequencing and CNA data: (311)/User-defined List/2genes! Case Set: Tumors with sequencing and CNA data: All tumor samples that have CNA and sequencing data (311 samples)! Altered in 4 (1%) of cases! R81T! MAPKAP1 1% PIK3CA 1% E545K! H1047R! Odds Ratio: < [strong tendency toward mutual exclusivity]! 95% Confidence Interval: < NaN! p-value: [Fisher's Exact Test]! 17
18 Figure S7. C-terminal tagging of KRas-CAAX to Sin1 could partially rescue the deficiency of the Sin1-CAA mutant in membrane recruitment and mtorc2 activation, Related to Figure 7. A, C-terminal addition of KRas-CAAX sequence in part rescues Sin1-CAA in phosphorylating Akt-S473 in cells. Immuno-blot (IB) analysis of whole cell lysates (WCLs) derived from Sin1 -/- MEFs transfected with indicated Sin1 constructs. Where indicated, 24 hr post-transfection, cells were serum starved for 24 hr and 100 nm insulin was added to culture medium for 30 min before cell collection. B, In vitro kinase assay indicating that in-frame addition of C-terminal KRas-CAAX sequence could in part rescue the Sin1-CAA mutant in phosphorylating Akt-S473 in vitro. C, Representative immuno-florescent (IF) images to illustrate that the C-terminal addition of KRas-CAAX sequence enables part of Sin1-WT-CAAX molecules to localize to plasma membrane even under serum starved conditions. Where indicated, cells transfected with HA-Sin1 were serum starved for 24 hr before addition of 100 nm insulin for 15 min. Cells were then fixed and stained as indicated. D, Representative immuno-florescent (IF) images to illustrate that the C-terminal addition of KRas-CAAX sequence rescues part of Sin1-CAA-CAAX molecules to localize to plasma membrane under insulin stimulation conditions. Where indicated, cells transfected with HA-Sin1 were serum starved for 24 hr before addition of 100 nm insulin for 15 min. Cells were then fixed and stained as indicated. E, Addition of a C-terminal CAAX tag mostly abolishes Akt phosphorylation in cells. IB analysis of WCLs and HA-IPs derived from HeLa cells tranfected with indicated HA-Akt1 constructs. Where indicated, cells were serum starved for 24 hrs and stimulated by 100 ng/ml EGF for the indicated periods before harvesting. F-G, A C-terminal addition of KRas-CAAX sequence in Sin1 leads to elevated Akt-pS473 signals in Akt1-E17K in cells. IB of WCLs derived from Sin1 -/- MEFs transfected with HA-Akt1-E17K and indicated HA-Sin1 constructs. Where indicated, 24 hr post-transfection, cells were serum starved for 24 hr before addition of 100 nm insulin for 30 min. H, Sin1 mutations and Akt amplifications are mutually exclusive in ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma patient samples (from cbio database). I, Sin1 and p110α/pik3ca mutations are mutually exclusive in ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma patient samples (from cbio database). 18
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1
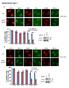 Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
William C. Comb, Jessica E. Hutti, Patricia Cogswell, Lewis C. Cantley, and Albert S. Baldwin
 Molecular Cell, Volume 45 Supplemental Information p85 SH2 Domain Phosphorylation by IKK Promotes Feedback Inhibition of PI3K and Akt in Response to Cellular Starvation William C. Comb, Jessica E. Hutti,
Molecular Cell, Volume 45 Supplemental Information p85 SH2 Domain Phosphorylation by IKK Promotes Feedback Inhibition of PI3K and Akt in Response to Cellular Starvation William C. Comb, Jessica E. Hutti,
Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3
 Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3 Sarbassov et al. 1 Material and Methods Materials Reagents were obtained from the following sources: protein
Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3 Sarbassov et al. 1 Material and Methods Materials Reagents were obtained from the following sources: protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh-
 1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
Infect MCF-7 cells carrying dcas9-vp64 + psm2-p65-hsf1 with SAM library or vector. Introduce AKT reporter
 Infect MCF-7 cells carrying dcas9-vp64 + psm2-p65-hsf1 with SM library or vector Introduce reporter Grow cells in presence of puromycin for 5 days Vector control SM library fewer surviving cells More surviving
Infect MCF-7 cells carrying dcas9-vp64 + psm2-p65-hsf1 with SM library or vector Introduce reporter Grow cells in presence of puromycin for 5 days Vector control SM library fewer surviving cells More surviving
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass
 Supplementary material Figure S1. Interaction between UBL5 and FANCI A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis of UBL5-interacting proteins,
Supplementary material Figure S1. Interaction between UBL5 and FANCI A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis of UBL5-interacting proteins,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3311 A B TSC2 -/- MEFs C Rapa Hours WCL 0 6 12 24 36 pakt.s473 AKT ps6k S6K CM IGF-1 Recipient WCL - + - + - + pigf-1r IGF-1R pakt ps6 AKT D 1 st SILAC 2 nd SILAC E GAPDH FGF21 ALKPGVIQILGVK
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3311 A B TSC2 -/- MEFs C Rapa Hours WCL 0 6 12 24 36 pakt.s473 AKT ps6k S6K CM IGF-1 Recipient WCL - + - + - + pigf-1r IGF-1R pakt ps6 AKT D 1 st SILAC 2 nd SILAC E GAPDH FGF21 ALKPGVIQILGVK
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
S1a S1b S1c. S1d. S1f S1g S1h SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. - si sc Il17rd Il17ra bp. rig/s IL-17RD (ng) -100 IL-17RD
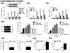 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
Tbk1-TKO! DN cells (%)! 15! 10!
 a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
Sin1 phosphorylation impairs mtorc2 complex integrity and inhibits downstream Akt signaling to suppress tumorigenesis
 Sin1 phosphorylation impairs mtorc2 complex integrity and inhibits downstream Akt signaling to suppress tumorigenesis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this
Sin1 phosphorylation impairs mtorc2 complex integrity and inhibits downstream Akt signaling to suppress tumorigenesis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
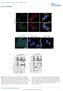 DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
a b G75 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server.
 a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS
 Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S2
 Supplementary Figure S A) The blots shown in Figure B were qualified by using Gel-Pro analyzer software (Rockville, MD, USA). The ratio of LC3II/LC3I to actin was then calculated. The data are represented
Supplementary Figure S A) The blots shown in Figure B were qualified by using Gel-Pro analyzer software (Rockville, MD, USA). The ratio of LC3II/LC3I to actin was then calculated. The data are represented
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. EBV-gB 23-431 mainly exists as trimer in HEK 293FT cells. (a) Western blotting analysis for DSS crosslinked FLAG-gB 23-431. HEK 293FT cells transfected
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. EBV-gB 23-431 mainly exists as trimer in HEK 293FT cells. (a) Western blotting analysis for DSS crosslinked FLAG-gB 23-431. HEK 293FT cells transfected
Supplementary material. Supplementary Figure legends
 Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3076 Supplementary Figure 1 btrcp targets Cep68 for degradation during mitosis. a) Cep68 immunofluorescence in interphase and metaphase. U-2OS cells were transfected with control sirna
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3076 Supplementary Figure 1 btrcp targets Cep68 for degradation during mitosis. a) Cep68 immunofluorescence in interphase and metaphase. U-2OS cells were transfected with control sirna
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Supplemental Data. Prolonged Rapamycin Treatment Inhibits mtorc2 Assembly and Akt/PKB. Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Supplemental Data Prolonged Rapamycin Treatment Inhibits mtorc2 Assembly and Akt/PKB Dos D. Sarbassov, Siraj M. Ali, Shomit Sengupta, Joon-Ho Sheen, Peggy P. Hsu, Alex F. Bagley, Andrew L. Markhard, and
Supplemental Data Prolonged Rapamycin Treatment Inhibits mtorc2 Assembly and Akt/PKB Dos D. Sarbassov, Siraj M. Ali, Shomit Sengupta, Joon-Ho Sheen, Peggy P. Hsu, Alex F. Bagley, Andrew L. Markhard, and
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol. absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1
 The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Jewell et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201007176/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. IR Munc18c association is independent of IRS-1. (A and
Supplemental material Jewell et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201007176/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. IR Munc18c association is independent of IRS-1. (A and
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/430/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The 4E-BP eif4e axis promotes rapamycinsensitive growth and proliferation in lymphocytes Lomon So, Jongdae Lee, Miguel
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/430/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The 4E-BP eif4e axis promotes rapamycinsensitive growth and proliferation in lymphocytes Lomon So, Jongdae Lee, Miguel
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Tel: ; Fax: ;
 Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
 SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Crystal violet assay Cells were seeded in 24-well plates and cultured in media supplemented with % FBS for 7 days. Media were then removed, plates were briefly washed
SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Crystal violet assay Cells were seeded in 24-well plates and cultured in media supplemented with % FBS for 7 days. Media were then removed, plates were briefly washed
Nature Immunology doi: /ni.3268
 Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Tumor stage : I II III IV. well differentiated. moderately differentiated. adenocarcinoma. normal colon (adjacent to cancer) Log (T/H) SLAP mrna level
 moderately differentiated well differentiated Log (T/H) mrna level a Tumor stage : I II III IV.4.4.8 1.2 1.6 2. 2.4 2.8 3.2 N 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 # patient b normal colon (adjacent
moderately differentiated well differentiated Log (T/H) mrna level a Tumor stage : I II III IV.4.4.8 1.2 1.6 2. 2.4 2.8 3.2 N 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 # patient b normal colon (adjacent
GFP-LC3 +/+ CLU -/- kda CLU GFP. Actin. GFP-LC3 +/+ CLU -/- kda CLU GFP. Actin
 Supplementary Fig. 1 a CQ treatment ScrB OGX11 MG132 I II AZD5363 I II b GFP / / GFP / / GFP / / GFP / / GFP GFP Actin Actin ctrl CQ GFP / / GFP / / GFP / / GFP / / GFP GFP Actin Actin rapamycin rapamycincq
Supplementary Fig. 1 a CQ treatment ScrB OGX11 MG132 I II AZD5363 I II b GFP / / GFP / / GFP / / GFP / / GFP GFP Actin Actin ctrl CQ GFP / / GFP / / GFP / / GFP / / GFP GFP Actin Actin rapamycin rapamycincq
The PI3K/AKT axis. Dr. Lucio Crinò Medical Oncology Division Azienda Ospedaliera-Perugia. Introduction
 The PI3K/AKT axis Dr. Lucio Crinò Medical Oncology Division Azienda Ospedaliera-Perugia Introduction Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway are a family of lipid kinases discovered in 1980s. They have
The PI3K/AKT axis Dr. Lucio Crinò Medical Oncology Division Azienda Ospedaliera-Perugia Introduction Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway are a family of lipid kinases discovered in 1980s. They have
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Palmisano et al. 10.1073/pnas.1202174109 Fig. S1. Expression of different transgenes, driven by either viral or human promoters, is up-regulated by amino acid starvation. (A) Quantification
Supporting Information Palmisano et al. 10.1073/pnas.1202174109 Fig. S1. Expression of different transgenes, driven by either viral or human promoters, is up-regulated by amino acid starvation. (A) Quantification
Targeted mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) for Olaparib pharmacokinetics. For LC/MS/MS of Olaparib pharmacokinetics metabolites were extracted from
 Supplementary Methods: Targeted mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) for Olaparib pharmacokinetics For LC/MS/MS of Olaparib pharmacokinetics metabolites were extracted from mouse tumor samples and analyzed as
Supplementary Methods: Targeted mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) for Olaparib pharmacokinetics For LC/MS/MS of Olaparib pharmacokinetics metabolites were extracted from mouse tumor samples and analyzed as
Gankyrin plays an essential role in Ras-induced tumorigenesis through regulation of the RhoA/ROCK pathway in mammalian cells
 Research article Gankyrin plays an essential role in Ras-induced tumorigenesis through regulation of the RhoA/ROCK pathway in mammalian cells Jiang-Hong Man, Bing Liang, Yue-Xi Gu, Tao Zhou, Ai-Ling Li,
Research article Gankyrin plays an essential role in Ras-induced tumorigenesis through regulation of the RhoA/ROCK pathway in mammalian cells Jiang-Hong Man, Bing Liang, Yue-Xi Gu, Tao Zhou, Ai-Ling Li,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Methods:
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods: Cell viability assay. Cells were seeded overnight at a density of 2,000 cells per well in 96-well plates in RPMI with 10% FBS and then treated with the relevant
Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods: Cell viability assay. Cells were seeded overnight at a density of 2,000 cells per well in 96-well plates in RPMI with 10% FBS and then treated with the relevant
SUPPLEMENT. Materials and methods
 SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
Supplementary Figure 1
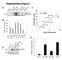 A B D Relative TAp73 mrna p73 Supplementary Figure 1 25 2 15 1 5 p63 _-tub. MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 HCC-1937 MDA-MB-468 ΔNp63_ TAp73_ TAp73β E C Relative ΔNp63 mrna TAp73
A B D Relative TAp73 mrna p73 Supplementary Figure 1 25 2 15 1 5 p63 _-tub. MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 HCC-1937 MDA-MB-468 ΔNp63_ TAp73_ TAp73β E C Relative ΔNp63 mrna TAp73
Predictive PP1Ca binding region in BIG3 : 1,228 1,232aa (-KAVSF-) HEK293T cells *** *** *** KPL-3C cells - E E2 treatment time (h)
 Relative expression ERE-luciferase activity activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) MCF-7 KPL-3C ZR--1 BT-474 T47D HCC15 KPL-1 HBC4 activity (pmole/min) a d
Relative expression ERE-luciferase activity activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) MCF-7 KPL-3C ZR--1 BT-474 T47D HCC15 KPL-1 HBC4 activity (pmole/min) a d
Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from murine
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or
 Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Increased ABHD5 expression in human colon cancer associated macrophages. (a) Murine peritoneal macrophages were treated with regular culture medium (Ctrl) or
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Increased ABHD5 expression in human colon cancer associated macrophages. (a) Murine peritoneal macrophages were treated with regular culture medium (Ctrl) or
(Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) (Supplemental Fig. 1A). A 5.4-kb EcoRI fragment
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Supplemental Methods Generation of RyR2-S2808D Mice Murine genomic RyR2 clones were isolated from a 129/SvEvTacfBR λ-phage library (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) (Supplemental Fig.
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Supplemental Methods Generation of RyR2-S2808D Mice Murine genomic RyR2 clones were isolated from a 129/SvEvTacfBR λ-phage library (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) (Supplemental Fig.
18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA. 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT. Acc1 AGCAGATCCGCAGCTTG ACCTCTGCTCGCTGAGTGC
 Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
supplementary information
 Figure S1 Nucleotide binding status of RagA mutants. Wild type and mutant forms of MycRagA was transfected into HEK293 cells and the transfected cells were labeled with 32 Pphosphate. MycRagA was immunoprecipitated
Figure S1 Nucleotide binding status of RagA mutants. Wild type and mutant forms of MycRagA was transfected into HEK293 cells and the transfected cells were labeled with 32 Pphosphate. MycRagA was immunoprecipitated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
 Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts
 Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Reagents and antibodies was purchased from iaffin GmbH & Co KG. Cisplatin (ristol-myers Squibb Co.) and etoposide (Sandoz Pharma Ltd.) were used. Antibodies recognizing
Supplementary Materials and Methods Reagents and antibodies was purchased from iaffin GmbH & Co KG. Cisplatin (ristol-myers Squibb Co.) and etoposide (Sandoz Pharma Ltd.) were used. Antibodies recognizing
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. IC261 inhibits a virus-induced type I interferon response.
 Supplementary Figure 1 IC261 inhibits a virus-induced type I interferon response. (a) HEK293T cells were cultured in 384 wells and transiently transfected with 50 ng of the IFN-β promoter-luc construct
Supplementary Figure 1 IC261 inhibits a virus-induced type I interferon response. (a) HEK293T cells were cultured in 384 wells and transiently transfected with 50 ng of the IFN-β promoter-luc construct
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
Supplements. Figure S1. B Phalloidin Alexa488
 Supplements A, DMSO, PP2, PP3 Crk-myc Figure S1. (A) Src kinase activity is necessary for recruitment of Crk to Nephrin cytoplasmic domain. Human podocytes expressing /7-NephrinCD () were treated with
Supplements A, DMSO, PP2, PP3 Crk-myc Figure S1. (A) Src kinase activity is necessary for recruitment of Crk to Nephrin cytoplasmic domain. Human podocytes expressing /7-NephrinCD () were treated with
Analyses of Intravesicular Exosomal Proteins Using a Nano-Plasmonic System
 Supporting Information Analyses of Intravesicular Exosomal Proteins Using a Nano-Plasmonic System Jongmin Park 1, Hyungsoon Im 1.2, Seonki Hong 1, Cesar M. Castro 1,3, Ralph Weissleder 1,4, Hakho Lee 1,2
Supporting Information Analyses of Intravesicular Exosomal Proteins Using a Nano-Plasmonic System Jongmin Park 1, Hyungsoon Im 1.2, Seonki Hong 1, Cesar M. Castro 1,3, Ralph Weissleder 1,4, Hakho Lee 1,2
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental
Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Inhibition of TGFβ enhances chemotherapy action against triple negative breast cancer by abrogation of
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Inhibition of TGFβ enhances chemotherapy action against triple negative breast cancer by abrogation of cancer stem cells and interleukin-8 Neil E. Bhola 1, Justin M. Balko 1, Teresa C.
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Inhibition of TGFβ enhances chemotherapy action against triple negative breast cancer by abrogation of cancer stem cells and interleukin-8 Neil E. Bhola 1, Justin M. Balko 1, Teresa C.
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables. File Name: Peer Review File Description:
 File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables File Name: Peer Review File Description: Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') AT ( C) RT-PCR USP21 F 5'-TTCCCATGGCTCCTTCCACATGAT-3'
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables File Name: Peer Review File Description: Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') AT ( C) RT-PCR USP21 F 5'-TTCCCATGGCTCCTTCCACATGAT-3'
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous
 Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or ALDH-positive cell population by qpcr. Data represent
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or ALDH-positive cell population by qpcr. Data represent
Impact of hyper-o-glcnacylation on apoptosis and NF-κB activity SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent
 Supplemental Material Supplemental Figure Legends Fig. S1 A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent and -deficient cell lines. HA-tagged H-ras V12 was stably expressed in
Supplemental Material Supplemental Figure Legends Fig. S1 A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent and -deficient cell lines. HA-tagged H-ras V12 was stably expressed in
